| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 7068 | Accepted: 3265 |
Description
A straight dirt road connects two fields on FJ's farm, but it changes elevation more than FJ would like. His cows do not mind climbing up or down a single slope, but they are not fond of an alternating succession of hills and valleys. FJ would like to add and remove dirt from the road so that it becomes one monotonic slope (either sloping up or down).
You are given N integers A1, ... , AN (1 ≤ N ≤ 2,000) describing the elevation (0 ≤ Ai ≤ 1,000,000,000) at each of N equally-spaced positions along the road, starting at the first field and ending at the other. FJ would like to adjust these elevations to a new sequence B1, . ... , BN that is either nonincreasing or nondecreasing. Since it costs the same amount of money to add or remove dirt at any position along the road, the total cost of modifying the road is
|A1 - B1| + |A2 - B2| + ... + |AN - BN |
Please compute the minimum cost of grading his road so it becomes a continuous slope. FJ happily informs you that signed 32-bit integers can certainly be used to compute the answer.
Input
* Line 1: A single integer: N
* Lines 2..N+1: Line i+1 contains a single integer elevation: Ai
Output
* Line 1: A single integer that is the minimum cost for FJ to grade his dirt road so it becomes nonincreasing or nondecreasing in elevation.
Sample Input
7 1 3 2 4 5 3 9
Sample Output
3
给定一个序列,以最小代价将其变成单调不增或单调不减序列,这里的代价看题目公式。
思路:
很容易想到是DP。
1.
对前i个序列,构成的最优解其实就是与两个参数有关。一个是这个序列处理后的最大值mx,和这个序列处理的代价值cost。
显然最大值mx最小最好(这样第i+1个值可以不花代价直接接在其后面的可能性更大),cost最小也最好(题意要求),但是两者往往是鱼和熊掌。
用dp[i][j]表示:前i个数构成的序列,这个序列最大值为j,dp[i][j]的值代表相应的cost。
所以状态转移方程如下:
dp[i][j]=abs(j-w[i])+min(dp[i-1][k]);(k<=j)
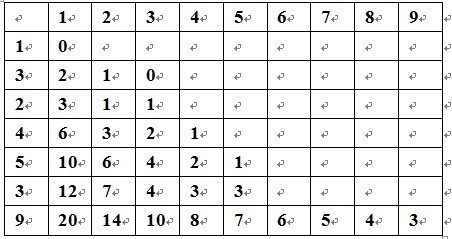
这个表格是根据转移方程写出来的dp数组。
再仔细看一下转移方程:dp[i][j]=abs(j-w[i])+min(dp[i-1][k]);(k<=j)
右边没填充的是因为填充的数字肯定比前面的数字大,无用,因为在求min( dp[i-1][k] )时,是求最小值,既然更大,则最小值时无需考虑。
又从表格中可以看出:
dp[i][j]=abs(j-w[i])+min(dp[i-1][k]);(k<=j)这里的k无需从1遍历到j。
只要在对j进行for循环的时候不断更新一个dp[i-1][j]的最小值mn=min(mn,dp[i-1][j]),
然后对dp[i][j]=abs(j-w[i])+mn即可;
这样改进之后即可从本来的时候时间复杂度O(NMM)改进为O(NM);
但是,这里的m是A[i]的最大值,显然TLE。
所以必须用离散化思想改进,因为N=2000。远小于A[i]的最大值。
离散化:将序列排序一下,然后用位置的前后关系来制定其值,这样时间复杂度变成O(N^2).
最后是这题数据有bug,只需要求不减序列即可。
?:谁能给我讲讲为什么这样离散化?为什么最后的结果中的每一个的数字都在原来的串中出现过?为什么这样得到的就是一个最优解?
附个解题报告,没太看懂他的证明
http://www.cnblogs.com/vb4896/p/5877962.html
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include<vector> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 #define Abs(a) ((a)>0?(a):-(a)) 6 #define Mod(a,b) (((a)-1+(b))%(b)+1) 7 using namespace std; 8 const int N=2005; 9 const long long inf=(1<<60); 10 int n; 11 int a[N],b[N]; 12 long long int dp[N][N]; 13 void solve() 14 { 15 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 16 { 17 long long mn=dp[i-1][1]; 18 for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) 19 { 20 mn=min(mn,dp[i-1][j]); 21 dp[i][j]=Abs(a[i]-b[j])+mn; 22 } 23 } 24 long long ans=dp[n][1]; 25 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 26 ans=min(ans,dp[n][i]); 27 printf("%lld ",ans); 28 } 29 int main() 30 { 31 scanf("%d",&n); 32 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 33 { 34 scanf("%d",a+i); 35 b[i]=a[i]; 36 } 37 sort(b+1,b+n+1); 38 solve(); 39 40 return 0; 41 }

1 //二维解法 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include<cmath> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 const int N=2010; 8 9 int n; 10 __int64 a[N]; 11 __int64 b[N]; 12 13 bool cmp(__int64 a,__int64 b) 14 { 15 return a<b; 16 } 17 18 __int64 dp[N][N]; 19 __int64 min(__int64 x,__int64 y) 20 { 21 return x<y?x:y; 22 } 23 int main() 24 { 25 //freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); 26 __int64 i,j,k,ans; 27 cin>>n; 28 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) { 29 scanf("%I64d",&a[i]); 30 } 31 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) { 32 b[i]=a[i]; 33 } 34 sort(b+1,b+1+n,cmp); 35 for(j=1; j<=n; j++) { 36 dp[1][j]=a[1]-b[j]; 37 if(dp[1][j]<0) { 38 dp[1][j]=-dp[1][j]; 39 } 40 } 41 __int64 t; 42 for(i=2; i<=n; i++) { // 非严格递增 43 k=dp[i-1][1]; 44 for(j=1; j<=n; j++) { 45 k=min(dp[i-1][j],k); 46 t=a[i]-b[j]; 47 if(t<0) { 48 t=-t; 49 } 50 dp[i][j]=k+t; //dp[i][j] = min{dp[i - 1][0...j] + ?abs(a[i] - b[j])} 51 } 52 } 53 ans=dp[n][n]; 54 for(i=n; i>=1; i--) { 55 ans=min(ans,dp[n][i]); 56 } 57 printf("%I64d ",ans); 58 return 0; 59 }

1 //一维 (滚动数组) 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include<cmath> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 const int N=2010; 8 __int64 a[N],b[N],dp[2][N]; 9 __int64 min(__int64 x,__int64 y) 10 { 11 return x<y?x:y; 12 } 13 int main() 14 { 15 int n,i,j; 16 __int64 k,t; 17 scanf("%d",&n); 18 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) { 19 scanf("%I64d",&a[i]); 20 } 21 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) { 22 b[i]=a[i]; 23 } 24 sort(b+1,b+1+n); 25 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) { 26 dp[0][i]=a[1]-b[i]; 27 if(dp[0][i]<0) { 28 dp[0][i]=-dp[0][i]; 29 } 30 } 31 for(i=2; i<=n; i++) { 32 k=dp[i%2][1]; 33 for(j=1; j<=n; j++) { 34 k=min(k,dp[i%2][j]); 35 t=a[i]-b[j]; 36 if(t<0) { 37 t=-t; 38 } 39 dp[(i+1)%2][j]=k+t; 40 } 41 } 42 j=(n+1)%2; 43 k=dp[j][1]; 44 for(i=2; i<=n; i++) { 45 k=min(k,dp[j][i]); 46 } 47 printf("%I64d ",k); 48 return 0; 49 }
