DOC - Using and understanding OpenMesh
- DOC - Using and understanding OpenMesh
- Features and Goals of OpenMesh
- The Halfedge Data Structure
- Mesh Iterators and Circulators
- How to navigate on mesh
- Read and write meshes from files
- Some basic operations: Flipping and collapsing edge
- Collapsing edges
- Conceptual Class Hierarchy
- Specifying your MyMesh
- Specifying an OpenMesh using Eigen3 vectors
本文是对OpenMesh文档中《Using and understanding OpenMesh》一节的学习摘录。
Features and Goals of OpenMesh
数据结构主要特征是:
- 并不受限于三角形网格,可处理一般的多边形网格;
- 顶点,半边,边,面的明确表示;
- 高效的访问一个顶点的邻域;
- 能够处理非流形顶点(如两个面,共享一个顶点)。
The Halfedge Data Structure
半边数据结构中是将一条边,划分成了两条方向相对的半边,不同元素之间的连接关系,如下图所示:
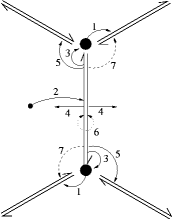
- 每个顶点存储了从它出发的半边,图中为1;
- 每个面存储了周围的一条半边,图中为2;
- 每个半边存储了以下handle:
- 指向的顶点,图中为3;
- 属于哪个面,图中为4;
- 共享面的下一个半边(逆时针方向),图中为5;
- 相对的半边,图中为6;
- 可选的,共享面的上一个半边,图中为7。
通过上面构建的关系,可以很方便的,对一个面周围的半边,顶点,相邻面进行遍历。
Mesh Iterators and Circulators
网格提供了迭代器,用来访问vertices,halfedges,edges,faces。所有的迭代器定义在OpenMesh::Iterators命名空间中,在具体使用的时候,可以用mesh内部的迭代器MyMesh::VertexIter取代OpenMesh::Iterators::VertexIterT<MyMesh>的形式。
迭代器的使用示例如下:
MyMesh mesh;
// iterate over all vertices
for (MyMesh::VertexIter v_it=mesh.vertices_begin(); v_it!=mesh.vertices_end(); ++v_it)
...; // do something with *v_it, v_it->, or *v_it
// iterate over all halfedges
for (MyMesh::HalfedgeIter h_it=mesh.halfedges_begin(); h_it!=mesh.halfedges_end(); ++h_it)
...; // do something with *h_it, h_it->, or *h_it
// iterate over all edges
for (MyMesh::EdgeIter e_it=mesh.edges_begin(); e_it!=mesh.edges_end(); ++e_it)
...; // do something with *e_it, e_it->, or *e_it
// iterator over all faces
for (MyMesh::FaceIter f_it=mesh.faces_begin(); f_it!=mesh.faces_end(); ++f_it)
...; // do something with *f_it, f_it->, or *f_it
删除的元素
如果mesh中没有元素被标记为删除,idx()返回的值依次从0到number of elements - 1。
但是如果有元素被标记为删除,同时没有执行垃圾回收(OpenMesh::ArrayKernel::garbage_collection() ),有效的idx并不是按顺序依次排列的。执行完垃圾回收之后,顺序会被重新调整。
OpenMesh使用惰性删除方案,以避免不必要的数据结构更新。 半边数据结构将始终直接进行更新,以确保以下算法具有正确的迭代器设置。
如果你删除一个面,这个面本身是存在的,但是位于hole的半边会更新,这意味着相邻顶点上的循环器将不再碰到该面。
如果删除了一条边,相邻的面也将被删除(标记它们已删除并更新周围的半边)。 边本身也将标记为已删除。 同样,循环器将不再看到删除的元素。
对于顶点,将使用上述方案删除所有相邻的面和边,并将顶点标记为已删除。
此时,迭代器仍然能够访问到所有的元素(包括,标记为删除的)。如果你使用skipping iterators,将会跳过删除的元素。
skipping iterators如下:
vertices_sbegin();edges_sbegin();halfedges_sbegin();faces_sbegin();
Circulators
用来快速访问邻域的迭代器。如,VertexVertexIter用来访问顶点的1-ring顶点;FaceHalfedgeIter用来访问属于这个面的半边;CenterItem_AuxiliaryInformation_TargetItem_Iter用来访问中心元素周围的所有相邻元素。主要有:
VertexVertexIter: 顶点的所有1-ring顶点;VertexIHalfedgeIter: 顶点的所有入半边;VertexOHalfedgeIter: 顶点的所有出半边;VertexEdgeIter: 顶点的所有相邻边;VertexFaceIter: 顶点的所有相邻面;FaceVertexIter:面上的顶点;FaceHalfedgeIter:面上的半边;FaceEdgeIter:面上的边;FaceFaceIter: 面的相邻面;HalfedgeLoopIter: 顺序链接的半边;
获取以上迭代器的函数如下(defined in OpenMesh::PolyConnectivity):
/**************************************************
* Vertex circulators
**************************************************/
// Get the vertex-vertex circulator (1-ring) of vertex _vh
VertexVertexIter OpenMesh::PolyConnectivity::vv_iter (VertexHandle _vh);
// Get the vertex-incoming halfedges circulator of vertex _vh
VertexIHalfedgeIter OpenMesh::PolyConnectivity::vih_iter (VertexHandle _vh);
// Get the vertex-outgoing halfedges circulator of vertex _vh
VertexOHalfedgeIter OpenMesh::PolyConnectivity::voh_iter (VertexHandle _vh);
// Get the vertex-edge circulator of vertex _vh
VertexEdgeIter OpenMesh::PolyConnectivity::ve_iter (VertexHandle _vh);
// Get the vertex-face circulator of vertex _vh
VertexFaceIter OpenMesh::PolyConnectivity::vf_iter (VertexHandle _vh);
/**************************************************
* Face circulators
**************************************************/
// Get the face-vertex circulator of face _fh
FaceVertexIter OpenMesh::PolyConnectivity::fv_iter (FaceHandle _fh);
// Get the face-halfedge circulator of face _fh
FaceHalfedgeIter OpenMesh::PolyConnectivity::fh_iter (FaceHandle _fh);
// Get the face-edge circulator of face _fh
FaceEdgeIter OpenMesh::PolyConnectivity::fe_iter (FaceHandle _fh);
// Get the face-face circulator of face _fh
FaceFaceIter OpenMesh::PolyConnectivity::ff_iter (FaceHandle _fh);
使用示例:
MyMesh mesh;
// (linearly) iterate over all vertices
for (MyMesh::VertexIter v_it=mesh.vertices_sbegin(); v_it!=mesh.vertices_end(); ++v_it)
{
// circulate around the current vertex
for (MyMesh::VertexVertexIter vv_it=mesh.vv_iter(*v_it); vv_it.is_valid(); ++vv_it)
{
// do something with e.g. mesh.point(*vv_it)
}
}
How to navigate on mesh
对半边进行顺序访问:
[...]
TriMesh::HalfedgeHandle heh, heh_init;
// Get the halfedge handle assigned to vertex[0]
heh = heh_init = mesh.halfedge_handle(vertex[0].handle());
// heh now holds the handle to the initial halfedge.
// We now get further on the boundary by requesting
// the next halfedge adjacent to the vertex heh
// points to...
heh = mesh.next_halfedge_handle(heh);
// We can do this as often as we want:
while(heh != heh_init) {
heh = mesh.next_halfedge_handle(heh);
}
[...]
判断边界相关的函数(OpenMesh::PolyConnectivity::is_boundary().):
// Test if a halfedge lies at a boundary (is not adjacent to a face)
bool is_boundary (HalfedgeHandle _heh) const
// Test if an edge lies at a boundary
bool is_boundary (EdgeHandle _eh) const
// Test if a vertex is adjacent to a boundary edge
bool is_boundary (VertexHandle _vh) const
// Test if a face has at least one adjacent boundary edge.
// If _check_vertex=true, this function also tests if at least one
// of the adjacent vertices is a boundary vertex
bool is_boundary (FaceHandle _fh, bool _check_vertex=false) const
获取边的from,to顶点:
// Get the handle of the to vertex
OpenMesh::Concepts::KernelT::to_vertex_handle();
// Get the handle of the from vertex
OpenMesh::Concepts::KernelT::from_vertex_handle();
Read and write meshes from files
示例如下:
#include <OpenMesh/Core/IO/MeshIO.hh>
MyMesh mesh;
if (!OpenMesh::IO::read_mesh(mesh, "some input file"))
{
std::cerr << "read error
";
exit(1);
}
// do something with your mesh ...
if (!OpenMesh::IO::write_mesh(mesh, "some output file"))
{
std::cerr << "write error
";
exit(1);
}
Some basic operations: Flipping and collapsing edge
Flipping edges
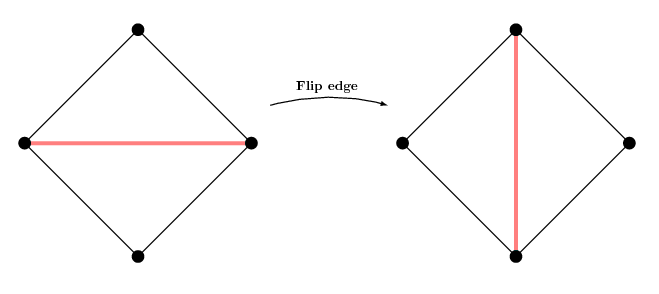
TriMesh mesh;
// Add some vertices
TriMesh::VertexHandle vhandle[4];
vhandle[0] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(0, 0, 0));
vhandle[1] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(0, 1, 0));
vhandle[2] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(1, 1, 0));
vhandle[3] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(1, 0, 0));
// Add two faces
std::vector<TriMesh::VertexHandle> face_vhandles;
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[2]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[1]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[0]);
mesh.add_face(face_vhandles);
face_vhandles.clear();
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[2]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[0]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[3]);
mesh.add_face(face_vhandles);
// Now the edge adjacent to the two faces connects
// vertex vhandle[0] and vhandle[2].
// Find this edge and then flip it
for(TriMesh::EdgeIter it = mesh.edges_begin(); it != mesh.edges_end(); ++it) {
if(!mesh.is_boundary(*it)) {
// Flip edge
mesh.flip(*it);
}
}
// The edge now connects vertex vhandle[1] and vhandle[3].
Collapsing edges

将from_vertex塌陷成to_vertex。
PolyMesh mesh;
// Request required status flags
mesh.request_vertex_status();
mesh.request_edge_status();
mesh.request_face_status();
// Add some vertices as in the illustration above
PolyMesh::VertexHandle vhandle[7];
vhandle[0] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(-1, 1, 0));
vhandle[1] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(-1, 3, 0));
vhandle[2] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(0, 0, 0));
vhandle[3] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(0, 2, 0));
vhandle[4] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(0, 4, 0));
vhandle[5] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(1, 1, 0));
vhandle[6] = mesh.add_vertex(MyMesh::Point(1, 3, 0));
// Add three quad faces
std::vector<PolyMesh::VertexHandle> face_vhandles;
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[1]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[0]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[2]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[3]);
mesh.add_face(face_vhandles);
face_vhandles.clear();
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[1]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[3]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[5]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[4]);
mesh.add_face(face_vhandles);
face_vhandles.clear();
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[3]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[2]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[6]);
face_vhandles.push_back(vhandle[5]);
mesh.add_face(face_vhandles);
// Now find the edge between vertex vhandle[2]
// and vhandle[3]
for(PolyMesh::HalfedgeIter it = mesh.halfedges_begin(); it != mesh.halfedges_end(); ++it) {
if( mesh.to_vertex_handle(*it) == vhandle[3] &&
mesh.from_vertex_handle(*it) == vhandle[2])
{
// Collapse edge
mesh.collapse(*it);
break;
}
}
// Our mesh now looks like in the illustration above after the collapsing.
Conceptual Class Hierarchy
概念相关类的继承关系如下(大多通过模板参数的形式实现集成):

Specifying your MyMesh
自定义一个mesh,需要有如下步骤:
- 明确是三角网格,还是多边形网格;(通常情况下选择三角网格)
- 选择mesh kernel;mesh kernel特例化了mesh 属性在内部的存储形式。默认的kernel是ArrayKernelT。
- 使用
Traits类,参数化mesh。可以向网格项添加任意items,如标量,点,法线和颜色类型,并使用预定义属性,例如Attributes :: Normal和Attributes :: Color。 - 使用自定义类型,动态绑定数据到mesh,或者是mesh的entities(vertex,(half-)edge,face)。
Mesh Traits
下面需要用户自定义实现,需要提供的类型有:
- point和scalar类型:
MyMesh::Point和MyMesh::Scalar; - mesh items:
MyMesh::Vertex,MyMesh::Halfedge,MyMesh::Edge,MyMesh::Face; - handle类型:
MyMesh::VertexHandle,MyMesh::HalfedgeHandle,MyMesh::EdgeHandle,MyMesh::FaceHandle。
默认的traits类似如下:
struct DefaultTraits
{
typedef Vec3f Point;
typedef Vec3f Normal;
typedef Vec2f TexCoord;
typedef Vec3uc Color;
VertexTraits {};
HalfedgeTraits {};
EdgeTraits {};
FaceTraits {};
VertexAttributes(0);
HalfedgeAttributes(Attributes::PreHalfedge);
EdgeAttributes(0);
FaceAttributes(0);
};
创建自定义traits的时候需要从上面继承创建。如果需要改变point的类型,可以进行如下操作:
struct MyTraits : public OpenMesh::DefaultTraits
{
typedef OpenMesh::Vec3d Point;
};
Adding Predefined Attributes
有一些预定义的attributes可以添加到mesh items中。这些全局的属性定义在OpenMesh::Attributes.命名看空间中。如果想要向顶点添加法向量和颜色,向面上添加法向量,那么可以如下操作:
struct MyTraits : public OpenMesh::DefaultTraits
{
VertexAttributes( OpenMesh::Attributes::Normal | OpenMesh::Attributes::Color);
FaceAttribtues(OpenMesh::Attributes::Normal);
};
对于属性提供运行时检测,和编译时检测,运行时检测如下:
if (OM_Check_Attrib(MyMesh::Vertex, Normal))
do_something_with_normals();
编译时检测如下:
#include <OpenMesh/Core/Utils/GenProg.hh>
// draw a face normal if we have one
void drawFaceNormal(const MyMesh::Face& _f) {
drawFaceNormal(_f, GenProg::Bool2Type<OM_Check_Attrib(MyMesh::Face, Normal)>());
}
// normal exists -> use it
void drawFaceNormal(const MyMesh::Face& _f, GenProg::Bool2Type<true>) {
glNormal3fv(_f.normal());
}
// empty dummy (no normals)
void drawFaceNormal(const MyMesh::Face& _f, GenProg::Bool2Type<false>){}
Adding User-Defined Elements
struct MyTraits : public OpenMesh::DefaultTraits
{
VertexTraits
{
int some_additional_index;
};
};
// 宏定义展开后得到如下形式:
struct MyTraits : public OpenMesh::DefaultTraits
{
template <class Base, class Refs> struct VertexT : public Base
{
int some_additional_index;
};
};
Final Implementation Example
#include <OpenMesh/Core/Mesh/TriMesh_ArrayKernelT.hh>
// define traits
struct MyTraits : public OpenMesh::DefaultTraits
{
// use double valued coordinates
typedef OpenMesh::Vec3d Point;
// use vertex normals and vertex colors
VertexAttributes( OpenMesh::DefaultAttributer::Normal |
OpenMesh::DefaultAttributer::Color );
// store the previous halfedge
HalfedgeAttributes( OpenMesh::DefaultAttributer::PrevHalfedge );
// use face normals
FaceAttributes( OpenMesh::DefaultAttributer::Normal );
// store a face handle for each vertex
VertexTraits
{
typename Base::Refs::FaceHandle my_face_handle;
};
};
// Select mesh type (TriMesh) and kernel (ArrayKernel)
// and define my personal mesh type (MyMesh)
typedef OpenMesh::TriMesh_ArrayKernelT<MyTraits> MyMesh;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
MyMesh mesh;
// -------------------- Add dynamic data
// for each vertex an extra double value
OpenMesh::VPropHandleT< double > vprop_double;
mesh.add_property( vprop_double );
// for the mesh an extra string
OpenMesh::MPropHandleT< string > mprop_string;
mesh.add_property( mprop_string );
// -------------------- do something
...;
}
Specifying an OpenMesh using Eigen3 vectors
#include <OpenMesh/Core/Geometry/EigenVectorT.hh>
struct EigenTraits : OpenMesh::DefaultTraits {
using Point = Eigen::Vector3d;
using Normal = Eigen::Vector3d;
using TexCoord2D = Eigen::Vector2d;
};
using EigenTriMesh = OpenMesh::TriMesh_ArrayKernelT<EigenTraits>;
EigenTriMesh mesh;