介绍
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h> int main(void) { int *p; //定义了一个指针变量,但并没有为期附初值;下面两个函数都是为其fu初值的操作 f(&p); //f函数,为指针变量p附了一个准确的值,所以是正确的操作 //g(&p);//g函数,虽然在g函数执行过程中未p附了一个准确的值,但g函数执行结束后指针变量的值,并非是一个准确的值 return 0; } void f(int ** q) { *q = (int *)malloc(4); // 动态分配的内存,程序员不手动释放的话,操作系统并不会自动为其释放内存 } void g(int ** q) { int r; //静态分配的内存,在该函数(g)调用完毕后,操作系统自动为期释放内存(出栈) *q = &r; }
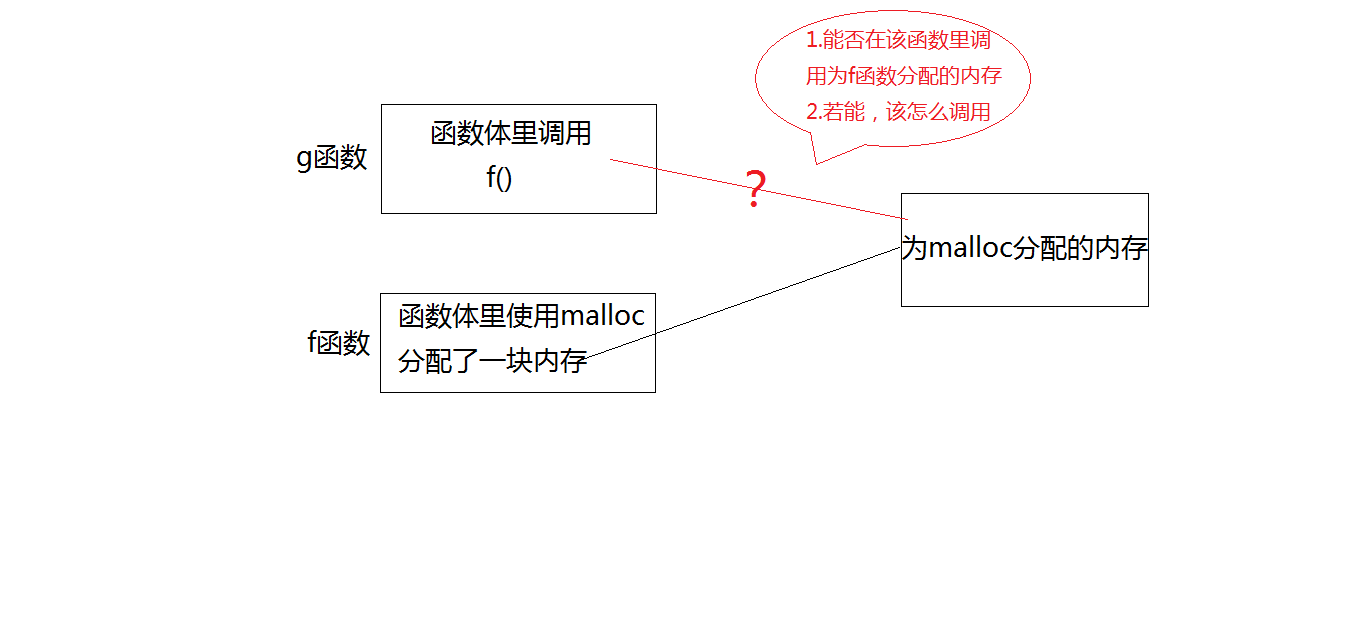
//要想实现跨函数使用内存,只能通过使用动态内存的方法
例子
#include <stdio.h> #include <malloc.h> struct Student { int sid; int age; }; struct Student * CreateStudent(void); void ShowStudent(struct Student *); int main(void) { struct Student * ps; ps = CreateStudent(); ShowStudent(ps); return 0; } void ShowStudent(struct Student * pst) { printf("%d %d ", pst->sid, pst->age); } struct Student * CreateStudent(void) { struct Student * p = (struct Student *)malloc(sizeof(struct Student)); p->sid = 99; p->age = 88; return p; } /* 输出结果:99 88 */