java搜索引擎有很多,比较熟悉的就是slor和lucene。
luncene:
概念:全文检索是计算机程序通过扫描文章中的每一个词,对每一个词建立一个索引,指明该词在文章中出现的次数和位置。当用户查询时根据建立的索引查找,类似于通过字典的检索字表查字的过程
luncene入门:
全文检索(Full-Text Retrieval)是指以文本作为检索对象,找出含有指定词汇的文本。全面、准确和快速是衡量全文检索系统的关键指标。 关于全文检索,我们要知道:
1,只处理文本。
2,不处理语义。
3,搜索时英文不区分大小写。
4,结果列表有相关度排序。 在信息检索工具中,全文检索是最具通用性和实用性的。
全文检索应用场景:
我们使用Lucene,主要是做站内搜索,即对一个系统内的资源进行搜索。如BBS、BLOG中的文章搜索,网上商店中的商品搜索等。使用Lucene的项目有Eclipse、Jira等。一般不做互联网中资源的搜索,因为不易获取与管理海量资源(专业搜索方向的公司除外)。
全文检索不同于数据库检索
全文检索不同于数据库的SQL查询。(他们所解决的问题不一样,解决的方案也不一样,所以不应进行对比)。在数据库中的搜索就是使用SQL,如:SELECT * FROM t WHERE content like ‘%ant%’。这样会有如下问题:
1、匹配效果:如搜索ant会搜索出planting。这样就会搜出很多无关的信息。
2、相关度排序:查出的结果没有相关度排序,不知道我想要的结果在哪一页。我们在使用百度搜索时,一般不需要翻页,为什么?因为百度做了相关度排序:为每一条结果打一个分数,这条结果越符合搜索条件,得分就越高,叫做相关度得分,结果列表会按照这个分数由高到低排列,所以第1页的结果就是我们最想要的结果。
3、全文检索的速度大大快于SQL的like搜索的速度。这是因为查询方式不同造成的,以查字典举例:数据库的like就是一页一页的翻,一行一行的找,而全文检索是先查目录,得到结果所在的页码,再直接翻到这一页。
准备Lucene的开发环境:
搭建Lucene的开发环境只需要加入Lucene的Jar包,要加入的jar包至少要有:
lucene-core-3.0.1.jar(核心包)
contrib\analyzers\common\lucene-analyzers-3.0.1.jar(分词器)
contrib\highlighter\lucene-highlighter-3.0.1.jar(高亮)
contrib\memory\lucene-memory-3.0.1.jar(高亮)
全文检索程序工作流程
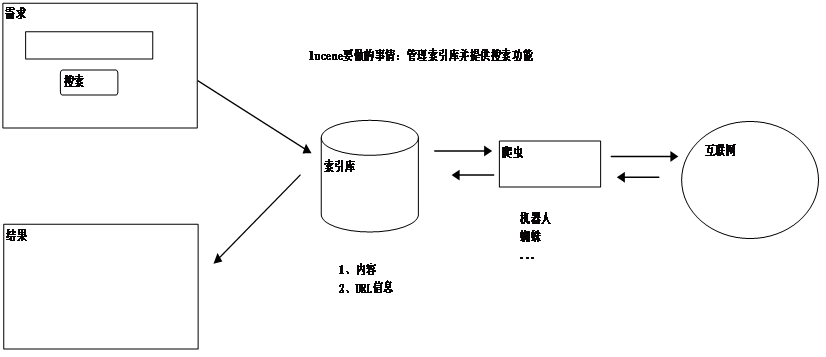
操作索引库的方法

下面是一个luncene的hello world
public class Article { private Integer id; //id private String title; //标题 private String content; //内容 }
建立索引库
@Test public void testCreateIndex() throws Exception { Article article = new Article(); article.setId(1); // 通过设置id的值模拟一个已保存到数据库中的数据 article.setTitle("Lucene是全文检索框架"); article.setContent("全文检索(Full-Text Retrieval)是指以文本作为检索对象,找出含有指定词汇的文本。"); // 建立索引 Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("./indexDir/")); // 索引库目录 Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(Version.LUCENE_30); // 分词器 // >> 把Aritcle转为Document Document doc = new Document(); doc.add(new Field("id", article.getId().toString(), Store.YES, Index.NOT_ANALYZED)); // 要把id转为String型 doc.add(new Field("title", article.getTitle(), Store.NO, Index.ANALYZED)); doc.add(new Field("content", article.getContent(), Store.YES, Index.ANALYZED)); // >> 保存到索引库中 IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory, analyzer, MaxFieldLength.LIMITED);//MaxFieldLength.LIMITED:表示限定分词,不超过10000 indexWriter.addDocument(doc); indexWriter.close(); }
// 搜索 @Test public void testSearch() throws Exception { // 搜索条件 String queryString = "lucene"; Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("./indexDir/")); // 索引库目录 Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(Version.LUCENE_30); // 分词器 // 1,把查询字符串转为Query对象(只在title中查询) QueryParser queryParser = new QueryParser(Version.LUCENE_30, "title", analyzer); Query query = queryParser.parse(queryString); // 2,执行搜索,得到中间结果 IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(directory); TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, 100); //100 返回查询出来的前n条结果 int count = topDocs.totalHits; // 总结果数 ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = topDocs.scoreDocs; // 前n条结果的信息 }
@Test public void testSearch() throws Exception { // 3,处理结果 List<Article> list = new ArrayList<Article>(); for (int i = 0; i < scoreDocs.length; i++) { ScoreDoc scoreDoc = scoreDocs[i]; System.out.println("得分:" + scoreDoc.score); // 根据内部编号取出真正的Document数据 int docId = scoreDoc.doc; System.out.println("docId内部编号="+docId); Document doc = indexSearcher.doc(docId); // 把Document转为Article Article article = new Article(); article.setId(Integer.parseInt(doc.get("id"))); // 要转型 article.setTitle(doc.get("title")); article.setContent(doc.get("content")); // doc.getField("content").stringValue() list.add(article); } indexSearcher.close(); // 显示结果 System.out.println("总结果数:" + count); for (Article article : list) { System.out.println("---------> id = " + article.getId()); System.out.println("title = " + article.getTitle()); System.out.println("content= " + article.getContent()); } }
索引库内部结构分析(创建)
1、把原始数据内容存储到数据的缓存区,会自动生成内部编号
2、在更新目录,会使用分词器
Store参数:
YES:存储本字段的原始值
NO:不存储本字段的原始值,这时,获取到信息字段为null
Index参数:
NO:不更新目录
ANALYZED:把本字段的值分词后更新到目录
NOT_ANALYZED不分词,而是把本字段的值当成一个词更新到目录
注意:一般情况下数据的唯一标识符使用不分词索引 如ID,Path,URL或是姓名、日期、数字
Store:能不能按照这个字段搜索到这个结果 Index:如果不更新目录,则不能按照本字段搜索到结果
lucene索引库操作CRUD
保持索引库和数据库状态一致
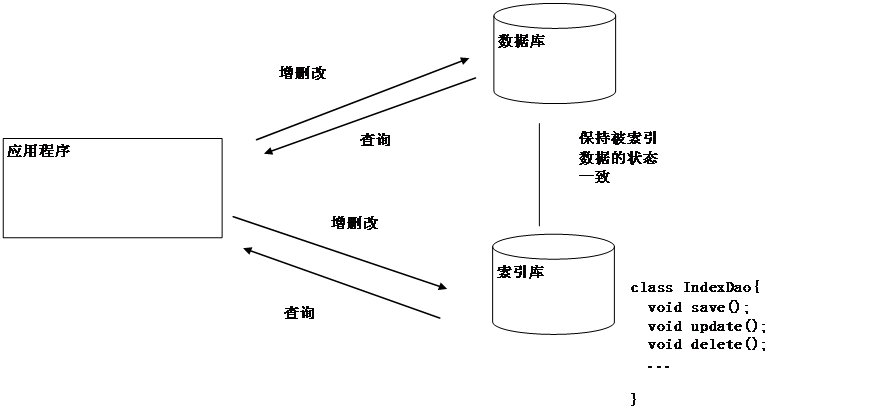
所有的数据(对象),我们都要存到数据库中。对于要进行搜索的数据,还要存到索引库中,以供搜索。一份数据同时存到数据库与索引库中(格式不同),就要想办法保证他们的状态一致。否则,就会影响搜索结果。
Article和Document之间的转换
/** * 把Article转为Document */ public static Document articleToDocument(Article article) { Document doc = new Document(); String idStr = article.getId().toString(); // 把Integer转为String型 doc.add(new Field("id", idStr, Store.YES, Index.NOT_ANALYZED)); doc.add(new Field("title", article.getTitle(), Store.YES, Index.ANALYZED)); doc.add(new Field("content", article.getContent(), Store.YES, Index.ANALYZED)); return doc; } /** * 把Document转为Article */ public static Article documentToArticle(Document doc) { Article article = new Article(); Integer id = Integer.parseInt(doc.get("id")); // 把String型转为Integer型 article.setId(id); article.setTitle(doc.get("title")); article.setContent(doc.get("content")); return article; }
public class Configuration { private static Directory directory; private static Analyzer analyzer; static { // 初始化所有配置,应通过读取配置文件得到配置的值 try { directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("./indexDir/")); analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(Version.LUCENE_30); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } public static Directory getDirectory() { return directory; } public static Analyzer getAnalyzer() { return analyzer; } }
public void save(Article article) { // 1,把对象转为Document Document doc = ArticleDocumentUtils.articleToDocument(article); IndexWriter indexWriter = null; // 2,添加到索引库中 try { indexWriter = new IndexWriter(Configuration.getDirectory(),Configuration.getAnalyzer(),MaxFieldLength.LIMITED); indexWriter.addDocument(doc); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally{ try { if(indexWriter!=null){ indexWriter.close(); } } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
public void delete(Integer id) { IndexWriter indexWriter = null; try { //term:某个字段的一个关键词 Term term = new Term("id", id.toString()); indexWriter = new IndexWriter(Configuration.getDirectory(),Configuration.getAnalyzer(),MaxFieldLength.LIMITED); indexWriter.deleteDocuments(term); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally{ try { if(indexWriter!=null){ indexWriter.close(); } } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } public void update(Article article) { IndexWriter indexWriter = null; try { //term:某个字段的一个关键词 Term term = new Term("id", article.getId().toString()); Document doc = ArticleDocumentUtils.articleToDocument(article); indexWriter = new IndexWriter(Configuration.getDirectory(),Configuration.getAnalyzer(),MaxFieldLength.LIMITED); //indexWriter.updateDocument(term, doc); // 更新就是先删除再创建 indexWriter.deleteDocuments(term); indexWriter.addDocument(doc); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally{ try { if(indexWriter!=null){ indexWriter.close(); } } catch (Exception e) { Throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
更新索引库
索引文件的检索与维护,更新是先删除后创建
维护倒排索引有三个操作:添加、删除和更新文档。但是更新操作需要较高的代价。因为文档修改后(即使是很小的修改),就可能会造成文档中的很多的关键词的位置都发生了变化,这就需要频繁的读取和修改记录,这种代价是相当高的。因此,一般不进行真正的更新操作,而是使用“先删除,再创建”的方式代替更新操作。
public SearchResult<Article> search(String queryString, int firstResult, int maxResults) { IndexSearcher indexSearcher = null; try { // 1,把查询字符串转为Query对象 // QueryParser queryParser = new QueryParser(Version.LUCENE_30, "title",Configuration.getAnalyzer()); // 默认只在title中查询 QueryParser queryParser = new MultiFieldQueryParser(Version.LUCENE_30, new String[] { "title", "content" }, Configuration.getAnalyzer()); // 默认在多个字段中查询 Query query = queryParser.parse(queryString); // 2,执行查询,得到中间结果 indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(Configuration.getDirectory()); TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, firstResult + maxResults); // 最多返回前n条结果 int count = topDocs.totalHits; // 总记录数 ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = topDocs.scoreDocs; // 前n条结果的信息 // 3,处理结果 List<Article> list = new ArrayList<Article>(); int endIndex = Math.min(firstResult + maxResults, scoreDocs.length); for (int i = firstResult; i < endIndex; i++) { // 只取一段数据 // 根据内部编号取出Document数据 Document doc = indexSearcher.doc(scoreDocs[i].doc); // 把Document转为Article Article article = ArticleDocumentUtils.documentToArticle(doc); list.add(article); } return new SearchResult<Article>(count,list); // 返回 } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally{ if(indexSearcher!=null){ try { indexSearcher.close(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
public class SearchResult<T> { private int count; private List<T> list; public SearchResult(int count, List<T> list) { this.count = count; this.list = list; } //提供set和get方法 } private ArticleIndexDao1 indexDao1 = new ArticleIndexDao1(); @Test public void testSave_1() { // 模拟了一个已保存到数据库中的数据 Article article = new Article(); article.setId(1); article.setTitle("Lucene全文检索的说明"); article.setContent("全文检索(Full-Text Retrieval)是指以文本作为检索对象,找出含有指定词汇的文本。"); indexDao1.save(article); } @Test public void testSave_25() { for(int i=1;i<=25;i++){ // 模拟了一个已保存到数据库中的数据 Article article = new Article(); article.setId(i); article.setTitle("Lucene全文检索的说明"); article.setContent("全文检索(Full-Text Retrieval)是指以文本作为检索对象,找出含有指定词汇的文本。"); indexDao1.save(article); } }
private ArticleIndexDao1 indexDao1 = new ArticleIndexDao1(); @Test public void testDelete() { Integer id = 1; indexDao1.delete(id); } @Test public void testUpdate() { // 模拟了一个已保存到数据库中的数据 Article article = new Article(); article.setId(1); article.setTitle("Lucene全文检索的说明123"); article.setContent("这是更新后的数据123"); indexDao1.update(article); }
private ArticleIndexDao1 indexDao1 = new ArticleIndexDao1(); @Test public void testSearch() { String queryString = "lucene"; //SearchResult<Article> queryResult = indexDao1.search(queryString, 0, 10000); //SearchResult<Article> queryResult = indexDao1.search(queryString, 0, 10); //SearchResult<Article> queryResult = indexDao1.search(queryString, 10, 10); SearchResult<Article> queryResult = indexDao1.search(queryString, 20, 10); System.out.println("总记录数是:"+ queryResult.getCount()); for(Article article: queryResult.getList()){ System.out.println("-----------> id = " + article.getId()); System.out.println("title = " + article.getTitle()); System.out.println("content= " + article.getContent()); } }
IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(Configuration.getDirectory(),Configuration.getAnalyzer(),MaxFieldLength.LIMITED); //indexWriter.close(); IndexWriter indexWriter2 = new IndexWriter(Configuration.getDirectory(),Configuration.getAnalyzer(),MaxFieldLength.LIMITED); //indexWriter2.close();