https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/900/
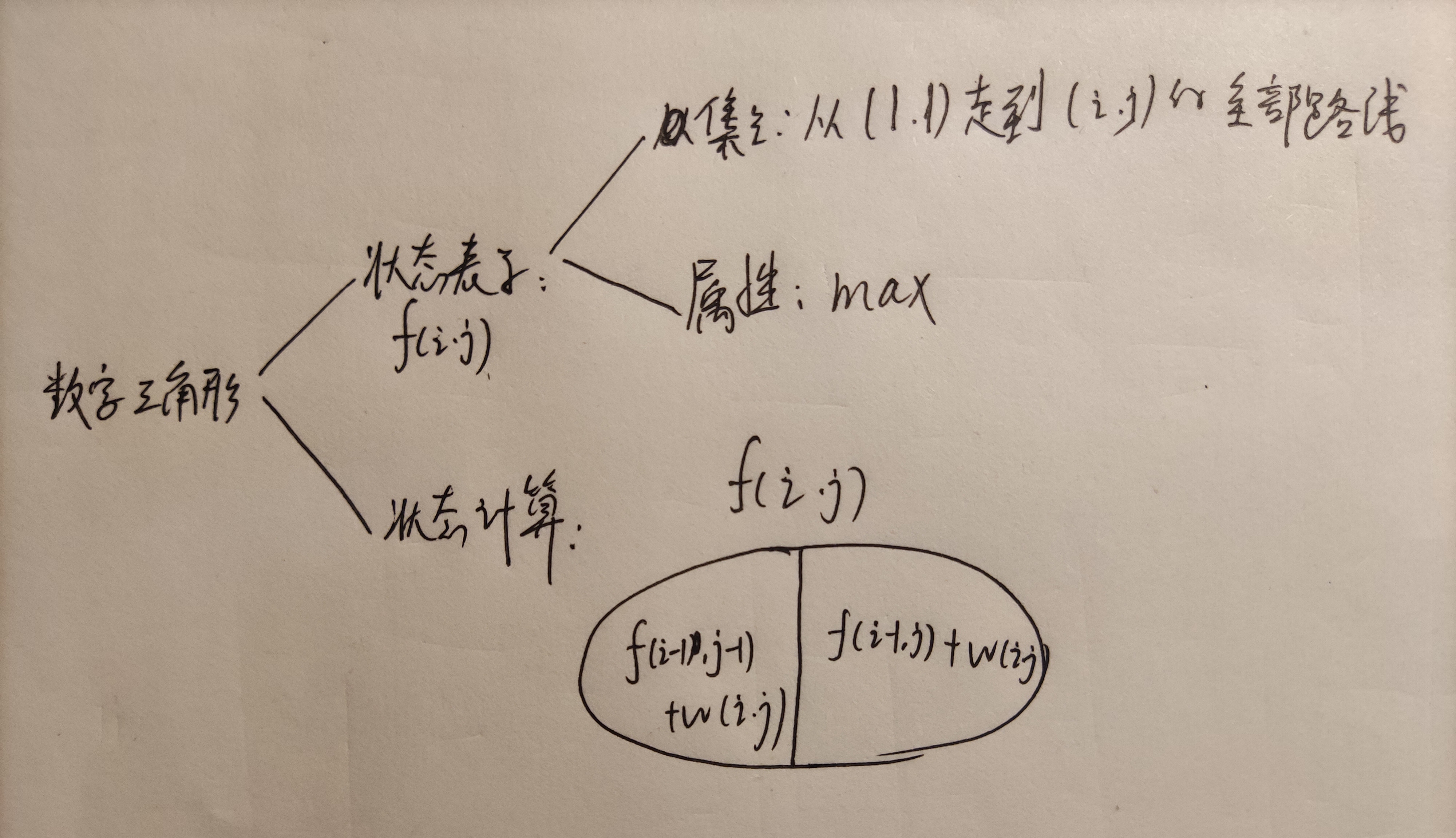
注意处理边界即可。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 const int N=510; 6 int a[N][N],f[N][N]; 7 int n; 8 int main() 9 { 10 cin>>n; 11 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 12 for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){ 13 cin>>a[i][j]; 14 } 15 } 16 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 17 for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){ 18 if(j==1){ 19 f[i][j]=f[i-1][j]+a[i][j]; 20 }else if(j==i){ 21 f[i][j]=f[i-1][j-1]+a[i][j]; 22 }else{ 23 f[i][j]=max(f[i-1][j-1],f[i-1][j])+a[i][j]; 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 int res=-10000*510; 28 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) res=max(res,f[n][i]); 29 cout<<res; 30 return 0; 31 }
扩展1:将区域扩展为矩形----摘花生
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1017/
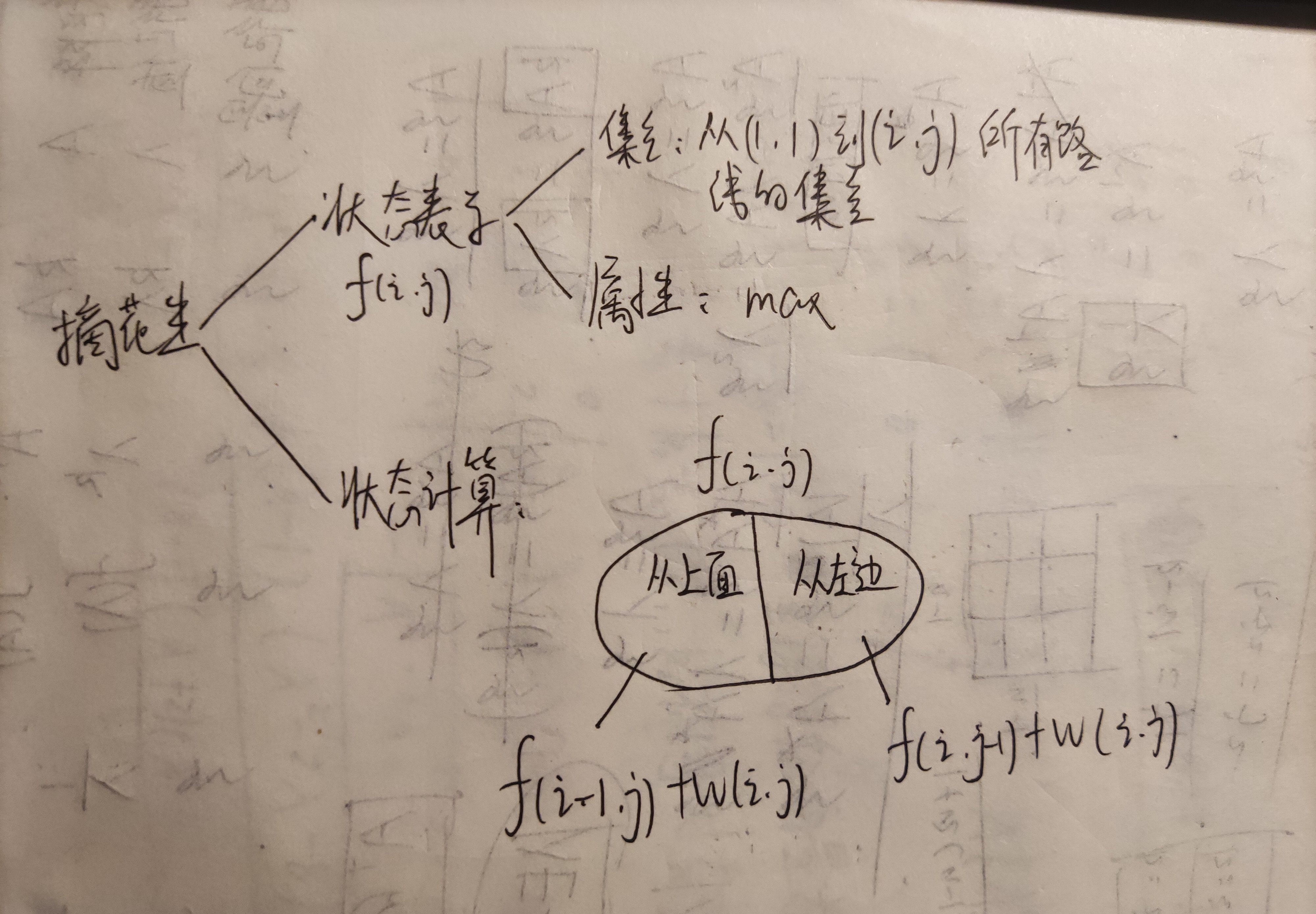
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 const int N=110; 6 int w[N][N]; 7 int f[N][N]; 8 int main() 9 { 10 int T; 11 cin>>T; 12 while(T--){ 13 memset(f,0,sizeof f); 14 int n,m; 15 cin>>n>>m; 16 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 17 for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ 18 cin>>w[i][j]; 19 } 20 } 21 f[1][1]=w[1][1]; 22 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 23 for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ 24 if(i!=1) f[i][j]=max(f[i][j],f[i-1][j]+w[i][j]); 25 if(j!=1) f[i][j]=max(f[i][j],f[i][j-1]+w[i][j]); 26 } 27 } 28 cout<<f[n][m]<<endl; 29 } 30 return 0; 31 }
扩展2:最低通行费,给定步数为2*n-1,而区域大小为n*n,故同摘花生。
但因为目标是获得最小值,故注意初始化。
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1020/
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 const int N = 110,INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 6 int w[N][N]; 7 int f[N][N]; 8 int main() 9 { 10 int n; 11 cin>>n; 12 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 13 for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){ 14 cin>>w[i][j]; 15 } 16 } 17 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 18 for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){ 19 f[i][j]=INF; 20 if(i==1&&j==1) f[i][j]=w[i][j]; 21 else{ 22 if(i!=1) f[i][j]=min(f[i][j],f[i-1][j]+w[i][j]); 23 if(j!=1) f[i][j]=min(f[i][j],f[i][j-1]+w[i][j]); 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 cout<<f[n][n]; 28 return 0; 29 }
扩展3:方格取数,或称为传纸条,题设同样为矩形,两条从左上到右下的路线,因为权值均大于0,所以二者都是两条路线不重合。
目标是使得权值最大。
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1029/

只需要在每次转移的时候判断两点是否重合即可。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 const int N = 15; 6 int w[N][N]; 7 int f[N][N][N][N]; 8 9 int main() 10 { 11 int n; 12 cin>>n; 13 int a,b,c; 14 while(cin>>a>>b>>c,a||b||c) w[a][b]=c; 15 for(int i1=1;i1<=n;i1++){ 16 for(int j1=1;j1<=n;j1++){ 17 for(int i2=1;i2<=n;i2++){ 18 for(int j2=1;j2<=n;j2++){ 19 int & x= f[i1][j1][i2][j2]; 20 int t=w[i1][j1]; 21 if(i1!=i2&&j1!=j2) 22 t+=w[i2][j2]; 23 x=max(x,f[i1-1][j1][i2-1][j2]+t); 24 x=max(x,f[i1][j1-1][i2-1][j2]+t); 25 x=max(x,f[i1-1][j1][i2][j2-1]+t); 26 x=max(x,f[i1][j1-1][i2][j2-1]+t); 27 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 cout<<f[n][n][n][n]<<endl; 33 return 0; 34 }
又因为步数+横坐标即可唯一确定位置,所以我们可以优化掉一维。
f [ k ] [ i1 ] [ i2 ]表示经过k步后,第一条停在( i1 , k - i1)的位置,第二条停在( i2 , k - i2)的位置。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 const int N = 15; 6 int w[N][N]; 7 int f[N*2][N][N]; 8 9 int main() 10 { 11 int n; 12 cin>>n; 13 int a,b,c; 14 while(cin>>a>>b>>c,a||b||c) w[a][b]=c; 15 for(int k=2;k<=n+n;k++){ 16 for(int i1=1;i1<=n;i1++){ 17 for(int i2=1;i2<=n;i2++){ 18 int j1=k-i1; 19 int j2=k-i2; 20 int & x= f[k][i1][i2]; 21 int t=w[i1][j1]; 22 if(i1!=i2&&j1!=j2) 23 t+=w[i2][j2]; 24 x=max(x,f[k-1][i1-1][i2-1]+t); 25 x=max(x,f[k-1][i1-1][i2]+t); 26 x=max(x,f[k-1][i1][i2-1]+t); 27 x=max(x,f[k-1][i1][i2]+t); 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 cout<<f[n+n][n][n]<<endl; 32 return 0; 33 }