React中的数据传递
在 react 的学习过程中,少不了会遇到各个组件之间数据传递的问题,本文主要是在个人学习做项目过程中,对数据在 react 组件中传递的小总结。
数据传递的流向:1、数据从父组件传递到子组件,2、数据从子组件传递到父组件,3、多个组件共享状态数据。
数据传递的方式:1、实例属性 props,2、函数,3、状态提升
当然,context 也可以实现组件间的数据传递,官网对其的描述为: “使用React可以非常轻松地追踪通过React组件的数据流,在有些场景中,你不想要向下每层都手动地传递你需要的 props. 这就需要强大的 context API了”。但是同样也提到:“绝大多数应用程序不需要使用 context,如果你想让你的应用更稳定,别使用context。因为这是一个实验性的API,在未来的React版本中可能会被更改”。具体使用方法可到官网查看。本文提供代码和注释以及运行的结果图,具体的代码说明可查看注释。
数据从父组件到子组件
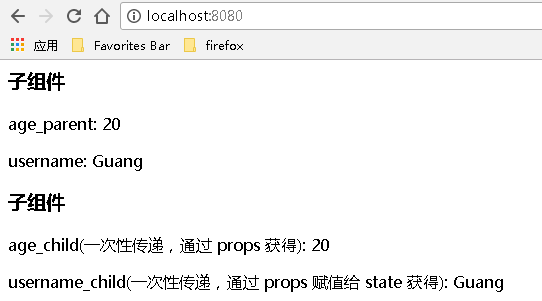
数据由父组件传递到子组件相对简单,一般的处理方法是,在父组件中定义、获取需要传递的数据,在父组件页面中通过 <子组件名称 props属性名称 = {传递的数据} /> 传递,最后在子组件中使用 this.props.props对应的属性名称 即可接受父组件传递过来的数据。
一、将数据从父组件传递到子组件,数据传递过程中,注意父组件和子组件中各自属性的名称要对应
父组件代码:
1 var React = require('react');
2 var ReactDOM = require('react-dom');
3 import BodyChild from './components/indexchild';
4
5 class Index extends React.Component {
6
7 constructor() {
8 //调用基类的所有的初始化方法
9 super();
10
11 // 设置当前组件的属性
12 this.state = {
13 username: "Guang",
14 age: 20
15 };
16 };
17
18 parentFunc(){
19 alert("我是父组件中的 parentFunc 函数");
20 }
21
22 render() {
23 return (
24 <div>
25 <h3>父组件</h3>
26
27 {/* 显示当前组件的属性作为对照 */}
28 <p>age_parent: {this.state.age}</p>
29 <p>username: {this.state.username}</p>
30
31 <BodyChild
32 //将当前组件的 state.xxx 属性传递给 子组件的 props.xxx_child
33 age_child={this.state.age}
34 username_child={this.state.username}
35 // 将 父组件的函数 this.parentFunc 传递给子组件 props.childFunc
36 childFunc={this.parentFunc.bind(this)}
37 />
38 </div>
39 );
40 }
41 }
42
43 ReactDOM.render(
44 <Index/>, document.getElementById('example'));
子组件代码:
1 import React from 'react';
2
3 export default class BodyChild extends React.Component{
4
5 constructor(props){
6 // React组件的构造函数将会在装配之前被调用。当为一个React.Component子类定义构造函数时,
7 // 你应该在任何其他的表达式之前调用super(props)。否则,this.props在构造函数中将是未定义,并可能引发异常
8 super(props);
9
10 // 父组件传递过来的属性存储在 props.username_child 中,将其赋值给当前组件的 state.username_child
11 this.state={username_child:props.username_child}
12 }
13
14 render(){
15 return(
16 <div>
17 <h3>子组件</h3>
18
19 {/* 父组件传递过来的属性存储在 props.age_child 中,获取并显示属性的值 */}
20 <p>age_child(通过 props 获得): {this.props.age_child}</p>
21
22 {/* 获取并显示 state.username_child,该属性的值是从父组件中获取的 */}
23 <p>username_child(通过 props 赋值给 state 获得): {this.state.username_child}</p>
24
25 {/* 这里获取并执行父组件传递过来的函数 */}
26 {this.props.childFunc()}
27 </div>
28 )
29 }
30 }
运行结果:
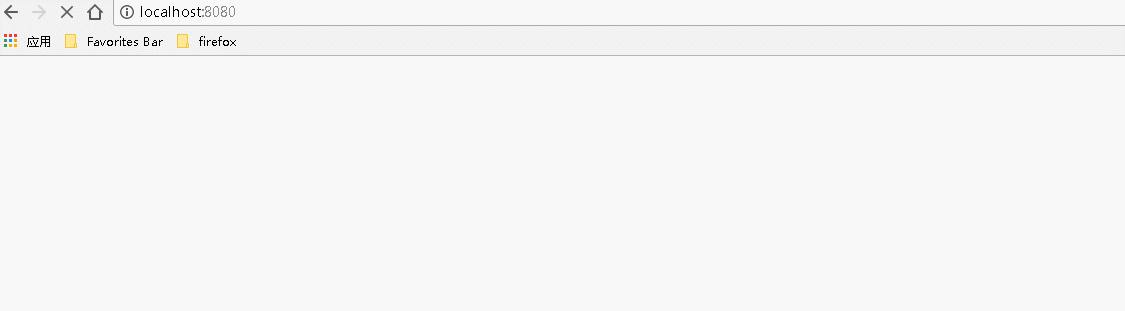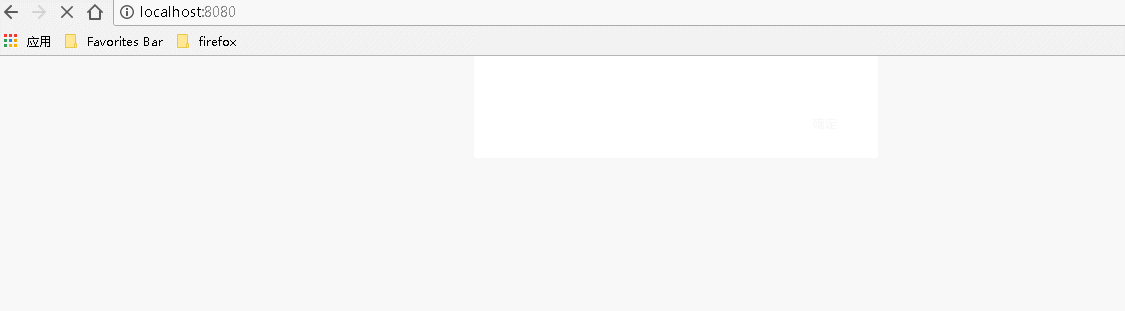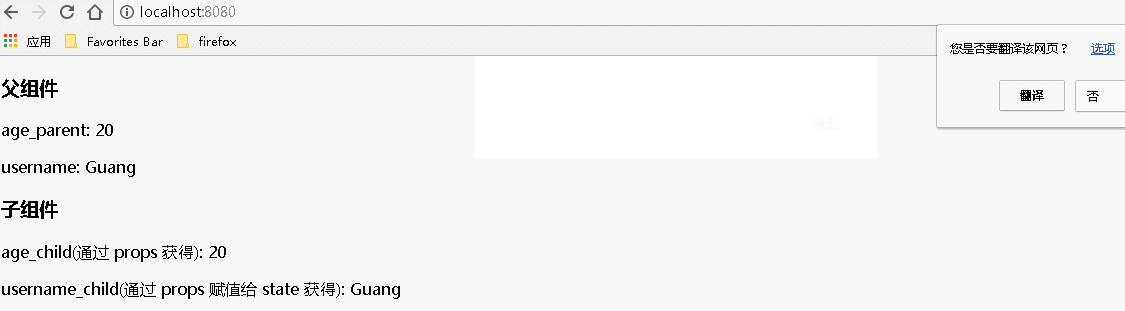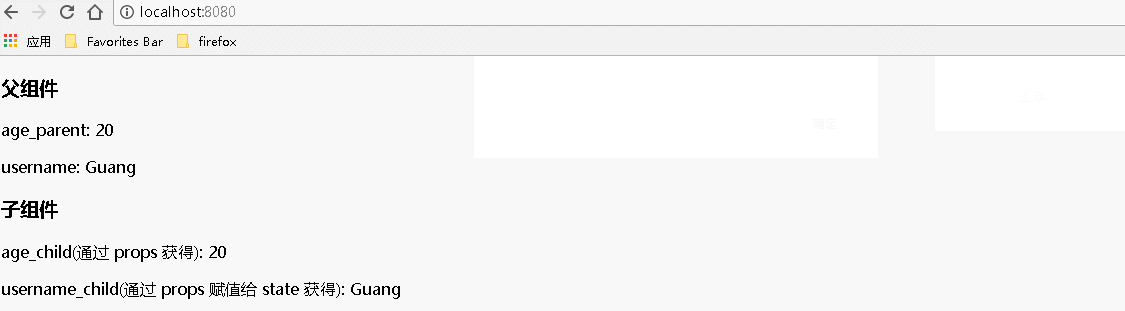
二、将数据从父组件传递到子组件,若有多个数据要传递,如1000个,可一次性传递,参数传递过程时,注意父组件和子组件中各自属性的名称,与前面代码相比,下列代码对应属性名称有所改变(父组件中的 state.xxx 在子组件中获取的形式为 props.xxx)
父组件代码
1 var React = require('react');
2 var ReactDOM = require('react-dom');
3 import BodyChild from './components/indexchild';
4
5 class Index extends React.Component {
6
7 constructor() {
8 //调用基类的所有的初始化方法
9 super();
10
11 // 设置当前组件的属性
12 this.state = {
13 username: "Guang",
14 age: 20
15 };
16 };
17
18 render() {
19 return (
20 <div>
21 <h3>子组件</h3>
22
23 {/* 显示当前组件的属性作为对照 */}
24 <p>age_parent: {this.state.age}</p>
25 <p>username: {this.state.username}</p>
26
27 {/* 一次性传递当期组件的所有 state 中的属性传给子组件 同理:传递 props 可使用 {...this.props} */}
28 <BodyChild{...this.state}/>
29
30 </div>
31 );
32 }
33 }
34
35 ReactDOM.render(
36 <Index/>, document.getElementById('example'));
子组件代码
1 import React from 'react';
2
3 export default class BodyChild extends React.Component{
4
5 constructor(props){
6 // React组件的构造函数将会在装配之前被调用。当为一个React.Component子类定义构造函数时,
7 // 你应该在任何其他的表达式之前调用super(props)。否则,this.props在构造函数中将是未定义,并可能引发异常
8 super(props);
9
10 // 父组件传递过来的属性存储在 props.username 中,将其赋值给当前组件的 state.username_child
11 this.state={username_child:props.username}
12 }
13
14 render(){
15 return(
16 <div>
17 <h3>子组件</h3>
18
19 {/* 父组件传递过来的属性存储在 props.age 中,获取并显示属性的值 */}
20 <p>age_child(一次性传递,通过 props 获得): {this.props.age}</p>
21
22 {/* 获取并显示 state.username_child,该属性的值是从父组件中获取的 */}
23 <p>username_child(一次性传递,通过 props 赋值给 state 获得): {this.state.username_child}</p>
24
25 </div>
26 )
27 }
28 }
运行结果:
说完了数据从父组件到子组件的传递,接下来是数据从子组件到父组件,与前者相比,后者的相对复杂,其传递方式一般为:在子组件中通过调用父组件传递过来的事件函数进行数据的传递 ,即
1、首先在父组件中定义一个函数(用于数据的传递,里面处理获取的各项数据)
2、将函数通过 “数据从父组件传递到子组件” 的方式将函数传递到子组件
3、在子组件中通过事件绑定或着直接调用的方式执行函数(执行时可以传入数据、事件等),最终实现数据的传递
数据从子组件到父组件
例1:直接传递数据
父组件代码:
1 var React = require('react');
2 var ReactDOM = require('react-dom');
3 import BodyChild from './components/indexchild';
4 class Index extends React.Component {
5 constructor() {
6 super(); //调用基类的所有的初始化方法
7 this.state = {
8 username: "Tom",
9 age: 20,
10 child_data:"子组件的输入在此显示",
11 }; //初始化赋值
12 };
13
14 parentGetData(child_username,child_age){
15 this.setState({child_username:child_username,child_age:child_age});
16 // console.log(child_username,child_age);
17 }
18
19 render() {
20 return (
21 <div>
22 <h3>子组件的信息 用户名为:Guang Zai 年龄为:18 开始时为空,点击按钮可获取</h3>
23 <p>子组件用户名:{this.state.child_username}</p>
24 <p>子组件年龄:{this.state.child_age}</p>
25 <BodyChild childGetData={(n1,n2)=>this.parentGetData(n1,n2)}/>
26 </div>
27 );
28 }
29 }
30 ReactDOM.render(
31 <Index/>, document.getElementById('example'));
子组件代码:
1 import React from 'react';
2
3 export default class BodyChild extends React.Component{
4
5 constructor(props){
6 // React组件的构造函数将会在装配之前被调用。当为一个React.Component子类定义构造函数时,
7 // 你应该在任何其他的表达式之前调用super(props)。否则,this.props在构造函数中将是未定义,并可能引发异常
8 super(props);
9 this.state={
10 username:"Guang Zai",
11 age:18
12 }
13 }
14 render(){
15 return(
16 <div>
17 <p>子组件按钮:<input type="button" value="点击获取子组件信息" onClick={()=>this.props.childGetData(this.state.username,this.state.age)}></input></p>
18 </div>
19 )
20 }
21 }
运行结果:

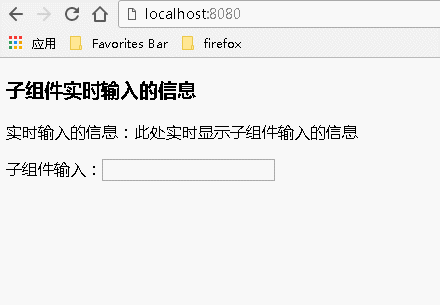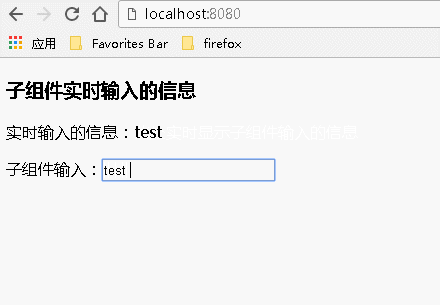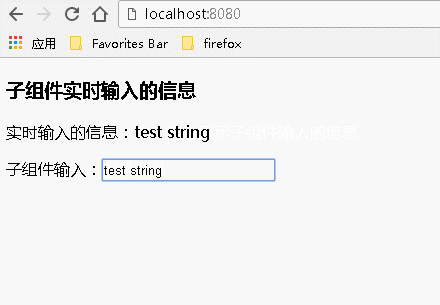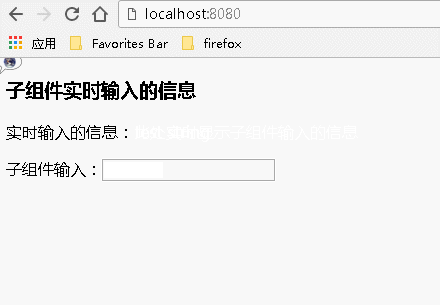
例2:通过事件传递数据
父组件代码:
1 var React = require('react');
2 var ReactDOM = require('react-dom');
3 import BodyChild from './components/indexchild';
4 class Index extends React.Component {
5 constructor() {
6 super(); //调用基类的所有的初始化方法
7 this.state={child_data:"此处实时显示子组件输入的信息"}
8
9 // 初始化时 函数 this 使用 bind 绑定当前类
10 this.parentPageInputBind=this.parentPageInputBind.bind(this);
11 };
12
13 parentPageInputBind(e){
14 this.setState({child_data:e.target.value});
15 };
16
17 render() {
18 return (
19 <div>
20 <h3>子组件实时输入的信息</h3>
21 <p>实时输入的信息:{this.state.child_data}</p>
22 <BodyChild childPageInputBind={this.parentPageInputBind}/>
23 </div>
24 );
25 }
26 }
27 ReactDOM.render(
28 <Index/>, document.getElementById('example'));
子组件代码:
1 import React from 'react';
2
3 export default class BodyChild extends React.Component{
4 render(){
5 return(
6 <div>
7 <p>子组件输入:<input type="text" onChange={this.props.childPageInputBind}></input></p>
8 </div>
9 )
10 }
11 }
运行结果:
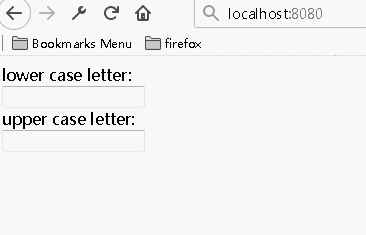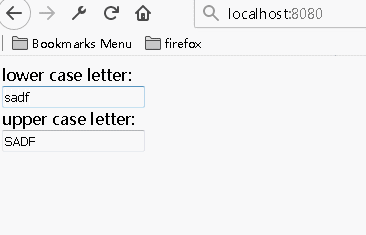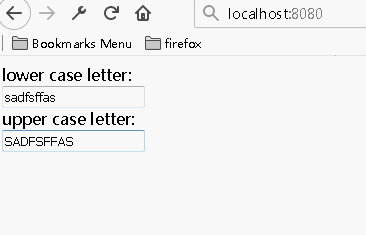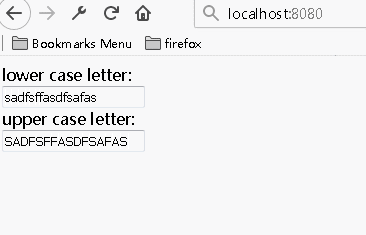
多个组件共享状态数据
综合上述参数的双向传递,通过将多个子组件输入的数据传递到同一个父组件,然后将该父组件中处理好的数据传递回给需要的子组件,实现数据间的共享
1 import React from 'react'; 2 3 class LettersInput extends React.Component{ 4 constructor(props){ 5 super(props); 6 } 7 handleChange(e){ 8 this.props.onLettersChange(e); 9 } 10 render(){ 11 const letters=this.props.letters; 12 return( 13 <div> 14 <input value={letters} onChange={(e)=>this.handleChange(e)}></input> 15 </div> 16 ) 17 } 18 } 19 20 class AppComponent extends React.Component { 21 constructor(props){ 22 super(props); 23 this.state={letters:''}; 24 this.handleChange=this.handleChange.bind(this); 25 } 26 27 handleChange(e){ 28 const letters=e.target.value; 29 const last=letters.substr(letters.length-1,1); 30 if(/[^a-z]/i.test(last)){ 31 return ''; 32 } 33 this.setState({letters:letters}); 34 } 35 36 render(){ 37 const letters=this.state.letters; 38 return( 39 <div> 40 <span>lower case letter:</span><LettersInput letters={letters.toLowerCase()} onLettersChange={this.handleChange}/> 41 <span>upper case letter:</span><LettersInput letters={letters.toUpperCase()} onLettersChange={this.handleChange}/> 42 </div> 43 ) 44 } 45 46 } 47 48 AppComponent.defaultProps = { 49 }; 50 51 export default AppComponent;
运行结果: