什么事代理?
就是对一个对象功能的增强,例如网上售票,代理的就是各个售票点的代理
java实现的代理两种办法
名词:代理对象、 目标对象 。代理和目标不是绝对的,例如:故宫售票、网上售票、黄牛售票。故宫售票对于网上售票来说,前者属于目标对象,后者属于代理对象,网上售票和黄牛售票也是同理,所以代理对象与目标对象不是绝对的,会随着代码的改变而改变。
静态代理:
继承:代理对象继承目标对象,重写需要增强的方法
缺点:对象太多,复杂。
下面代码模拟静态继承代理
1、父类dao
package dao;
public class IndexDao implements Dao {
public void query() {
System.out.println("IndexDao_Query");
}
}
2、子类(继承静态代理)
package dao;
public class LogDao extends IndexDao {
@Override
public void query() {
System.out.println("插入日志_LogDao");
super.query();
}
}
3、测试
package test;
import dao.Dao;
import dao.LogDao;
import dao.TimeDao;
public class ProxyStaticTest {
public static void main(String args[]){
Dao dao = new LogDao();
dao.query();
Dao dao1 = new TimeDao();
dao1.query();
}
}
4、截图
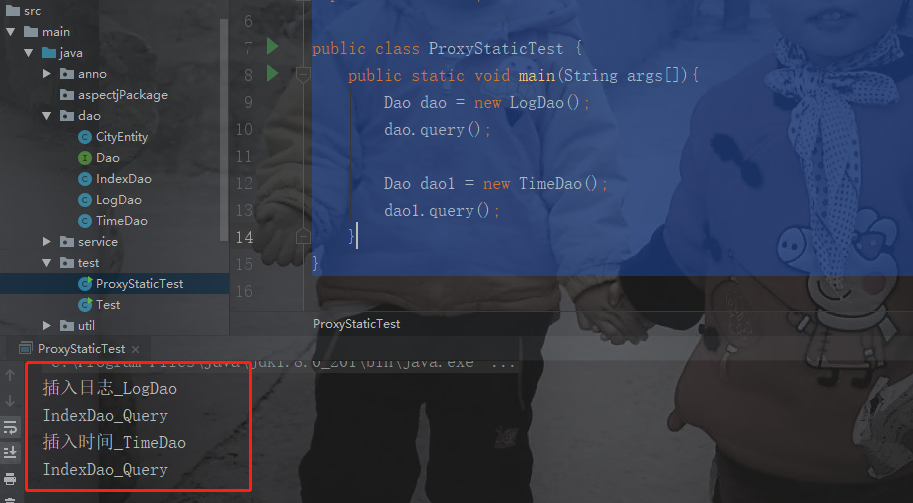
聚合:目标对象和代理对象实现同一接口,代理对象当中要包含目标对象(通过构造或者set),再次重新调用目标对象的方法并增强此方法
缺点:也会产生过多的类(内存溢出)
下面代码模拟静态聚合代理
1、日志dao
package dao;
public class LogDao {
Dao dao;
public LogDao(Dao dao) {
this.dao = dao;
}
public void query() {
System.out.println("日志管理——LogDao");
dao.query();
}
}
2、测试
package test;
import dao.Dao;
import dao.LogDao;
import dao.TimeDao;
public class ProxyStaticTest {
public static void main(String args[]){
Dao dao1 = new TimeDao();
LogDao LogDao = new LogDao(dao1);
LogDao.query();
}
}
3、截图
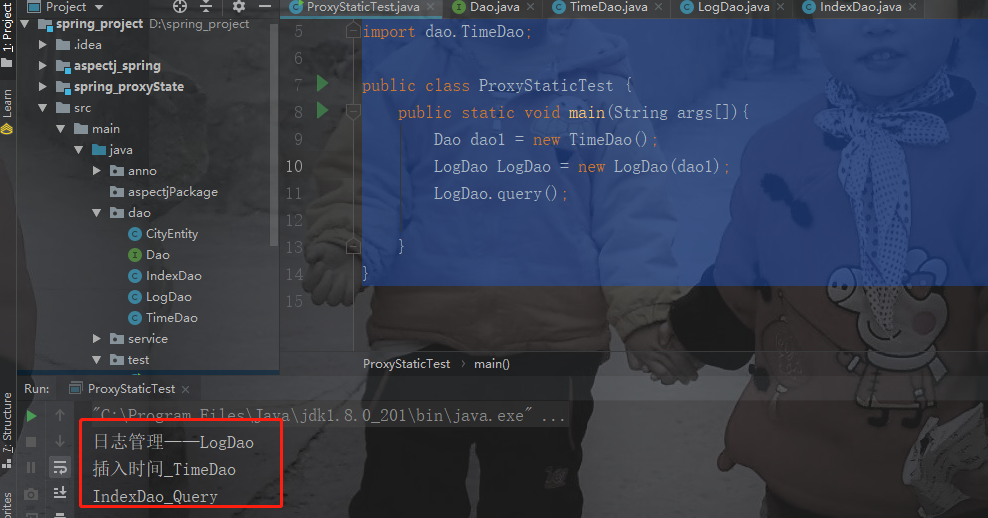
总结:静态代理只适合确定类的数量的情况下才能使用,否则就会出现类爆炸(类过多的问题)
扩展:聚合静态代理很类似装饰者设计模式,只不过装饰者设计模式是用set方法将对象赋值。而聚合代理是用构造方法将对象赋值(IO中的类是用的就是装饰者设计模式)
相关博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/ChrisRIM/archive/2012/08/21/2648372.html
动态代理
1、接口
package com.dao;
public interface ObjectDao {
public void query();
}
2、实现类
package com.dao;
public class User_Defined_Dao implements ObjectDao {
public User_Defined_Dao() {
}
public void query() {
System.out.println("自定义Dao中的query方法");
}
}
3、代理类
package com.proxy;
/*
* 对象是如何生成的?
* java
* class
* new
* **/
import javax.tools.JavaCompiler;
import javax.tools.StandardJavaFileManager;
import javax.tools.ToolProvider;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLClassLoader;
public class ProxyUtil {
public static Object getInstance(Object target) {
Object proxy = null;
Class targetInfo = target.getClass().getInterfaces()[0];
String tab = " ";
String line = "
";
String implName = targetInfo.getSimpleName();
//创建java内容
String javaContent = "";
//package
String packageContent = "package com.proxy;" + line;
//importClass
String impPackageContent = "import " + targetInfo.getName() + ";" + line;
//创建类体
String classContent = "public class $Proxy implements " + implName + " {" + line;
//创建私有变量
String privateObject = tab + "private " + implName + " target;" + line;
//创建构造
String constructorContent = tab + "public $Proxy (" + implName + " target ){" + line;
constructorContent = constructorContent + tab + tab + "this.target = target;" + line;
constructorContent = constructorContent + tab + "}" + line;
//创建方法
String methedContent = "";
Method[] methods = targetInfo.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
//获取方法的返回类型
String methodTypeName = method.getReturnType().getSimpleName();
//获取方法的名字
String methodName = method.getName();
methedContent = tab + "public " + methodTypeName + " " + methodName + " (";
//创建参数
Object[] args = method.getParameterTypes();
String argContent = "";
for (int i = 0; i < args.length - 1; i++) {
//获取参数的类型
String argsTypeName = args[i].getClass().getSimpleName();
//获取参数名称 i1 i2
argContent = argsTypeName + " i" + i;
if (i != args.length - 1) {
//多个参数的情况下需要使用','但是最后一个不需要
argContent += ",";
}
}
//组装方法内容,方法体中的逻辑先写死
methedContent += argContent + "){"
+ line + tab + tab + "System.out.println("自定义Dao方法");" + line
+ tab;
methedContent += tab + tab + "target." + methodName + "(" + argContent + ");";
methedContent += line + tab + "}";
}
javaContent = packageContent + impPackageContent + classContent + privateObject + constructorContent + methedContent + line + "}";
//1、使用IO字符流将创建好String 放到D盘中,用于查看是否存在问题。
String filePath = "D:\com\proxy\";
String classFileName = "com.proxy.$Proxy";
File fileDir = new File("D:\com\proxy\");
try {
if (!fileDir.isDirectory()) {
fileDir.mkdirs();
}
File file = new File("D:\com\proxy\$Proxy.java");
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(file);
fileWriter.write(javaContent);
fileWriter.flush();
fileWriter.close();
//创建java编译器
JavaCompiler javaCompiler = ToolProvider.getSystemJavaCompiler();
//第三方管理器
StandardJavaFileManager fileMgr = javaCompiler.getStandardFileManager(null, null, null);
//将java文件放到管理器中
Iterable units = fileMgr.getJavaFileObjects(file);
//创建编译任务
JavaCompiler.CompilationTask task = javaCompiler.getTask(null, fileMgr, null, null, null, units);
//开始启动任务
task.call();
fileMgr.close();
//使用反射获取编译后的$Proxy对象
URL [] urls = new URL[]{new URL("file:D:\\")};
URLClassLoader ucl = new URLClassLoader(urls);
Class clazz = ucl.loadClass(classFileName);
Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor(targetInfo);
proxy = constructor.newInstance(target);
System.out.println("成功!");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("失败!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return proxy;
}
}
4、测试
public static void main(String args[]){
ObjectDao objectDao = (ObjectDao) ProxyUtil.getInstance(new User_Defined_Dao());
objectDao.query();
}
5测试结果
