String构造方法初始化和常量赋值初始化区别
下面的代码是一个String对象的两种不同的初始化方式,关于这两种不同初始化方式的区别,本文通过画内存图来进行解释,首先代码如下:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = new String("hello"); String s2 = "hello"; System.out.println(s1 == s2); System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); } }
s1是通过String类的构造方法进行初始化的,s2是通过字符串常量进行赋值初始化的,该程序在内存中的图如下:
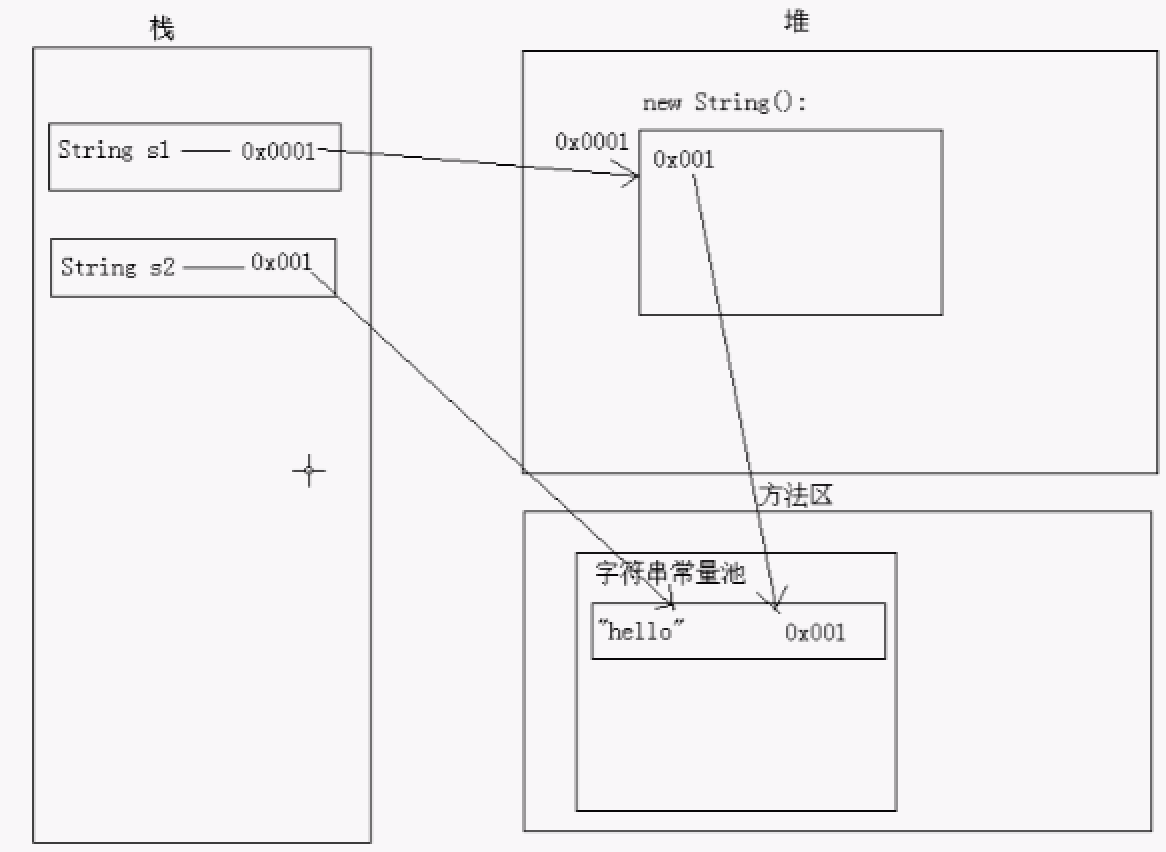
字符串常量都是存储在方法区的字符串常量池中,所以第一种方式的初始化是先在堆中建立一个对象,然后该对象的值来自方法区的“hello”,所以方式1的初始化方式最多会创建2个对象,最少创建1个;方式2的初始化由于是字符串常量直接赋值,所以直接去方法区里面查找,最后返回已有对象,所以方式2的初始化方式最多创建1个对象,最少创建0个,例如本例中,由于方法区中已有“hello”,所以创建0个。
String常量值不可以变,但引用可以变
直接上代码来解释了:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "hello"; String s1 = s; System.out.println("s: " + s); System.out.println("s1: " + s1); System.out.println("---------------"); s = "world"; System.out.println("s: " + s); System.out.println("s1: " + s1); } }
结果:
s: hello s1: hello --------------- s: world s1: hello Process finished with exit code 0
可以看出,对s进行重新复制,并没有改变原来的hello,只是将s指向了新的“world”。
String中常量拼接和变量拼接效果不同
首先看下面这段代码中的helloworld的不同拼接方式:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "hello"; String s2 = "world"; String s3 = "helloworld"; System.out.println(s3 == s1 + s2); System.out.println(s3.equals(s1 + s2)); System.out.println("-------------------"); System.out.println(s3 == "hello" + "world"); System.out.println(s3.equals("hello" + "world")); } }
程序运行的结果是:
false true ------------------- true true Process finished with exit code 0
equals的比较由于内容相同,为true并不奇怪,但是变量拼接和s3比较的结果为false,而常量拼接结果却为true。这就是String中常量拼接和变量拼接的区别了。
- 变量拼接:先开辟空间,再去拼接;
所以s1+s2结果存储在新开辟的空间中,地址自然和s3不一样。反编译的代码是:System.out.println(s3 == (new StringBuffer(String.valueOf(s1)).append(String.valueOf(s2))).toString());
- 常量拼接:先拼接,再在常量池中查找,如果有,则返回找到的地址,否则创建新的常量。
所以”hello“+”world“拼接后再常量池中找到了s3,所以返回s3的地址,所以结果为true。反编译的代码是:System.out.println(s3 == "helloworld");//所以可以看出,编译器对变量的拼接直接做了优化
内容为空和null的区别
直接上代码看结果解释:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = ""; String s2 = null; System.out.println(s1.isEmpty()); System.out.println(s2.isEmpty()); } } true Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException at Test.main(Test.java:6) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:57) at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:606) at com.intellij.rt.execution.application.AppMain.main(AppMain.java:140) Process finished with exit code 1
很明显,s1是可以调用String对象的方法的,而s2由于是null的,所以s2没有指向任何字符串对象,所以调用对象的方法会报空指针错误。