CGAL - user manual - Intersecting Sequences of dD Iso-oriented Boxes
See: https://doc.cgal.org/latest/Box_intersection_d/index.html
1 简介
当几何对象变得复杂的时候,像相交计算,距离计算等这些简单的问题求解需要很高的代价,比如,三维三角形和多面体表面网格的相交计算。实际应用中,这些几何计算会变慢。对求解优化的常见方式是对每个几何图元,给出沿着轴线的包围盒,对算法进行适当修改应用于包围盒相关计算中,仅在相交的包围盒上面,执行复杂表面的相关计算。
2 定义
box有两种类型,一种是半开区间的,定义为:({[lo_i,hi_i)|0le ilt d}),一种是闭区间的({[lo_i,hi_i]|0le ilt d}).需要注意的是闭区间的box支持宽度为0,他们可以在边界上相交。
此外,一个box有唯一的id。这样即使boxes的坐标完全相同,也能够得到一致的排序。(比如boxes A,B两个的坐标完全相同,那么在排序的时候,有可能第一次A在B的前面,打乱顺序第二次排序的时候有可能B在A的前面,而通过id,那么能够保证这个顺序一定是不变的。)同时也能够保证,相同的相交对只会出现一次。
box相交算法有两种风格:第一种是对单个序列中的盒子的所有对进行相交计算,比如,自相交测试;第二种是对两个序列中的盒子进行相交计算。
3 软件设计
接口设计如下:
#include <CGAL/box_intersection_d.h>
template< class RandomAccessIterator, class Callback >
void box_intersection_d(RandomAccessIterator begin, // 迭代器
RandomAccessIterator end,
Callback callback); // 回调函数
template< class RandomAccessIterator1,
class RandomAccessIterator2,
class Callback >
void box_intersection_d(RandomAccessIterator1 begin1, RandomAccessIterator1 end1,
RandomAccessIterator2 begin2, RandomAccessIterator2 end2,
Callback callback);
还有其他额外的参数,如,cutoff,用于调整性能折中的参数,topology用来确定是开区间的,还是闭区间的。
在算法中会对boxes进行重排。支持对象拷贝,和指针拷贝两种方式。
详见原文。
4 Examples
对其中的部分示例进行摘录介绍。
4.1 minimal Example
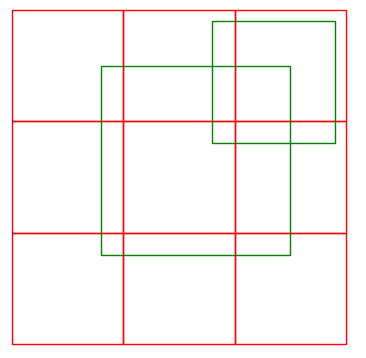
九宫格示例(如下图):
#include <CGAL/box_intersection_d.h>
#include <CGAL/Bbox_2.h>
#include <iostream>
typedef CGAL::Box_intersection_d::Box_d<double, 2> Box;
typedef CGAL::Bbox_2 Bbox;
Box boxes[9] = { Bbox(0,0,1,1), Bbox(1,0,2,1), Bbox(2,0,3,1), // low
Bbox(0,1,1,2), Bbox(1,1,2,2), Bbox(2,1,3,2), // middle
Bbox(0,2,1,3), Bbox(1,2,2,3), Bbox(2,2,3,3) };// upper
// 2 selected boxes as query; center and upper right
Box query[2] = { Bbox(0.8,0.8,2.5,2.5), Bbox(1.8,1.8,2.9,2.9) };
void callback(const Box& a, const Box& b) {
std::cout << "box " << a.id() << " intersects box " << b.id() << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
CGAL::box_intersection_d(boxes, boxes + 9, query, query + 2, callback);
return 0;
}
4.2 使用自定义box
由于CGAL的设计基于concept,参见:TODO:链接。可以很方便的进行自定义扩展。
Concept BoxIntersectionBox_d
{
typedef unknow_type NT;
typedef unknow_type ID;
static int dimension();
ID id() const;
NT min_coord(int d) const;
NT max_coord(int d) const;
};
在自定义box的时候满足上面的concept即可,如下:
#include <CGAL/box_intersection_d.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
#include <cassert>
struct Box {
typedef int NT;
typedef std::ptrdiff_t ID;
int lo[2], hi[2];
Box(int lo0, int lo1, int hi0, int hi1) : lo{ lo0, lo1 }, hi{ hi0, hi1 } {}
static int dimension() { return 2; }
NT min_coord(int dim) const { return lo[dim]; }
NT max_coord(int dim) const { return hi[dim]; }
ID id() const { return (ID)(this); }
};
完整示例见原文。
4.3 Example for Point Proximity Search with a Custom Traits Class
除了4.2中介绍的BoxIntersectionBox_d概念之外,还提供了BoxIntersectionTraits_d用来自定义扩展。该概念如下:
Concept BoxIntersectionTraits_d
{
typedef unknow_type Box_parameter; // 比BoxIntersectionBox_d多了这个类型
typedef unknow_type NT;
typedef unknow_type ID;
static int dimension();
ID id(Box_parameter box) const;
NT min_coord(Box_parameter box, int d) const;
NT max_coord(Box_parameter box, int d) const;
};
对该概念的实现如下:
#include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h>
#include <CGAL/box_intersection_d.h>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<float> Kernel;
typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point_3;
std::vector<Point_3> points;
std::vector<Point_3*> boxes; // boxes are just pointers to points
const float eps = 0.1f; // finds point pairs of distance < 2*eps
// Boxes are just pointers to 3d points. The traits class adds the
// +- eps size to each interval around the point, effectively building
// on the fly a box of size 2*eps centered at the point.
struct Traits {
typedef float NT;
typedef Point_3* Box_parameter;
typedef std::ptrdiff_t ID;
static int dimension() { return 3; }
static float coord( Box_parameter b, int d) {
return (d == 0) ? b->x() : ((d == 1) ? b->y() : b->z());
}
static float min_coord( Box_parameter b, int d) { return coord(b,d)-eps;}
static float max_coord( Box_parameter b, int d) { return coord(b,d)+eps;}
// id-function using address of current box,
// requires to work with pointers to boxes later
static std::ptrdiff_t id(Box_parameter b) { return (std::ptrdiff_t)(b); }
};
完整示例见原文。