Mike is a bartender at Rico's bar. At Rico's, they put beer glasses in a special shelf. There are n kinds of beer at Rico's numbered from 1 to n. i-th kind of beer has ai milliliters of foam on it.

Maxim is Mike's boss. Today he told Mike to perform q queries. Initially the shelf is empty. In each request, Maxim gives him a number x. If beer number x is already in the shelf, then Mike should remove it from the shelf, otherwise he should put it in the shelf.
After each query, Mike should tell him the score of the shelf. Bears are geeks. So they think that the score of a shelf is the number of pairs (i, j) of glasses in the shelf such that i < j and 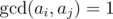 where
where 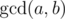 is the greatest common divisor of numbers a and b.
is the greatest common divisor of numbers a and b.
Mike is tired. So he asked you to help him in performing these requests.
The first line of input contains numbers n and q (1 ≤ n, q ≤ 2 × 105), the number of different kinds of beer and number of queries.
The next line contains n space separated integers, a1, a2, ... , an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 5 × 105), the height of foam in top of each kind of beer.
The next q lines contain the queries. Each query consists of a single integer integer x (1 ≤ x ≤ n), the index of a beer that should be added or removed from the shelf.
For each query, print the answer for that query in one line.
5 6
1 2 3 4 6
1
2
3
4
5
1
0
1
3
5
6
2

1 #include<vector> 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 typedef long long ll ; 6 const int M = 5e5 + 10 ; 7 int n , q ; 8 int a[M] ; 9 int dp[M] , cnt[M] ; 10 bool vis[M] ; 11 std::vector <int> g[M] ; 12 13 void table () 14 { 15 dp[1] = 1 ; 16 for (int i = 1 ; i < M ; i ++) { 17 if (dp[i]) g[i].push_back(i) ; 18 for (int j = i + i ; j < M ; j += i ) { 19 if (dp[i]) g[j].push_back(i) ; 20 dp[j] -= dp[i] ; 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 25 int main () 26 { 27 //freopen ("a.txt" , "r" , stdin ) ; 28 table () ; 29 scanf ("%d%d" , &n , &q) ; 30 for (int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) scanf ("%d" , &a[i]) ; 31 ll ans = 0 ; 32 while (q --) { 33 int x ; 34 scanf ("%d" , &x) ; 35 if (vis[x]) { 36 for (int i : g[ a[x] ]) ans -= 1ll * dp[i] * (-- cnt [i]) ; 37 } else { 38 for (int i : g[ a[x] ]) { 39 ans += 1ll * dp[i] * (cnt[i] ++) ; 40 } 41 } 42 vis[x] ^= 1 ; 43 printf ("%I64d " , ans) ; 44 } 45 return 0 ; 46 }
第一次接触容斥问题,但已接触过默比乌斯反演。orz
容斥简单来说是这样的:
有n个群学生选了A课程,B课程,C课程。其中选了A课程的为集合{A},B的为集合{B}人,C的为集合{C}。
那么n = A + B + C - A&B - B&C - A&C + A&B&C ;
通过观察,我们可以yy出这样的性质:
奇数集合:A , B , C , A&B&C …… 指奇数个集合形成的交集。
偶数集合:A&B , B&C , A&C …… 指偶数个集合形成的交集。
so n = sum(奇数集合) - sum(偶数集合);
再回到这道题目上来:
用单纯的想法来思考:initial cnt = 0 , set = {} ; cnt 用来记录当前的set中互质的对数 。
while (query --)
get (x) ;
travel set ---> if (find set(i) 互质 x)cnt ++ ;
set.insert (x) ;
end;
复杂度O(n^2);
来优化一下吧,如过我们知道1~5e5 里每个数的所有因数。并用一个cnt[ 50000 ]来表示当前集合中放的因数的出现次数:
比如说放了2 : 1 , 2, 3 : 1 , 3, 6 : 1 , 2 , 3 , 6 。
那么cnt[1] = 3 , cnt[2] = 2 , cnt [3] = 3 , cnt[6] = 1 ;
........然后自己yy吧。
感谢PauGra非常简单明了的code:

1 #include<vector> 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 typedef long long ll ; 6 const int M = 5e5 + 10 ; 7 int n , q ; 8 int a[M] ; 9 int dp[M] , cnt[M] ; 10 bool vis[M] ; 11 std::vector <int> g[M] ; 12 13 void table () 14 { 15 dp[1] = 1 ; 16 for (int i = 1 ; i < M ; i ++) { 17 if (dp[i]) g[i].push_back(i) ; 18 for (int j = i + i ; j < M ; j += i ) { 19 if (dp[i]) g[j].push_back(i) ; 20 dp[j] -= dp[i] ; 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 25 int main () 26 { 27 //freopen ("a.txt" , "r" , stdin ) ; 28 table () ; 29 printf ("27: %d " , dp[54]) ; 30 scanf ("%d%d" , &n , &q) ; 31 for (int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) scanf ("%d" , &a[i]) ; 32 ll ans = 0 ; 33 while (q --) { 34 int x ; 35 scanf ("%d" , &x) ; 36 if (vis[x]) { 37 for (int i : g[ a[x] ]) ans -= 1ll * dp[i] * (-- cnt [i]) ; 38 } else { 39 for (int i : g[ a[x] ]) { 40 ans += 1ll * dp[i] * (cnt[i] ++) ; 41 } 42 } 43 vis[x] ^= 1 ; 44 printf ("%I64d " , ans) ; 45 } 46 return 0 ; 47 }
