1. 标准库类型 string
string表示可变长的字符序列,使用string必须首先包含string头文件。如何初始化类的对象是由类本身决定的。
1 int n; 2 string s1;//默认初始化,s1是空字符串 3 string s2(s1);//s2是s1的副本,等价于string s2 = s1; 4 string s3("value");//s3是字面值"value"的副本,除了字面值后面的那个空字符外,等价于string s3 = "value"; 5 string s4(n,'c');//把s4初始化为连续n个字符c组成的串;即s4=cccccccc(n个c);
2.读写string对象
2.1 读取string操作,string对象会自动忽略开头的空白(即空格符、换行符、制表符等)并从第一个真正的字符开始读起,直到遇见下一处空白为止。
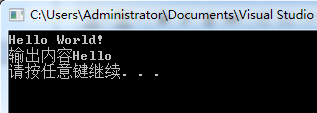
1 string s; 2 cin >> s; 3 cout <<"输出内容"<< s << endl; 4 system("pause");
2.2 有时希望能在最终得到的字符串中保留输入时的空白符,则getline代替原来的>>可以实现;
1 string line; 2 while(getline(cin,line)) 3 cout<<"输出内容"<<line<<endl; 4 system("pause");

3.string对象相加
PS:两个string对象可直接相加,string和字符字面值及字符串字面值一条语句中使用时,必须确保每个加法运算符(+)的两侧运算对象至少有一个是string对象。
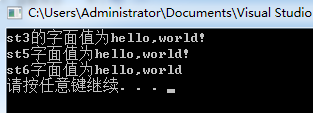
1 string st1 = "hello,",st2 = "world!"; 2 string st3 = st1+st2; 3 cout<<"st3的字面值为"<<st3<<endl; 4 5 string st4 = "hello"; 6 string st5 = st4+','+st2; 7 cout <<"st5字面值为"<<st5<<endl; 8 9 string st6 = st4+","+"world";//正确 st4是string对象,st4+","还是string对象 10 cout << "st6字面值为"<<st6<<endl; 11 //string st7 = "hello"+","+st4;//错误"hello"和","都不是string对象 12 system("pause");