题目:https://www.luogu.org/problem/show?pid=1514
题目描述
在一个遥远的国度,一侧是风景秀美的湖泊,另一侧则是漫无边际的沙漠。该国的行政区划十分特殊,刚好构成一个N 行M 列的矩形,如上图所示,其中每个格子都代表一座城市,每座城市都有一个海拔高度。
为了使居民们都尽可能饮用到清澈的湖水,现在要在某些城市建造水利设施。水利设施有两种,分别为蓄水厂和输水站。蓄水厂的功能是利用水泵将湖泊中的水抽取到所在城市的蓄水池中。
因此,只有与湖泊毗邻的第1 行的城市可以建造蓄水厂。而输水站的功能则是通过输水管线利用高度落差,将湖水从高处向低处输送。故一座城市能建造输水站的前提,是存在比它海拔更高且拥有公共边的相邻城市,已经建有水利设施。由于第N 行的城市靠近沙漠,是该国的干旱区,所以要求其中的每座城市都建有水利设施。那么,这个要求能否满足呢?如果能,请计算最少建造几个蓄水厂;如果不能,求干旱区中不可能建有水利设施的城市数目。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
输入文件的每行中两个数之间用一个空格隔开。输入的第一行是两个正整数N 和M,表示矩形的规模。接下来N 行,每行M 个正整数,依次代表每座城市的海拔高度。
输出格式:
输出有两行。如果能满足要求,输出的第一行是整数1,第二行是一个整数,代表最少建造几个蓄水厂;如果不能满足要求,输出的第一行是整数0,第二行是一个整数,代表有几座干旱区中的城市不可能建有水利设施。
输入输出样例
【输入样例1】 2 5 9 1 5 4 3 8 7 6 1 2 【输入样例2】 3 6 8 4 5 6 4 4 7 3 4 3 3 3 3 2 2 1 1 2
【输出样例1】 1 1 【输出样例2】 1 3
说明
【样例1 说明】
只需要在海拔为9 的那座城市中建造蓄水厂,即可满足要求。
【样例2 说明】
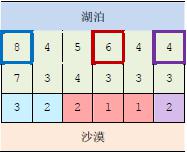
上图中,在3 个粗线框出的城市中建造蓄水厂,可以满足要求。以这3 个蓄水厂为源头
在干旱区中建造的输水站分别用3 种颜色标出。当然,建造方法可能不唯一。
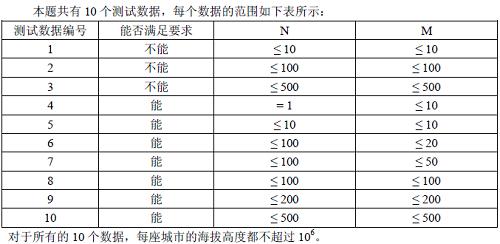
【数据范围】
比较好的题目啊,挑错挑了一下午。。。。。。
参考了各位神犇的意见。。。。。。
首先从第一行往下灌水,记录有木有访问完最后一行所有的点。回答第一问。
让后,从下往上倒着灌水,计算对于第一行的每一个位置,往下灌水的边界是多少。
最后用线段覆盖一遍,解决。
(话说最后为啥我总是忘了要+1orz)
附上我丑陋的代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #include<queue> 5 #include<cstring> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 struct node{ 9 int x,y; 10 node(){} 11 node(int _x,int _y):x(_x),y(_y){} 12 }; 13 14 //作用1:代表位置 15 //作用2:代表左端点右端点 16 17 const int maxn=510; 18 19 int dx[4]={-1,0,1,0}; 20 int dy[4]={0,1,0,-1}; 21 22 int n,m,tot; 23 int map[maxn][maxn]; 24 int vis[maxn][maxn]; 25 26 int l[maxn][maxn]; 27 int r[maxn][maxn]; 28 29 node gou[maxn]; 30 bool cmp(const node &a,const node &b){ 31 if (a.x==b.x) return a.y<b.y; 32 else return a.x<b.x; 33 } 34 35 void bfsdown(int s){ 36 queue<node> q; 37 node t=node(1,s); 38 q.push(t); 39 vis[t.x][t.y]=1; 40 while (!q.empty()){ 41 node now=q.front(); 42 q.pop(); 43 for (int i=0;i<4;++i){ 44 int nx=now.x+dx[i],ny=now.y+dy[i]; 45 if (nx<1||ny<1||nx>n||ny>m||map[nx][ny]>=map[now.x][now.y]||vis[nx][ny]) continue; 46 vis[nx][ny]=1; 47 q.push(node(nx,ny)); 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 52 void bfsup(int ha[maxn][maxn],int s){ 53 queue<node> q; 54 node t=node(n,s); 55 q.push(t); 56 ha[t.x][t.y]=s; 57 while (!q.empty()){ 58 node now=q.front(); 59 q.pop(); 60 for (int i=0;i<4;++i){ 61 int nx=now.x+dx[i],ny=now.y+dy[i]; 62 if (nx<1||ny<1||nx>n||ny>m||map[nx][ny]<=map[now.x][now.y]||ha[nx][ny]) continue; 63 ha[nx][ny]=s; 64 q.push(node(nx,ny)); 65 } 66 } 67 } 68 69 int main(){ 70 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 71 for (int i=1;i<=n;++i) 72 for (int j=1;j<=m;++j) 73 scanf("%d",&map[i][j]); 74 75 for (int i=1;i<=m;++i) 76 bfsdown(i); 77 for (int i=1;i<=m;++i) 78 if (!vis[n][i]) ++tot; 79 80 if (tot){ 81 cout<<"0"<<endl<<tot<<endl; 82 return 0; 83 } 84 85 for (int i=1;i<=m;++i) if (!l[n][i]) bfsup(l,i); 86 for (int i=m;i>=1;--i) if (!r[n][i]) bfsup(r,i); 87 88 for (int i=1;i<=m;++i){ 89 if (!l[1][i]) l[1][i]=r[1][i]; 90 if (!r[1][i]) r[1][i]=l[1][i]; 91 gou[i].x=l[1][i]; 92 gou[i].y=r[1][i]; 93 } 94 95 sort(gou+1,gou+m+1,cmp); 96 97 int nw=0,nx=0; 98 for (int i=1;i<=m;++i){ 99 if (nw+1>=gou[i].x) nx=max(nx,gou[i].y); 100 else{ 101 nw=nx; 102 nx=max(nx,gou[i].y); 103 ++tot; 104 } 105 } 106 if (nw!=m) ++tot; 107 108 cout<<"1"<<endl<<tot<<endl; 109 110 111 return 0; 112 }

