父组件通过props属性向子组件传递数据,定义组件的时候可以定义一个props属性,值可以是一个字符串数组或一个对象。
例如:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.5.16/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"><child :title="message"></child></div>
<script>
Vue.component('child',{
template:'<h1>{{title}}</h1>',props:['title'] //这里props是一个字符串数组
})
var app = new Vue({
el:'#app',data:{message:'Hello World'}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
这里我们给child这个组件定义了名为title的props,父组件通过title特性传递给子组件,渲染为:
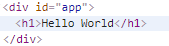
props除了数组,也可以是一个对象,此时对象的键对应的props的名称,值又是一个对象,可以包含如下属性:
type: ;类型,可以设置为:String、Number、Boolean、Array、Object、Date等等 ;如果只设置type而未设置其他选项,则值可以直接用类型,例如:props:{title:Object}
default ;默认值
required ;布尔类型,表示是否必填项目
validator ;自定义验证函数
例如:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.5.16/dist/vue.js"></script>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"><child></child></div>
<script>
Vue.component('child',{
template:'<h1>{{title}}</h1>',props:{title:{default:'Hello World'}} //这里我们定义的title是个对象,含有默认值
})
var app = new Vue({
el:'#app'
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
这里父组件app没有给子组件child传递数据,子组件使用了默认值Hello World,渲染的结果和第一个例子是一样的。
源码分析
以上面的例1为例,Vue.component()注册组件的时候会调用Vue.extend()生成一个Vue基础构造器,内部会调用mergeOptions函数合并属性, mergeOptions又会调用normalizeProps对props的属性进行一些规范化的修饰,如下:
function normalizeProps (options, vm) { //第1361行 规范化props属性 var props = options.props; //尝试获取props属性 if (!props) { return } var res = {}; var i, val, name; if (Array.isArray(props)) { //如果props是个数组 ;这是props的数组用法的分支 i = props.length; while (i--) { //遍历props val = props[i]; if (typeof val === 'string') { //如果值是一个字符串 name = camelize(val); res[name] = { type: null }; //保存到res里面 ;例如:{ title: {type: null} } } else { warn('props must be strings when using array syntax.'); } } } else if (isPlainObject(props)) { //如果props是个对象 ;这是props的对象用法的分支 for (var key in props) { val = props[key]; name = camelize(key); res[name] = isPlainObject(val) ? val : { type: val }; } } else { warn( "Invalid value for option "props": expected an Array or an Object, " + "but got " + (toRawType(props)) + ".", vm ); } options.props = res; }
经过normalizeProps规范后,props被修饰为一个对象格式,例子里的执行到这里等于:

接下来_render函数执行遇到该组件时会执行createComponent函数,该函数又会执行extractPropsFromVNodeData(data, Ctor, tag)函数,如下:
function extractPropsFromVNodeData ( //第2109行 获取原始值 data, Ctor, tag ) { // we are only extracting raw values here. // validation and default values are handled in the child // component itself. var propOptions = Ctor.options.props; //获取组件的定义的props对象,例如:{message: {type: null}} if (isUndef(propOptions)) { return } var res = {}; var attrs = data.attrs; //获取data的attrs属性,例如:{title: "Hello Vue"} var props = data.props; //获取data的props属性,这应该是建立父子组件时的关系 if (isDef(attrs) || isDef(props)) { //如果data有定义了attrs或者props属性 for (var key in propOptions) { //遍历组件的props属性 var altKey = hyphenate(key); { var keyInLowerCase = key.toLowerCase(); //hyphenate:如果key是是驼峰字符串,则转换为-格式 if ( key !== keyInLowerCase && attrs && hasOwn(attrs, keyInLowerCase) //转换为小写格式 ) { tip( "Prop "" + keyInLowerCase + "" is passed to component " + (formatComponentName(tag || Ctor)) + ", but the declared prop name is" + " "" + key + "". " + "Note that HTML attributes are case-insensitive and camelCased " + "props need to use their kebab-case equivalents when using in-DOM " + "templates. You should probably use "" + altKey + "" instead of "" + key + ""." ); } } checkProp(res, props, key, altKey, true) || //调用checkProp优先从props里拿对应的属性,其次从attrs里拿(对于attrs的话第五个参数为false,即会删除对应的attrs里的属性) checkProp(res, attrs, key, altKey, false); } } return res }
checkProp是检测props或attrs是否含有key对应的值,如下:
function checkProp ( //第2150行 检测prop是否存在 res, hash, key, altKey, preserve ) { if (isDef(hash)) { //如果hash存在 if (hasOwn(hash, key)) { //如果hash里面有定义了key res[key] = hash[key]; if (!preserve) { delete hash[key]; } return true } else if (hasOwn(hash, altKey)) { //如果有驼峰的表示法,也找到了 res[key] = hash[altKey]; if (!preserve) { delete hash[altKey]; } return true } } return false //如果在res里未找到则返回false }
extractPropsFromVNodeData只是获取值,验证理验证和默认值是子组件完成执行的,执行到这里就获取到了props的值,例子里执行到这里等于

整个对象会作为propsData属性保存到组件的VNode里面,如下:
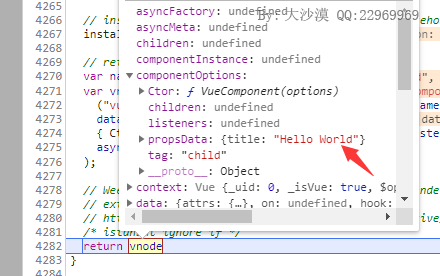
当子组件实例化的时候会执行_init()函数,首先会执行initInternalComponent函数,对于props的操作如下:
function initInternalComponent (vm, options) { //第4632行 子组件初始化子组件 var opts = vm.$options = Object.create(vm.constructor.options); //组件的配置信息 // doing this because it's faster than dynamic enumeration. var parentVnode = options._parentVnode; //该组件的占位符VNode opts.parent = options.parent; opts._parentVnode = parentVnode; opts._parentElm = options._parentElm; opts._refElm = options._refElm; var vnodeComponentOptions = parentVnode.componentOptions; //占位符VNode初始化传入的配置信息 opts.propsData = vnodeComponentOptions.propsData; //这就是上面经过extractPropsFromVNodeData()得到的propsData对象 opts._parentListeners = vnodeComponentOptions.listeners; opts._renderChildren = vnodeComponentOptions.children; opts._componentTag = vnodeComponentOptions.tag; if (options.render) { opts.render = options.render; opts.staticRenderFns = options.staticRenderFns; } }
这样组件实例化时就得到了propsData了,如下
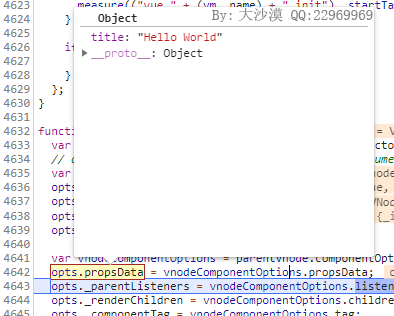
然后回到_init()初始化函数,会执行initState()函数,该函数首先会判断是否有props属性,如果有则执行initProps初始化props,如下:
function initProps (vm, propsOptions) { //第3319行 初始化props属性 var propsData = vm.$options.propsData || {}; //获取propsData属性,也就是例子里的{title:"Hello World"} var props = vm._props = {}; // cache prop keys so that future props updates can iterate using Array // instead of dynamic object key enumeration. var keys = vm.$options._propKeys = []; //用于保存当前组件的props里的key ;以便之后在父组件更新props时可以直接使用数组迭代,而不需要动态枚举键值 var isRoot = !vm.$parent; // root instance props should be converted if (!isRoot) { toggleObserving(false); } var loop = function ( key ) { //定义一个loop函数,一会儿会循环调用它 keys.push(key); //保存key var value = validateProp(key, propsOptions, propsData, vm); //执行validateProp检查propsData里的key值是否符合propsOptions里对应的要求,并将值保存到value里面 /* istanbul ignore else */ { var hyphenatedKey = hyphenate(key); if (isReservedAttribute(hyphenatedKey) || config.isReservedAttr(hyphenatedKey)) { warn( (""" + hyphenatedKey + "" is a reserved attribute and cannot be used as component prop."), vm ); } defineReactive(props, key, value, function () { //将key变成响应式,同时也定义了props的key属性的值为value if (vm.$parent && !isUpdatingChildComponent) { warn( "Avoid mutating a prop directly since the value will be " + "overwritten whenever the parent component re-renders. " + "Instead, use a data or computed property based on the prop's " + "value. Prop being mutated: "" + key + """, vm ); } }); } // static props are already proxied on the component's prototype // during Vue.extend(). We only need to proxy props defined at // instantiation here. if (!(key in vm)) { proxy(vm, "_props", key); } }; for (var key in propsOptions) loop( key ); //遍历每个props 依次调用loop()函数 toggleObserving(true); }
至此整个流程跑完了,前面说了extractPropsFromVNodeData只是获取值,而验证理验证和默认值就是在validateProp()函数内做的判断,如下:
function validateProp ( //第1582行 检查props key, propOptions, propsData, vm ) { var prop = propOptions[key]; //获取对应的值,例如:{type: null} var absent = !hasOwn(propsData, key); //如果propsData没有key这个键名,则absent为true var value = propsData[key]; //尝试获取propsData里key这个键的值 // boolean casting var booleanIndex = getTypeIndex(Boolean, prop.type); //调用getTypeIndex()含糊判断prop.type是否包含布尔类型 if (booleanIndex > -1) { if (absent && !hasOwn(prop, 'default')) { value = false; } else if (value === '' || value === hyphenate(key)) { // only cast empty string / same name to boolean if // boolean has higher priority var stringIndex = getTypeIndex(String, prop.type); if (stringIndex < 0 || booleanIndex < stringIndex) { value = true; } } } // check default value if (value === undefined) { //如果value未定义 value = getPropDefaultValue(vm, prop, key); //尝试获取默认值 // since the default value is a fresh copy, // make sure to observe it. var prevShouldObserve = shouldObserve; toggleObserving(true); observe(value); toggleObserving(prevShouldObserve); } { assertProp(prop, key, value, vm, absent); //判断Prop是否有效 } return value //最后返回value }
剩下来就几个工具函数了,比较简单,大致如此。
注:在Vue这么多属性里面,props是最有意思,最好玩的。虽然props的用法比较简单,但是它的原理实现我觉得是最复杂的,理解了props的实现原理,可以说是对Vue源码算是有比较大的深入了解了