写在前面的话
相关背景及资源:
曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享
曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,咱们对着接口,逐个方法讲解
曹工说Spring Boot源码(3)-- 手动注册Bean Definition不比游戏好玩吗,我们来试一下
曹工说Spring Boot源码(4)-- 我是怎么自定义ApplicationContext,从json文件读取bean definition的?
工程结构图:

整体思路
bean definition实在太过重要,可以说是基础中的基础,所以我们花了很多讲在这上面,本讲的主题,还是这个。这次,我们是从properties文件里读取bean definition。
但是,上次,从json读取,我们自己实现了org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader,使用fastjson从json文件内读取。
这次,我们不需要自己实现,是因为spring-beans包内,居然自带了从properties文件读取bean的实现类。

所以,这样就变得很简单了,我们只需要定义一个applicationContext,让它使用这个开箱即用的reader即可。
闲言少叙,let's code!
本场大佬简介--PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader
本类的javadoc如是说:
* Bean definition reader for a simple properties format. * * <p>Provides bean definition registration methods for Map/Properties and * ResourceBundle. Typically applied to a DefaultListableBeanFactory.
这里说,就是一个从properties格式的文件读取bean definition的,那么,是不是properties可以随便怎么写呢?嗯,按理说,是可以随便写,你别管我怎么写,形式重要吗,重要的是,有这个数据。
bean definition的核心数据有哪些?再回忆一下,beanClassName、scope、lazy-init、parent、abstract等。
parent和abstract,是个新概念,前面我也没有提,大家看下面的例子可能就懂了(来自于PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader的注释,我自己梳理了一下)。
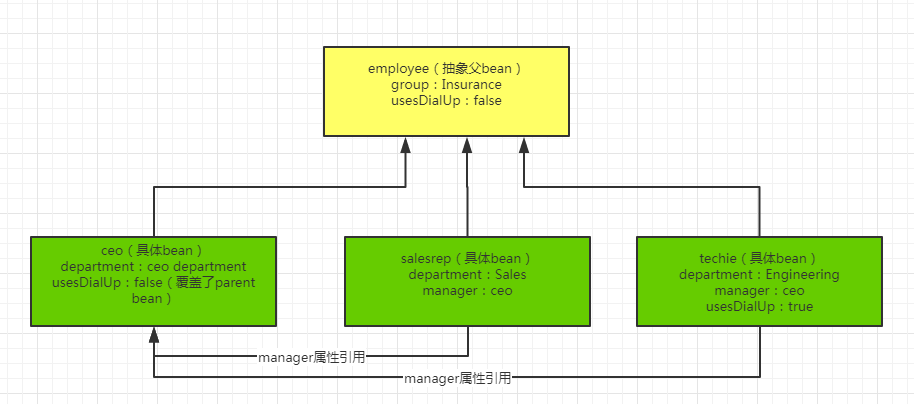
这个reader,对properties的格式是有要求的,参考下面这份:
//定义一个抽象bean,名称为employee(句号前面为bean的名称),表示为员工,类型为Employee,两个属性:组名:Insurance;useDialUp(我理解为工位是否配电话):true
employee.(class)=org.springframework.simple.Employee
employee.(abstract)=true
employee.group=Insurance
employee.usesDialUp=false
//定义一个非抽象bean,parent为抽象的employee,department属性为CEOdepartment,usesDialUp为true,覆盖了parent的false
ceo.(parent)=employee
ceo.department=ceo department
ceo.usesDialUp=true
//定义另一个非抽象bean,表示销售人员,lazy-init,经理字段:引用了另一个bean,name为ceo;部门为Sales
salesrep.(parent)=employee
salesrep.(lazy-init)=true
salesrep.manager(ref)=ceo
salesrep.department=Sales
//这个类似
techie.(parent)=employee
techie.(scope)=prototype
techie.department=Engineering
techie.usesDialUp=true
techie.manager(ref)=ceo
贴心的我给大家花了个图:
详细剖析
接下来,我们还是先看看这个类:

实现接口
看一个类,其实主要看接口,才能快速了解一个类的用途,这里,它实现了org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionReader接口。
这个接口的方法如下:
public interface BeanDefinitionReader {
//获取bean definition 注册中心,老朋友DefaultListableBeanFactory实现了该接口
BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry();
// 获取资源加载器
ResourceLoader getResourceLoader();
//获取classloader
ClassLoader getBeanClassLoader();
//获取bean名称生成器
BeanNameGenerator getBeanNameGenerator();
//从指定资源充,加载bean definition
int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
//重载
int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
//重载
int loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
//重载
int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
}
大体,可以看出来,这个bean definition reader接口,就是使用指定的classloader,从指定的resource,去加载bean definition。
加载bean definition
我们先看看PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader怎么构造:
//调用父类,参数传入了bean definition 注册表
public PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
super(registry);
}
//构造默认的资源加载器、environment
protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this.registry = registry;
// Determine ResourceLoader to use.
if (this.registry instanceof ResourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = (ResourceLoader) this.registry;
}
else {
this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
}
// Inherit Environment if possible
if (this.registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) {
this.environment = ((EnvironmentCapable)this.registry).getEnvironment();
}
else {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
}
再看主要的loadBeanDefinition方法,是怎么实现的:
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource), null);
}
调用了内部的:
//加载bean definition
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource, String prefix)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//读取properties文件内容到props变量
Properties props = new Properties();
InputStream is = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(is, encodedResource.getEncoding());
props.load(reader);
}
else {
props.load(is);
}
//注册bean definition
return registerBeanDefinitions(props, prefix, null);
}
继续深入上面的倒数第二行的函数:
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Map map, String prefix, String resourceDescription)
throws BeansException {
if (prefix == null) {
prefix = "";
}
int beanCount = 0;
for (Object key : map.keySet()) {
String keyString = (String) key;
if (keyString.startsWith(prefix)) {
// Key is of form: prefix<name>.property
String nameAndProperty = keyString.substring(prefix.length());
// Find dot before property name, ignoring dots in property keys.
int sepIdx = nameAndProperty.lastIndexOf(SEPARATOR);
if (sepIdx != -1) {
String beanName = nameAndProperty.substring(0, sepIdx);
if (!getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// 如果之前没注册这个bean,则注册之,这里的prefix:prefix+beanName,其实就是从properties文件中筛选出beanName一致的key-value
registerBeanDefinition(beanName, map, prefix + beanName, resourceDescription);
++beanCount;
}
}
}
}
return beanCount;
}
主要就是遍历map,将property的key用.分割,前面的就是beanName,用beanName作为前缀,然后调用下一层函数:
public static final String CLASS_KEY = "(class)";
public static final String PARENT_KEY = "(parent)";
public static final String SCOPE_KEY = "(scope)";
public static final String SINGLETON_KEY = "(singleton)";
public static final String ABSTRACT_KEY = "(abstract)";
public static final String LAZY_INIT_KEY = "(lazy-init)";
public static final String REF_SUFFIX = "(ref)";
protected void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, Map<?, ?> map, String prefix, String resourceDescription)
throws BeansException {
String className = null;
String parent = null;
String scope = GenericBeanDefinition.SCOPE_SINGLETON;
boolean isAbstract = false;
boolean lazyInit = false;
ConstructorArgumentValues cas = new ConstructorArgumentValues();
MutablePropertyValues pvs = new MutablePropertyValues();
for (Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()) {
String key = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getKey());
if (key.startsWith(prefix + SEPARATOR)) {
String property = key.substring(prefix.length() + SEPARATOR.length());
//核心属性,bean的ClassName
if (CLASS_KEY.equals(property)) {
className = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue());
}//parent属性
else if (PARENT_KEY.equals(property)) {
parent = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue());
}//是否抽象bean definition
else if (ABSTRACT_KEY.equals(property)) {
String val = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue());
isAbstract = TRUE_VALUE.equals(val);
}//scope
...此处不重要的属性代码进行省略
//通过构造器注入其他bean,我们例子里没涉及
else if (property.startsWith(CONSTRUCTOR_ARG_PREFIX)) {
if (property.endsWith(REF_SUFFIX)) {
int index = Integer.parseInt(property.substring(1, property.length() - REF_SUFFIX.length()));
cas.addIndexedArgumentValue(index, new RuntimeBeanReference(entry.getValue().toString()));
}
else {
int index = Integer.parseInt(property.substring(1));
cas.addIndexedArgumentValue(index, readValue(entry));
}
}
// 这里引用其他bean,语法是我们例子用到的,(ref)
else if (property.endsWith(REF_SUFFIX)) {
property = property.substring(0, property.length() - REF_SUFFIX.length());
String ref = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue());
Object val = new RuntimeBeanReference(ref);
pvs.add(property, val);
}
else {
// It's a normal bean property.
pvs.add(property, readValue(entry));
}
}
}
//构造一个bean definition
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.createBeanDefinition(
parent, className, getBeanClassLoader());
bd.setScope(scope);
bd.setAbstract(isAbstract);
bd.setLazyInit(lazyInit);
//下面这两行,进行构造器注入和属性注入
bd.setConstructorArgumentValues(cas);
bd.setPropertyValues(pvs);
//注册
getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(beanName, bd);
}
本类的主要代码就这些,删减了部分,主要是避免太冗余,代码有删减就会使用...表示。
定义applicationContext
package org.springframework.beans.extend.properties.applicationcontext;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ClassPathPropertyFileApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext {
/**
* Loads the bean definitions via an XmlBeanDefinitionReader.
* @see XmlBeanDefinitionReader
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions
*/
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// 构造一个propertiesBeanDefinitionReader,就是前面我们的主角
PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
//使用reader,加载bean definition
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
String[] configResources = getConfigLocations();
if (configResources != null) {
//看这,兄弟
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
}
public ClassPathPropertyFileApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
}
测试代码
@Slf4j
public class BootStrap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathPropertyFileApplicationContext context = new ClassPathPropertyFileApplicationContext("beanDefinition.properties");
Map<String, Employee> beansOfType = context.getBeansOfType(Employee.class);
for (Map.Entry<String, Employee> entry : beansOfType.entrySet()) {
log.info("bean name:{},bean:{}",entry.getKey(),entry.getValue());
}
}
}
output:
22:17:26.083 [main] INFO o.s.b.extend.properties.BootStrap - bean name:techie,bean:Employee(group=Insurance, usesDialUp=true, department=Engineering, manager=Employee(group=Insurance, usesDialUp=true, department=ceo department, manager=null))
22:17:26.083 [main] INFO o.s.b.extend.properties.BootStrap - bean name:salesrep,bean:Employee(group=Insurance, usesDialUp=false, department=Sales, manager=Employee(group=Insurance, usesDialUp=true, department=ceo department, manager=null))
22:17:26.083 [main] INFO o.s.b.extend.properties.BootStrap - bean name:ceo,bean:Employee(group=Insurance, usesDialUp=true, department=ceo department, manager=null)
这里可以看出来,子bean是继承了父bean的bean definition,并override了父bean中已经存在的属性。
总结
工程源码:
这一讲,主要是讲解了另一种读取bean definition的方式,其实就是告诉我们要打破思想束缚,bean的来源可以用很多,不一定只有xml和注解。另外,也是培养我们的抽象思维,至少bean definition reader这个接口,给我们的感觉就是如此,我不管你resource来自哪里,只要能读取bean definition即可,正所谓:英雄不问出处!
我们作为技术从业人员也是如此,只要技术够ok,到哪都能混得走。
下一讲,我们将继续讲解bean definition,主要是bean definition的继承和override相关内容。
觉得有帮助的话,大家点个赞哈