监听器Listener
jservlet规范包括三个技术点:servlet ;listener ;filter;监听器就是监听某个对象的的状态变化的组件。监听器的相关概念事件源:
- 被监听的对象(三个域对象 request,session,servletContext)
- 监听器:监听事件源对象, 事件源对象的状态的变化都会触发监听器 。
- 注册监听器:将监听器与事件源进行绑定。
- 响应行为:监听器监听到事件源的状态变化时,所涉及的功能代码(程序员编写代码)
按照被监听的对象划分:ServletRequest域 ;HttpSession域 ;ServletContext域。按照监听的内容分:监听域对象的创建与销毁的; 监听域对象的属性变化的。
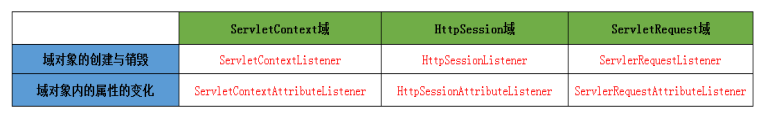
三大域对象的创建与销毁的监听器
ServletContextListener
监听ServletContext域的创建与销毁的监听器,Servlet域的生命周期:在服务器启动创建,服务器关闭时销毁;监听器的编写步骤:
- 编写一个监听器类去实现监听器接口
- 覆盖监听器的方法
- 需要在web.xml中进行配置(注册)
1、监听的方法:
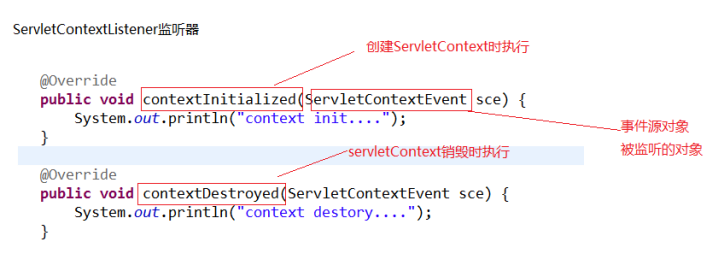
2、配置文件:
ServletContextListener监听器的主要作用:
- 初始化的工作:初始化对象;初始化数据。比如加载数据库驱动,对连接池的初始化。
- 加载一些初始化的配置文件;比如spring的配置文件。
- 任务调度(定时器Timer/TimerTask)
例子:MyServletContextListener.java
package com.itheima.create; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent; import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener; public class MyServletContextListener implements ServletContextListener{ @Override //监听context域对象的创建 public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) { //就是被监听的对象---ServletContext //ServletContext servletContext = sce.getServletContext(); //getSource就是被监听的对象 是通用的方法 //ServletContext source = (ServletContext) sce.getSource(); //System.out.println("context创建了...."); //开启一个计息任务调度----每天晚上12点 计息一次 //Timer timer = new Timer(); //task:任务 firstTime:第一次执行时间 period:间隔执行时间 //timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(task, firstTime, period); /*timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("银行计息了....."); } } , new Date(), 5000);*/ //修改成银行真实计息业务 //1、起始时间: 定义成晚上12点 //2、间隔时间:24小时 /*SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss"); //String currentTime = "2016-08-19 00:00:00"; String currentTime = "2016-08-18 09:34:00"; Date parse = null; try { parse = format.parse(currentTime); } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("银行计息了....."); } } , parse, 24*60*60*1000);*/ } //监听context域对象的销毁 @Override public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) { System.out.println("context销毁了...."); } }
web.xml
<listener> <listener-class>com.itheima.attribute.MyServletContextAttributeListener</listener-class> </listener>
HttpSessionListener
监听Httpsession域的创建与销毁的监听器。HttpSession对象的生命周期:第一次调用request.getSession时创建;销毁有以下几种情况(服务器关闭、session过期、 手动销毁)
1、HttpSessionListener的方法
package listener; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionEvent; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener; /** * Created by yang on 2017/7/27. */ public class listenerDemo implements HttpSessionListener { @Override public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent httpSessionEvent) { System.out.println("session创建"+httpSessionEvent.getSession().getId()); } @Override public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent httpSessionEvent) { System.out.println("session销毁"); } }
web.xml:
<listener> <listener-class>listener.listenerDemo</listener-class> </listener>
创建session代码:
package session; import cn.dsna.util.images.ValidateCode; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; /** * Created by yang on 2017/7/24. */ public class SessionDemo extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { //1 生成验证码 ValidateCode code = new ValidateCode(200, 80, 4, 100); //2 将验证码保存到session中 System.out.println(code.getCode()); request.getSession().setAttribute("code", code.getCode()); //3 将验证码图片输出到 浏览器 resp.setContentType("image/jpeg"); code.write(resp.getOutputStream()); } }
当创建session时,监听器中的代码将执行。
ServletRequestListener
监听ServletRequest域创建与销毁的监听器。ServletRequest的生命周期:每一次请求都会创建request,请求结束则销毁。
1、ServletRequestListener的方法
package listener; import javax.servlet.ServletRequestEvent; import javax.servlet.ServletRequestListener; /** * Created by yang on 2017/7/27. */ public class RequestListenerDemo implements ServletRequestListener { @Override public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent servletRequestEvent) { System.out.println("request被销毁了"); } @Override public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent servletRequestEvent) { System.out.println("request被创建了"); } }
web.xml
<listener> <listener-class>listener.RequestListenerDemo</listener-class> </listener>
只要客户端发起请求,监听器中的代码就会被执行。
监听三大域对象的属性变化的
域对象的通用的方法
setAttribute(name,value)
- 触发添加属性的监听器的方法
- 触发修改属性的监听器的方法
getAttribute(name)
removeAttribute(name):触发删除属性的监听器的方法
ServletContextAttibuteListener监听器
package listener; import javax.servlet.ServletContextAttributeEvent; import javax.servlet.ServletContextAttributeListener; /** * Created by yang on 2017/7/27. */ public class ServletContextAttrDemo implements ServletContextAttributeListener { @Override public void attributeAdded(ServletContextAttributeEvent scab) { //放到域中的属性 System.out.println(scab.getName());//放到域中的name System.out.println(scab.getValue());//放到域中的value } @Override public void attributeRemoved(ServletContextAttributeEvent scab) { System.out.println(scab.getName());//删除的域中的name System.out.println(scab.getValue());//删除的域中的value } @Override public void attributeReplaced(ServletContextAttributeEvent scab) { System.out.println(scab.getName());//获得修改前的name System.out.println(scab.getValue());//获得修改前的value } }
web.xml
<listener> <listener-class>listener.ServletContextAttrDemo</listener-class> </listener>
测试代码:
package listener; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; /** * Created by yang on 2017/7/27. */ public class ListenerTest extends HttpServlet{ @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { ServletContext context=getServletContext(); context.setAttribute("aaa","bbb"); context.setAttribute("aaa","ccc"); context.removeAttribute("aaa"); doPost(req, resp); } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { } }
HttpSessionAttributeListener监听器(同上)
ServletRequestAriibuteListenr监听器(同上)
与session中的绑定的对象相关的监听器(对象感知监听器)
将要被绑定到session中的对象有几种状态
- 绑定状态:就一个对象被放到session域中
- 解绑状态:就是这个对象从session域中移除了
- 钝化状态:是将session内存中的对象持久化(序列化)到磁盘
- 活化状态:就是将磁盘上的对象再次恢复到session内存中
对象感知监听器不用在web.xml中配置。
面试题:当用户很对时,怎样对服务器进行优化?
绑定与解绑的监听器HttpSessionBindingListener
package listener; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionBindingEvent; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionBindingListener; public class Person implements HttpSessionBindingListener{ private String id; private String name; public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override //绑定的方法 public void valueBound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) { System.out.println("person被绑定了"); } @Override //解绑方法 public void valueUnbound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) { System.out.println("person被解绑了"); } }
测试类:
package listener; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession; public class TestPersonBindingServlet extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { HttpSession session = request.getSession(); //将person对象绑到session中 Person p = new Person(); p.setId("100"); p.setName("zhangsanfeng"); session.setAttribute("person", p); //将person对象从session中解绑 session.removeAttribute("person"); } protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); } }
钝化与活化的监听器HttpSessionActivationListener
package listener; import java.io.Serializable; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionActivationListener; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionEvent; public class Customer implements HttpSessionActivationListener,Serializable{ private String id; private String name; public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override //钝化 public void sessionWillPassivate(HttpSessionEvent se) { System.out.println("customer被钝化了"); } @Override //活化 public void sessionDidActivate(HttpSessionEvent se) { System.out.println("customer被活化了"); } }
测试钝化类:
package listener; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession; public class TestCustomerActiveServlet extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { HttpSession session = request.getSession(); //将customer放到session中 Customer customer =new Customer(); customer.setId("200"); customer.setName("lucy"); session.setAttribute("customer", customer); System.out.println("customer被放到session域中了"); } protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); } }
当访问TestCustomerActiveServlet 之后,停止服务器,就会被钝化,钝化的文件存在tomcat的work文件加下。
活化类:
package listener; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession; public class TestCustomerActiveServlet2 extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { //从session域中获得customer HttpSession session = request.getSession(); Customer customer = (Customer) session.getAttribute("customer"); System.out.println(customer.getName()); } protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); } }
服务器再次启动,访问TestCustomerActiveServlet2之后,就会被活化。可以通过配置文件,指定对象钝化时间(对象多长时间不用被钝化)
在META-INF下创建一个context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Context>
<!-- maxIdleSwap:session中的对象多长时间(分钟)不使用就钝化 -->
<!-- directory:钝化后的对象的文件写到磁盘的哪个目录下 配置钝化的对象文件在 work/catalina/localhost/钝化文件 -->
<Manager className="org.apache.catalina.session.PersistentManager" maxIdleSwap="1">
<Store className="org.apache.catalina.session.FileStore" directory="itheima32" />
</Manager>
</Context>
邮箱服务器
邮件的客户端:可以只安装在电脑上的也可以是网页形式的;邮件服务器:起到邮件的接受与推送的作用
邮件发送的协议:
协议:就是数据传输的约束。接受邮件的协议:POP3 IMAP;发送邮件的协议:SMTP
邮箱的发送过程
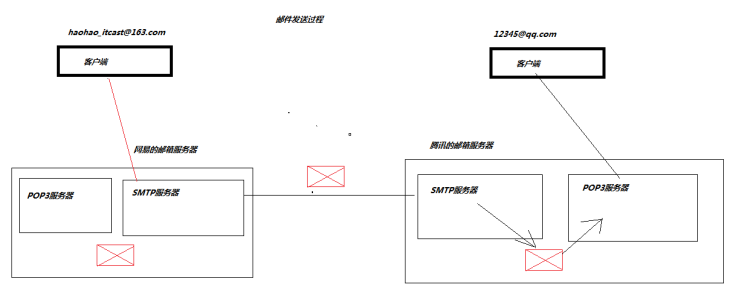
邮箱服务器的安装
双击邮箱服务器软件

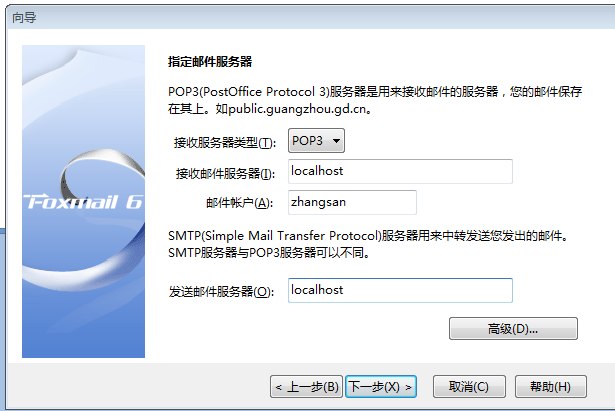
对邮箱服务器进行配置
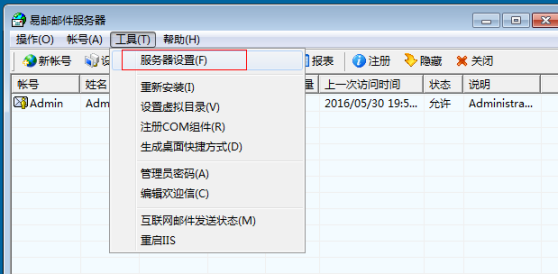
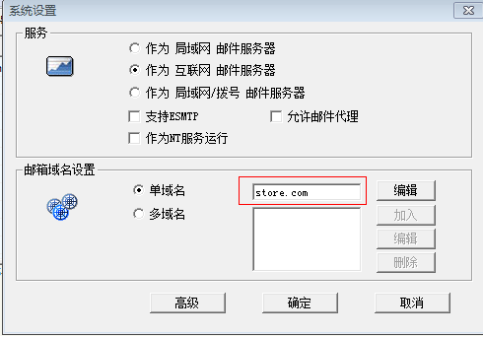
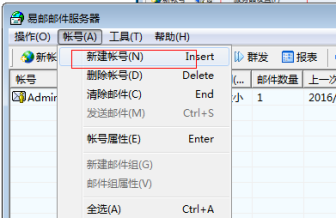
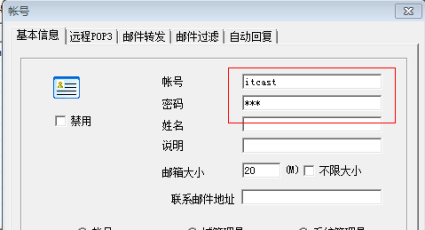
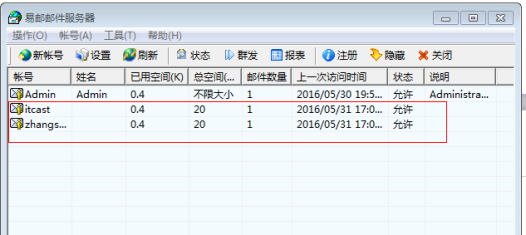
邮箱客户端的安装
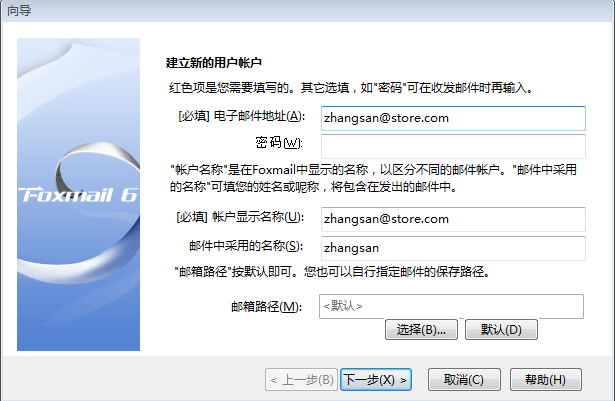
邮件发送代码
package com.itheima.mail; import java.util.Properties; import javax.mail.Authenticator; import javax.mail.Message; import javax.mail.MessagingException; import javax.mail.PasswordAuthentication; import javax.mail.Session; import javax.mail.Transport; import javax.mail.internet.AddressException; import javax.mail.internet.InternetAddress; import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage; import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage.RecipientType; public class MailUtils { //email:邮件发给谁 subject:主题 emailMsg:邮件的内容 public static void sendMail(String email, String subject, String emailMsg) throws AddressException, MessagingException { // 1.创建一个程序与邮件服务器会话对象 Session Properties props = new Properties(); props.setProperty("mail.transport.protocol", "SMTP");//发邮件的协议 props.setProperty("mail.host", "localhost");//发送邮件的服务器地址 props.setProperty("mail.smtp.auth", "true");// 指定验证为true // 创建验证器 Authenticator auth = new Authenticator() { public PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication() { return new PasswordAuthentication("tom", "12345");//发邮件的账号的验证 } }; Session session = Session.getInstance(props, auth); // 2.创建一个Message,它相当于是邮件内容 Message message = new MimeMessage(session); message.setFrom(new InternetAddress("tom@itheima32.com")); // 设置发送者 message.setRecipient(RecipientType.TO, new InternetAddress(email)); // 设置发送方式与接收者 message.setSubject(subject);//邮件的主题 message.setContent(emailMsg, "text/html;charset=utf-8"); // 3.创建 Transport用于将邮件发送 Transport.send(message); } }
测试代码:
package com.itheima.mail; import javax.mail.MessagingException; import javax.mail.internet.AddressException; public class SendMailTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws AddressException, MessagingException { MailUtils.sendMail("lucy@itheima32.com", "测试邮件","这是一封测试邮件"); } }