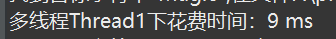
多线程查找文件内容
遍历所有文件,当遍历到文件名是.java结尾的时候,创建一个线程去查找这个文件的内容(是否包含“Magic”字符串),不必等待这个线程结束,继续遍历下一个文件。
1 package multiplethread; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.File; 5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 6 import java.io.FileReader; 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 9 public class searchFileInDirectory { 10 // 实现Runnable接口方式的多线程 11 public static void funcThread1(String path) { 12 File f = new File(path); 13 if (f.exists()) { 14 File[] fs = f.listFiles(); 15 for (File x : fs) { 16 if (x.isDirectory()) 17 funcThread1(x.getAbsolutePath()); 18 if (x.isFile() && x.getName().contains(".java")) { 19 new Thread(new searchInFile(x)).start(); 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 25 public static void checkFile(File x) { 26 Thread t = new Thread() { 27 public void run() { 28 try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(x));) { 29 while (true) { 30 String line = br.readLine(); 31 if (line == null) 32 break; 33 if (line.contains("Magic")) { 34 System.out.printf("找到目标字符串"Magic",在文件%s%n", x.getAbsoluteFile());
break;// 只要文件含有content,不管出现多少次,只打印一次文件地址 35 } 36 } 37 } catch (IOException e) { 38 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 39 e.printStackTrace(); 40 } 41 } 42 43 }; 44 t.start(); 45 } 46 47 // 匿名类的方式的多线程 48 public static void funcThread2(String path) { 49 File f = new File(path); 50 if (f.exists()) { 51 File[] fs = f.listFiles(); 52 for (int i = 0; i < fs.length; i++) { 53 File x = fs[i]; 54 if (x.isDirectory()) { 55 funcThread2(x.getAbsolutePath()); 56 } 57 if (x.isFile() && x.getName().contains(".java")) { 58 checkFile(x); // 理论上直接写到这里可以,但是为了美观便于阅读,就单独写到checkFile()中 59 } 60 } 61 62 } 63 } 64 65 // 单线程 66 public static void funcNoThread(String path) { 67 File f = new File(path); 68 if (f.exists()) { 69 File[] fs = f.listFiles(); 70 for (File x : fs) { 71 if (x.isDirectory()) 72 funcNoThread(x.getAbsolutePath()); 73 if (x.isFile() && x.getName().contains(".java")) { 74 try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(x));) { 75 while (true) { 76 String line = br.readLine(); 77 if (line == null) 78 break; 79 if (line.contains("Magic")) { 80 System.out.printf("找到目标字符串"Magic",在文件%s%n", x.getAbsoluteFile()); 81 } 82 } 83 } catch (IOException e) { 84 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 85 e.printStackTrace(); 86 } 87 88 } 89 } 90 } 91 } 92 93 public static void main(String[] args) { 94 String path = "F:\project\javastudy"; 95 long st1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 96 funcThread1(path); 97 long et1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 98 System.out.printf("多线程Thread1下花费时间:%d ms", et1 - st1); 99 100 long st2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 101 funcThread2(path); 102 long et2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 103 System.out.printf("多线程Thread2下花费时间:%d ms", et2 - st2); 104 105 long st3 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 106 funcNoThread(path); 107 long et3 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 108 System.out.printf("单线程下花费时间:%d ms", et3 - st3); 109 } 110 }
效果图:
...

...
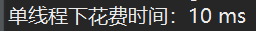
由于文件数量较少,多线程与单线程所耗时间基本一致。
练习-英雄充能
英雄有可以放一个技能叫做: 波动拳-a du gen。
每隔一秒钟,可以发一次,但是只能连续发3次。
发完3次之后,需要充能5秒钟,充满,再继续发。
1 package multiplethread; 2 3 import charactor.Hero; 4 5 public class ThreadTest2 { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Thread t1 = new Thread() { 9 private int cnt = 0; 10 11 public void run() { 12 while (true) { 13 if ((++cnt) % 4 != 0) { 14 System.out.printf("波动拳第%d发 ", cnt); 15 try { 16 Thread.sleep(1000); 17 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 18 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 } else { 22 cnt = 0; 23 try { 24 System.out.println("开始为时5秒的充能"); 25 Thread.sleep(5000); 26 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 27 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 }; 34 t1.start(); 35 36 } 37 }
效果图:

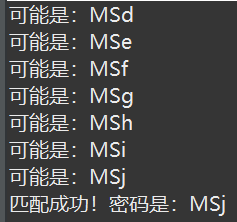
练习-破解密码
1. 生成一个长度是3的随机字符串,把这个字符串当作密码
2. 创建一个破解线程,使用穷举法,匹配这个密码
3. 创建一个日志线程,打印都用过哪些字符串去匹配,这个日志线程设计为守护线程:setDaemon(true)
提示: 破解线程把穷举法生成的可能密码放在一个容器中,日志线程不断的从这个容器中拿出可能密码,并打印出来。 如果发现容器是空的,就休息1秒,如果发现不是空的,就不停的取出,并打印。
1 package multiplethread; 2 3 import java.util.LinkedList; 4 import java.util.Random; 5 6 public class Test2 { 7 public static String getRandomString(int length) { 8 String str = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789"; 9 Random random = new Random(); 10 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); 11 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { 12 int number = random.nextInt(62); 13 sb.append(str.charAt(number)); 14 } 15 return sb.toString(); 16 } 17 18 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 19 String pwd = getRandomString(3); 20 LinkedList<String> pwdList = new LinkedList<>(); 21 System.out.println("pwd :" + pwd); 22 Thread t1 = new Thread() { 23 String str = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789"; 24 int n = str.length(); 25 char[] cs = new char[3]; 26 27 public void run() { 28 ok: for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 29 for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { 30 for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) { 31 cs[0] = str.charAt(i); 32 cs[1] = str.charAt(j); 33 cs[2] = str.charAt(k); 34 String guess = new String(cs); 35 pwdList.add(guess); 36 // t1和t2这两个线程并发执行,但是t2由于要挨个打印,必然晚于t1结束,而t1早已经匹配到密码 37 // 不妨令t1匹配到密码时等一等t2,等t2打印完。 38 // 这里设置为等5秒钟(5秒钟基本能匹配成功) 39 if (guess.equals(pwd)) { 40 try { 41 Thread.sleep(3000); 42 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 43 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } 46 System.out.println("匹配成功!密码是:" + guess); 47 break ok; 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 }; 54 Thread t2 = new Thread() { 55 public void run() { 56 while (true) { 57 String tmp = pwdList.poll(); 58 // 发现容器是空的,就休息1秒 59 if (tmp == null) { 60 try { 61 Thread.sleep(1000); 62 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 63 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 64 e.printStackTrace(); 65 } 66 } else { 67 System.out.println("可能是:" + tmp); 68 } 69 } 70 } 71 }; 72 t2.setDaemon(true); 73 t1.start(); 74 t2.start(); 75 } 76 }
效果图:
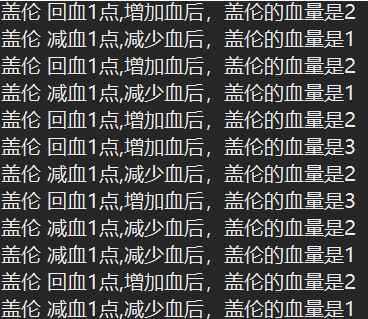
练习-多线程交互
对同一个对象(Hero),有2个加血线程,5个扣血线程,同时运行。最大血量1000,最小血量1。
使用wait()、notify()。
其中Hero类的加血、扣血方法如下:
1 //回血 2 public synchronized void recover(){ 3 if(hp==1000){ 4 try { 5 this.wait(); //满血不能再加血 6 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 7 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 8 e.printStackTrace(); 9 } 10 }else{ 11 hp=hp+1; 12 System.out.printf("%s 回血1点,增加血后,%s的血量是%.0f%n", name, name, hp); 13 this.notify(); //不满血则可以扣血(自然可以加血) 14 } 15 } 16 17 //扣血 18 public synchronized void hurt(){ 19 if(hp<=1){ 20 try { 21 this.wait(); //空血不能再扣血 22 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 23 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 }else{ 27 hp-=1; 28 System.out.printf("%s 减血1点,减少血后,%s的血量是%.0f%n", name, name, hp); 29 this.notify(); //非空血可以加血(自然可以扣血) 30 } 31 }
多线程交互:
1 package multiplethread; 2 3 import charactor.Hero; 4 5 public class Test_wait_notify { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 final Hero gareen = new Hero(); 9 gareen.name = "盖伦"; 10 gareen.hp = 616; 11 12 Thread addHP[]=new Thread[2]; 13 Thread reduceHP[]=new Thread[5]; 14 //2条加血线程 15 for(int i=0;i<2;i++){ 16 Thread t=new Thread(){ 17 public void run(){ 18 while(true){ 19 gareen.recover(); 20 //加血间隔 10ms 21 try { 22 Thread.sleep(10); 23 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 24 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 }; 30 t.start(); 31 addHP[i]=t; 32 } 33 //5条扣血线程 34 for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ 35 Thread t=new Thread(){ 36 public void run(){ 37 while(true){ 38 gareen.hurt(); 39 //扣血间隔 10ms 40 try { 41 Thread.sleep(10); 42 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 43 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 }; 49 t.start(); 50 reduceHP[i]=t; 51 } 52 53 } 54 }
效果图: