Problem Description
Fill the following 8 circles with digits 1~8,with each number exactly once . Conntcted circles cannot be filled with two consecutive numbers.
There are 17 pairs of connected cicles:
A-B , A-C, A-D
B-C, B-E, B-F
C-D, C-E, C-F, C-G
D-F, D-G
E-F, E-H
F-G, F-H
G-H
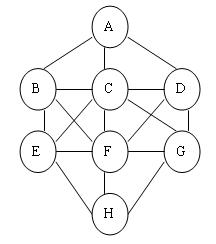
Filling G with 1 and D with 2 (or G with 2 and D with 1) is illegal since G and D are connected and 1 and 2 are consecutive .However ,filling A with 8 and B with 1 is legal since 8 and 1 are not consecutive .
In this problems,some circles are already filled,your tast is to fill the remaining circles to obtain a solution (if possivle).
There are 17 pairs of connected cicles:
A-B , A-C, A-D
B-C, B-E, B-F
C-D, C-E, C-F, C-G
D-F, D-G
E-F, E-H
F-G, F-H
G-H

Filling G with 1 and D with 2 (or G with 2 and D with 1) is illegal since G and D are connected and 1 and 2 are consecutive .However ,filling A with 8 and B with 1 is legal since 8 and 1 are not consecutive .
In this problems,some circles are already filled,your tast is to fill the remaining circles to obtain a solution (if possivle).
Input
The first line contains a single integer T(1≤T≤10),the number of test cases. Each test case is a single line containing 8 integers 0~8,the numbers in circle A~H.0 indicates an empty circle.
Output
For each test case ,print the case number and the solution in the same format as the input . if there is no solution ,print “No answer”.If there more than one solution,print “Not unique”.
Sample Input
3
7 3 1 4 5 8 0
0 7 0 0 0 0 0 0
0
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Sample Output
Case 1: 7 3 1 4 5 8 6 2
Case 2: Not unique
Case 3: No answer
题解:类似数独问题,将8个数字填入图中,连线两端的数字不能连续,因为线有17条,所以check函数写得非常长,其他的跟一般的DFS题目没有大区别,就是其他的题目只需恢复标记数组,而这个题目还需要恢复填写数字的数组。
#include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <sstream> #include <cstring> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <map> #define PI acos(-1.0) #define ms(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a)) #define msp memset(mp,0,sizeof(mp)) #define msv memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)) using namespace std; //#define LOCAL int sign[10]; int mp[10]; int ans,res[10]; bool check(int n) { switch(n) { case 1: { if(abs(mp[0]-mp[1])==1)return 0; return 1; } case 2: { if(abs(mp[0]-mp[2])==1)return 0; if(abs(mp[1]-mp[2])==1)return 0; return 1; } case 3: { if(abs(mp[0]-mp[3])==1)return 0; if(abs(mp[2]-mp[3])==1)return 0; return 1; } case 4: { if(abs(mp[2]-mp[4])==1)return 0; if(abs(mp[1]-mp[4])==1)return 0; return 1; } case 5: { if(abs(mp[1]-mp[5])==1)return 0; if(abs(mp[2]-mp[5])==1)return 0; if(abs(mp[3]-mp[5])==1)return 0; if(abs(mp[4]-mp[5])==1)return 0; return 1; } case 6: { if(abs(mp[2]-mp[6])==1)return 0; if(abs(mp[3]-mp[6])==1)return 0; if(abs(mp[5]-mp[6])==1)return 0; return 1; } case 7: { if(abs(mp[4]-mp[7])==1)return 0; if(abs(mp[5]-mp[7])==1)return 0; if(abs(mp[6]-mp[7])==1)return 0; return 1; } } return 1; } void dfs(int n) { if(n==7) { if(mp[n]==0) { for(int i=1; i<=8; i++) { if(sign[i]==0) { mp[n]=i; sign[i]=1; if(check(n)) { ans++; for(int j=0; j<8; j++) res[j]=mp[j]; } sign[i]=0; mp[n]=0; } } } else { if(check(n)) { ans++; for(int j=0; j<8; j++) res[j]=mp[j]; } } } else { if(mp[n]==0) { for(int i=1; i<=8; i++) { if(sign[i]==0) { mp[n]=i; sign[i]=1; if(check(n))dfs(n+1); sign[i]=0; mp[n]=0; } } } else { if(check(n))dfs(n+1); } } return; } int main() { #ifdef LOCAL freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); #endif // LOCAL ios::sync_with_stdio(false); int n,cas=0; cin>>n; while(n--) { cas++; ans=0,ms(res),ms(mp),ms(sign); for(int i=0; i<8; i++) { cin>>mp[i]; if(mp[i]!=0)sign[mp[i]]=1; } for(int i=0; i<8; i++) { if(mp[i]==0) { dfs(i); break; } } if(ans==1) { printf("Case %d:",cas); for(int i=0; i<8; i++) printf(" %d",res[i]); printf(" "); } else if(ans==0)printf("Case %d: No answer ",cas); else printf("Case %d: Not unique ",cas); } return 0; }