ARM架构中的程序执行与调用
1. 几个名词
- ABI :
- 可执行文件必须遵守的规范,以在特定执行环境中运行;
- 单独产生的可重定址的文件必须遵守的规范,以用来链接和执行。
-
EABI:
适用于嵌入式环境的ABI -
PCS:
程序调用规范(Procedure Call Standard) -
AAPCS:
PCS for ARM Architecture
AAPCS定义了单独编译、单独汇编的程序是如何一起工作的。 -
Routine、subroutine
控制可以进入的一段程序,调用之后,可以将控制返回给它的调用者。这里可分别理解为程序调用者、被调用者 -
Procedure:
A routine returns no result value. -
Function;
A routine returns a result value. -
Active stack、call-frame stack:
调用者栈帧
2. 数据类型
2.1 基础数据类型
-
整型
unsigned byte(8), signed byte(8), unsigned half-word(16), signed half-word(16), unsigned word(32), signed word(32), unsigned double-word(64), signed double-word(64) -
浮点型
half precision(2), single precision(4), double precision(8) -
容器向量
64-bit vector(8),128-bit vector(16) -
指针
数据指针(4),指令指针(4)
字节序
从软件视角看,内存是字节的阵列,每一个字节都是可寻址的。
-
小端字节序
数据在内存中,数据的最低字节放在内存中最低地址上。 -
大端字节序
数据在内存中,数据的最低字节放在内存中的最高地址上。
复合类型
-
an aggregate, 类似于C中的结构体, where the members are laid out sequentially in memmory
-
a union, 枚举类型内的元素有相同的地址
-
数组, 相同类型数据的集合,连续地址存储
2.2 数据对齐
-
数据自身对齐
比如,byte对齐为1个字节,word对齐为4个字节。如果数据的对齐值为N,则该数据的存放地址位于N的整数倍的位置,即“数据地址 % N == 0”。 -
结构体对齐值
结构体成员中最大的对齐值即为结构体对齐值。同样,该结构体存放的地址为对齐值N的整数倍。 -
在C中可以使用 #pragma pack(N) 来指定对齐值
下面以C语言为例,看一下结构体的对齐方式:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct s{
int a;
char b;
long long c;
short d
} s;
s t;
int main(void)
{
char *c;
t.a = 1;
t.b = 1;
t.c = 1;
t.d = 1;
printf("size of t is %d
", sizeof(t));
for(c = (char*)&t + sizeof(t) -1; c>=(char*)&t; c--)
{
printf("0x%x: |--%x--|
",c,*c);
}
return 0;
}
程序输出如下:
size of t is 24
0x40ea3f: |--0--|
0x40ea3e: |--0--|
0x40ea3d: |--0--|
0x40ea3c: |--0--|
0x40ea3b: |--0--|
0x40ea3a: |--0--|
0x40ea39: |--0--|
0x40ea38: |--1--|
0x40ea37: |--0--|
0x40ea36: |--0--|
0x40ea35: |--0--|
0x40ea34: |--0--|
0x40ea33: |--0--|
0x40ea32: |--0--|
0x40ea31: |--0--|
0x40ea30: |--1--|
0x40ea2f: |--0--|
0x40ea2e: |--0--|
0x40ea2d: |--0--|
0x40ea2c: |--1--|
0x40ea2b: |--0--|
0x40ea2a: |--0--|
0x40ea29: |--0--|
0x40ea28: |--1--|
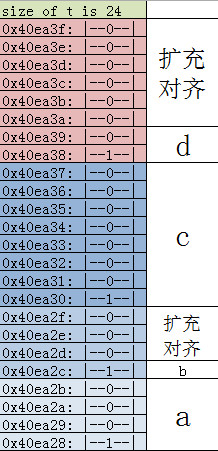
可以看出这是小端字节序,即数据的最低字节存放在最低地址。b的存放位置位于0x40ea2c地址处,虽然只占一个字节。但是由于成员c是8字节对齐的,c的起始地址8位对齐,所以c应该位于0x40ea30,0x40ea2d到0x40ea2f这三个字节是为了对齐而扩充的。而该结构体的对齐值为成员的最大对齐值也为8,所以最后一个成员d,虽然只占2字节,但是需要扩充的8字节对齐。
3. 程序调用
ARM架构定义了一组核心指令集和一些有协处理实现的附加指令。核心指令集可以访问核心寄存器,协处理器合一提供附加的寄存器用于某些特殊操作。
3.1 ARM寄存器
ARMv7架构中包含了16个32位寄存器,可以用R0-R15表示。下表中描述了每个寄存器的特定应用。
| 寄存器 | 特殊名称 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| R15 | PC | 程序计数器 Program Counter |
| R14 | LR | 链接寄存器 Link Register |
| R13 | SP | 栈指针 Stack Pointer |
| R12 | IP | The Intra-Procedure-call scratch register |
| R11 | 变量寄存器8 Variable-register 8 | |
| R10 | 变量寄存器7 Variable-register 7 | |
| R9 | v6 SB TR | 平台寄存器,其功能是由平台定义的 |
| R8 | 变量寄存器5 Variable-register 5 | |
| R7 | 变量寄存器4 Variable-register 4 | |
| R6 | 变量寄存器3 Variable-register 3 | |
| R5 | 变量寄存器2 Variable-register 2 | |
| R4 | 变量寄存器1 Variable-register 1 | |
| R3 | 参数寄存器4 Argument, scratch register 4 | |
| R2 | 参数寄存器3 Argument , scratch register 3 | |
| R1 | 参数、结果寄存器2 Argument, result, scratch register 2 | |
| R0 | 参数、结果寄存器1 Argument, result, scratch register 1 |
r0-r3四个寄存器用来向被调用程序传递参数,以及从一个函数返回结果。ARMv7中用寄存器传递参数最多可以有四个,更多的参数传递,则需要用到栈来实现。这几个寄存器也可以当做普通寄存器来存储临时值。
寄存器r12(IP)被链接器使用,在调用程序和子程序之间作为一个scratch register 。
r9寄存器功能是对应平台定义的,一个虚拟平台可以任意使用该寄存器,但要给出说明。比如,它可以作为一个静态基地址(static base, SB)在一个位置无关数据中; 或者也可以作为线程寄存器(thread register, TR)。
一个被调用程序必须保存寄存器r4-r8,r10,r11的值,因为这些值可能保存着调用程序的某些局部变量。被调用程序还必须保存SP寄存器,以在返回时恢复调用前的栈信息。
在所有的程序调用标准中,寄存器 r12-r15都有着特殊的角色,用IP、SP、IR、PC来表示。
寄存器CPSR(当前程序状态寄存器)包含以下特性:
-
The N, Z, C, V and Q bits (bits 27-31) and the GE[3:0] bits (bits 16-19) are undefined on entry to or return from a public interface. The Q and GE[3:0] bits may only be modified when executing on a processor where these features are present。
-
On ARM Architecture 6, the E bit (bit 8) can be used in applications executing in little-endian mode, or in bigendian-8 mode to temporarily change the endianness of data accesses to memory. An application must have a designated endianness and at entry to and return from any public interface the setting of the E bit must match the designated endianness of the application
-
The T bit (bit 5) and the J bit (bit 24) are the execution state bits. Only instructions designated for modifying these bits may change them
-
The A, I, F and M[4:0] bits (bits 0-7) are the privileged bits and may only be modified by applications designed to operate explicitly in a privileged mode.
-
All other bits are reserved and must not be modified. It is not defined whether the bits read as zero or one, or whether they are preserved across a public interface.
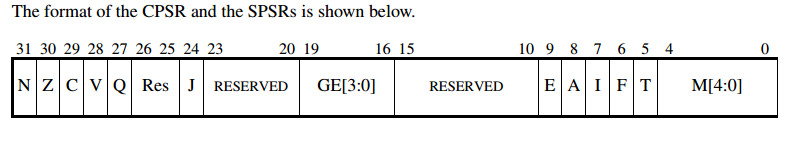
| 位 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| N | 负标志位,当运算结果为负时,该位被置1 |
| Z | 零标志位,当运算结果为零时,该位被置1 |
| C | 进位and借位标志,当运算结果为负时,该位被置1 |
| V | 溢出标志,有符号溢出时,该位被置1 |
| Q | 溢出饱和标志,在一些DSP指令中,该位指示是否发生溢出或者饱和 |
| GE[3:0] | 大于等于标志 |
| E | 装载、存储字节序 |
| A | disable data aborts when it is set |
| I | disable IRQ when it is set |
| F | disable FIQ when it is set |
| M[4:0] | 处理器运行模式 |
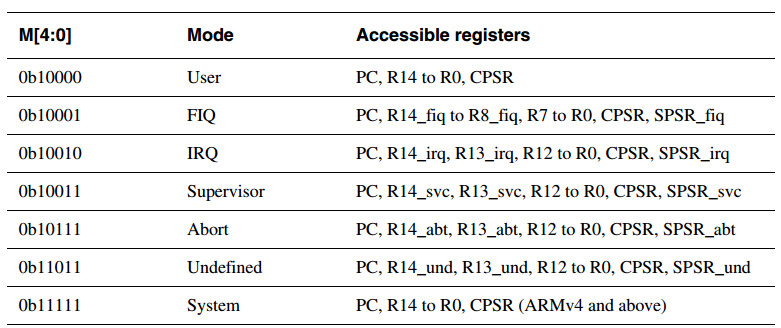
处理器的运行模式如下所示:
3.2 ARM中程序的栈、内存
AAPCS 应用于单线程执行,程序状态保存在机器寄存器及该程序可访问的内存里面。一个进程可访问的内存是可以在执行中变化的。
程序的内存可以分为以下五个部分:
- Code 代码段,只读,存放指令代码
- Read-only static data, 只读的静态数据区
- Writable static data, 可写的静态数据区
- the heap, 堆
- the stack, 栈
其中,可写的静态数据区可以进一步分为初始化的、零初始化、未初始化的数据区。除了栈,其他部分不必占用连续的内存地址。一个程序必须有栈和代码区,其他部分不是必须的。
堆是一段由进程自己管理的内存区域,比如在C中通过malloc分配的空间就在堆上。堆常用于动态创建数据对象。
程序只能执行位于代码段的指令。
3.2.1 栈
栈用来保存局部变量和传递参数,当参数寄存器不够用时就是通过栈来传递参数的。
栈被设计为向下增长的,即栈顶在最低地址,栈顶的位置保存在寄存器SP中。一般情况下,栈有一个基地址base和一个栈大小限制limit。栈可以用固定的大小,或者是动态变化的(通过调整limit来实现)。
栈的一些规则:
- 栈指针在基地址与栈限制之间, stack_limit < SP <= stack_base
- SP mod 4 = 0, 栈地址保持4字节对齐
- 程序只能访问闭区间[SP, stack_base-1]的栈内存范围
3.3 子程序调用
ARM指令集中的BL指令表示带链接寄存器的跳转,当执行 BL 指令时,会把PC中下一条指令地址存到LR寄存器中,然后将跳转的目的地址存到PC中。跳转到r4中地址的代码可以用如下的指令实现,其效果等效于 BL r4。
MOV LR, PC
BX r4
3.4 结果返回
返回的方式取决于返回结果的类型:
- 半精度浮点类型占2个字节,返回在r0的低16位
- 小于四个字节的数据类型返回到r0中,但是做了0扩展或是符号扩展
- 四个字节的数据类型,直接返回到r0中
- 双字的类型返回到r0和r1中
- 128位的类型返回到 r0~r3中
- 小于等于四个字节的复合类型返回到r0中。
- 大于四个字节的复合类型,存在内存中,内存的地址是通过参数传进子函数的。
3.5 参数传递
程序调用通过寄出去你r0-r3和栈来传递参数,参数较少时便用不到栈。
参数传递被定义为两层概念模型:
- 一种从源码语言参数到机器类型的映射 A mapping from a source language argument onto a machine type
- 整理机器类型来产生最终的参数列表 The marshalling of machine types to produce the final parameter list