From a high level, Struts2 is a pull-MVC (or MVC2) framework. The Model-View-Controller pattern in Struts2 is realized with following five core components:
- Actions
- Interceptors
- Value Stack / OGNL
- Results / Result types
- View technologies
Struts 2 is slightly different from a traditional MVC framework in that the action takes the role of the model rather than the controller, although there is some overlap.
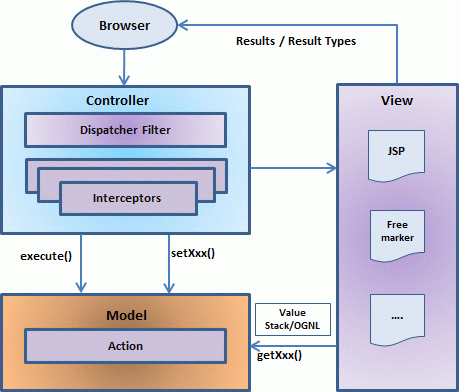
The above diagram depicts the Model, View and Controller to the Struts2 high level architecture. The controller is implemented with a Struts2 dispatch servlet filter as well as interceptors, the model is implemented with actions, and the view as a combination of result types and results. The value stack and OGNL provide common thread, linking and enabling integration between the other components.
Apart from the above components, there will be a lot of information that relates to configuration. Configuration for the web application, as well as configuration for actions, interceptors, results, etc.
This is the architectural overview of the Struts 2 MVC pattern. We will go through each component in more detail in the subsequent chapters.
Request life cycle
Based on the above digram, one can explain the user's request life cycle in Struts 2 as follows:
- User sends a request to the server for requesting for some resource (i.e pages).
- The FilterDispatcher looks at the request and then determines the appropriate Action.
- Configured interceptors functionalities applies such as validation, file upload etc.
- Selected action is executed to perform the requested operation.
- Again, configured interceptors are applied to do any post-processing if required.
- Finally the result is prepared by the view and returns the result to the user.