一、多态
1、什么是多态?
- 多种形态
- 是指一个对象在不同时刻,表现出来不同的状态
- 比如说,水滴,液态、气态、固态。
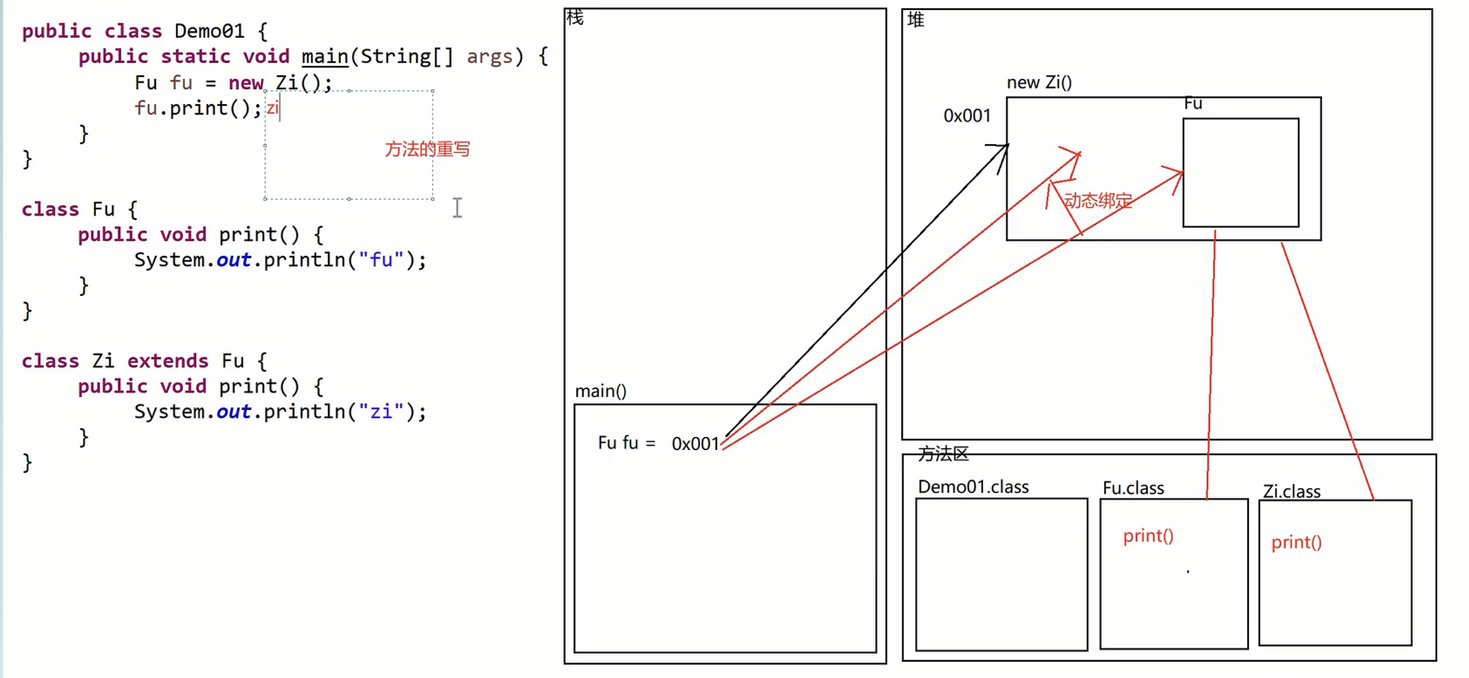
2、多态的前提条件
- 要有继承关系
- 要有方法重写
- 要有父类引用指向子类对象
口诀:
1.在多态,成员变量/静态方法/静态变量 编译、运行看左边。
2.在多态,方法重写编译看左边、运行看右边。
package com.ppl.day; /* com.ppl.day:学习项目 @user:广深-小龙 @date:2022/1/3 15:51 */ /* 口诀: 1.在多态,成员变量/静态方法/静态变量 编译、运行看左边。 2.在多态,方法重写编译看左边、运行看右边。 */ public class Day13 { public static void main(String[] args) { Fu1 f = new Zi1(); System.out.println(f.i); System.out.println(f.j); // Fu1 没有变量 j f.print(); f.printFu(); } } class Fu1 { int i = 1; int j = 3; public void printFu() { System.out.println("printFu"); } public void print() { System.out.println("Fu1"); } } class Zi1 extends Fu1 { int j = 2; public void print() { System.out.println("Zi1"); } }
输出:
1
3
Zi1
printFu
3、多态的优劣
优点:
- 提高代码扩展性
- 父类引用作为形式参数,子类对象作为实际参数
/* 多态的应用 1.提高代码扩展性 2.父类引用作为形式参数,子类对象作为实际参数 */ class Anima { public void eat() { } } class AnimalTool { // 继承结合多态的应用,一个工具类的方法即可 public static void print(Anima anima) { anima.eat(); } // 原每个子类调用时,都需要+一个工具类方法 // public static void print(Cat cat) { // cat.eat(); // } // public static void print(Dog dog) { // dog.eat(); // } } class Cat extends Anima { public void eat() { System.out.println("猫吃鱼..."); } } class Dog extends Anima { public void eat() { System.out.println("狗啃骨头..."); } }
缺点:
- 父类引用不能使用子类中的内容,解决:向下转型
package com.ppl.day; /* com.ppl.day:学习项目 @user:广深-小龙 @date:2022/1/3 16:46 */ public class Day14 { public static void main(String[] args) { PPerson p = new Student(); // 向上转型 p.eat(); // 吃 // p.play(); // 编译看左边,左边p没该方法,所以报错,需要向下转型 Student s = (Student) p; // 向下转型 s.play(); } } class PPerson { public void eat() { System.out.println("吃..."); } } class Student extends PPerson { public void eat() { System.out.println("学生吃面条..."); } public void play() { System.out.println("学生玩游戏..."); } }
注意:PPerson p = new Student(); // 向上转型
向下转型时必须是 Student x = (Student)p,不能是其它;否则运行时报错,编译不会报错。ClassCastException
多态:同一个对象在不同时刻表现不同的状态。可上下转型。如狗 --> 动物 --> 生物
欢迎来大家QQ交流群一起学习:482713805,博主微信+:gogsxl