一、在ES6以前实现类和继承
实现类的代码如下:
function Person(name, age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } Person.prototype.speakSomething = function () { console.log("I can speek chinese"); };
实现继承的代码如下:一般使用原型链继承和call继承混合的形式
function Person(name) { this.name = name; } Person.prototype.showName = function () { return `名字是:${this.name}`; }; function Student(name, skill) { Person.call(this, name);//继承属性 this.skill = skill; } Student.prototype = new Person();//继承方法
二、ES6使用class定义类
class Parent { constructor(name,age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } speakSomething(){ console.log("I can speek chinese"); } }
经过babel转码之后
function _classCallCheck(instance, Constructor) { if (!(instance instanceof Constructor)) { throw new TypeError("Cannot call a class as a function"); } } var Parent = function () { function Parent(name, age) { _classCallCheck(this, Parent); this.name = name; this.age = age; } _createClass(Parent, [{ key: "speakSomething", value: function speakSomething() { console.log("I can speek chinese"); } }]); return Parent; }();
可以看到ES6类的底层还是通过构造函数去创建的。
通过ES6创建的类,是不允许你直接调用的。在ES5中,构造函数是可以直接运行的,比如Parent()。但是在ES6就不行。我们可以看到转码的构造函数中有_classCallCheck(this, Parent)语句,这句话是防止你通过构造函数直接运行的。你直接在ES6运行Parent(),这是不允许的,ES6中抛出Class constructor Parent cannot be invoked without 'new'错误。转码后的会抛出Cannot call a class as a function.能够规范化类的使用方式。
转码中_createClass方法,它调用Object.defineProperty方法去给新创建的Parent添加各种属性。defineProperties(Constructor.prototype, protoProps)是给原型添加属性。如果你有静态属性,会直接添加到构造函数defineProperties(Constructor, staticProps)上。
三、ES6实现继承
我们给Parent添加静态属性,原型属性,内部属性。
class Parent { static height = 12 constructor(name,age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } speakSomething(){ console.log("I can speek chinese"); } } Parent.prototype.color = 'yellow' //定义子类,继承父类 class Child extends Parent { static width = 18 constructor(name,age){ super(name,age); } coding(){ console.log("I can code JS"); } }
经过babel转码之后
"use strict";
var _createClass = function () {
function defineProperties(target, props) {
for (var i = 0; i < props.length; i++) {
var descriptor = props[i];
descriptor.enumerable = descriptor.enumerable || false;
descriptor.configurable = true;
if ("value" in descriptor) descriptor.writable = true;
Object.defineProperty(target, descriptor.key, descriptor);
}
}
return function (Constructor, protoProps, staticProps) {
if (protoProps) defineProperties(Constructor.prototype, protoProps);
if (staticProps) defineProperties(Constructor, staticProps);
return Constructor;
};
}();
function _possibleConstructorReturn(self, call) {
if (!self) {
throw new ReferenceError("this hasn't been initialised - super() hasn't been called");
}
return call && (typeof call === "object" || typeof call === "function") ? call : self;
}
function _inherits(subClass, superClass) {
if (typeof superClass !== "function" && superClass !== null) {
throw new TypeError("Super expression must either be null or a function, not " + typeof superClass);
}
subClass.prototype = Object.create(superClass && superClass.prototype, {
constructor: {
value: subClass,
enumerable: false,
writable: true,
configurable: true
}
});
if (superClass) Object.setPrototypeOf ? Object.setPrototypeOf(subClass, superClass) : subClass.__proto__ = superClass;
}
function _classCallCheck(instance, Constructor) {
if (!(instance instanceof Constructor)) {
throw new TypeError("Cannot call a class as a function");
}
}
var Parent = function () {
function Parent(name, age) {
_classCallCheck(this, Parent);
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
_createClass(Parent, [{
key: "speakSomething",
value: function speakSomething() {
console.log("I can speek chinese");
}
}]);
return Parent;
}();
Parent.height = 12;
Parent.prototype.color = 'yellow';
//定义子类,继承父类
var Child = function (_Parent) {
_inherits(Child, _Parent);
function Child(name, age) {
_classCallCheck(this, Child);
return _possibleConstructorReturn(this, (Child.__proto__ || Object.getPrototypeOf(Child)).call(this, name, age));
}
_createClass(Child, [{
key: "coding",
value: function coding() {
console.log("I can code JS");
}
}]);
return Child;
}(Parent);
Child.width = 18;
构造类的方法都没变,只是添加了_inherits核心方法来实现继承。具体步骤如下:
首先是判断父类的类型,然后:
subClass.prototype = Object.create(superClass && superClass.prototype, { constructor: { value: subClass, enumerable: false, writable: true, configurable: true } });
这段代码翻译下来就是
function F(){} F.prototype = superClass.prototype subClass.prototype = new F() subClass.prototype.constructor = subClass
接下来就是subClass.__proto__ = superClass
_inherits核心思想就是下面两句:
subClass.prototype.__proto__ = superClass.prototype
subClass.__proto__ = superClass
如下图所示:
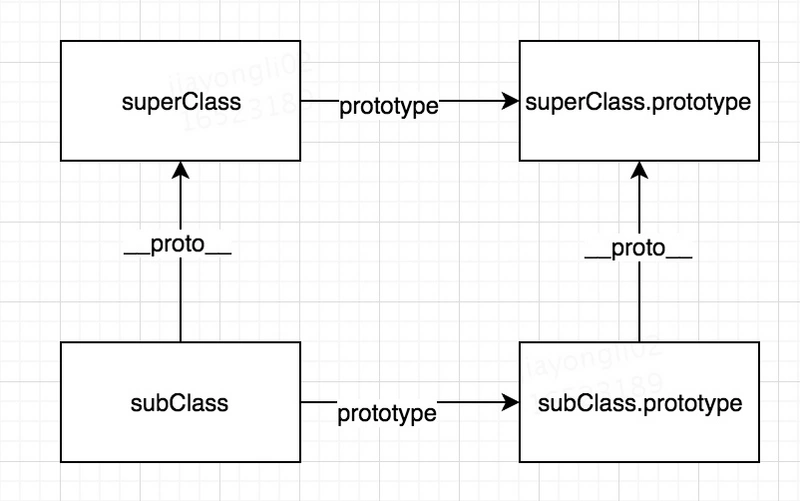
首先 subClass.prototype.__proto__ = superClass.prototype保证了子类的实例instanceof父类是true,子类的实例可以访问到父类的属性,包括内部属性,以及原型属性。
其次,subClass.__proto__ = superClass,保证了静态属性也能访问到,也就是这个例子中的Child.height。