还有几天就要程设期考了/无奈,我的链表和文件还是一团糟,趁着这个机会,复习一下文件的基础操作吧!
先打上几个重要的头文件:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h>
一、使用文件的方式:
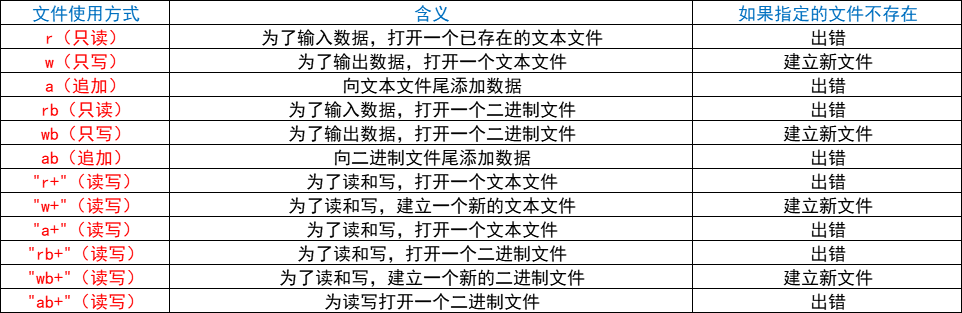
二、一些基础的操作函数(都包含在stdio.h库函数中了!)
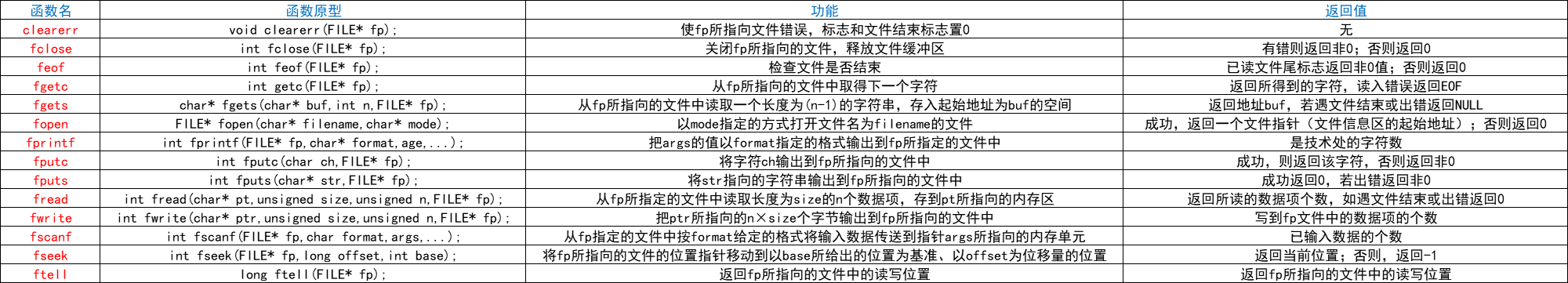
三、读写文件典型例题:
①
要用到的函数:fgetc和fputc
1 /* 2 题目: 3 从键盘输入一些字符,并逐个将它们送到磁盘上去,直到用户输入一个“#”为止。 4 思路: 5 用fgetc函数从键盘逐个输入字符,然后用fputc函数写到磁盘文件即可。 6 */ 7 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <stdlib.h> 10 #include <string.h> 11 int main() 12 { 13 FILE* fp; 14 char ch, filename[10]; 15 printf("请输入所用的文件名:"); 16 scanf("%s",filename); 17 getchar(); 18 if ((fp = fopen(filename, "w")) == NULL) 19 { 20 printf("cannot open the file "); 21 exit(0); 22 } 23 printf("请输入一个准备存储到磁盘中的字符串(以#结束):"); 24 ch=getchar(); 25 while (ch != '#') 26 { 27 fputc(ch, fp); 28 putchar(ch); 29 ch = getchar(); 30 } 31 fclose(fp); 32 putchar(10); 33 return 0; 34 }
②
要用到的函数:feof
1 /* 2 题目: 3 将一个磁盘文件中的信息复制到另一个磁盘文件中。 4 把已经建立好的file1.dat文件中的内容复制到另外一个磁盘文件file2.dat中 5 思路: 6 从file1.dat文件中逐个读入字符,然后逐个输出到file2.dat中 7 */ 8 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 9 #include <stdio.h> 10 #include <stdlib.h> 11 #include <string.h> 12 int main() 13 { 14 FILE* in; 15 FILE* out; 16 char ch, infile[10], outfile[10];; 17 printf("输入读入文件的名字:"); 18 scanf("%s", infile); 19 printf("输入输出文件的名字:"); 20 scanf("%s", outfile); 21 if ((in = fopen(infile, "r")) == NULL) 22 { 23 printf("无法打开此文件 "); 24 exit(0); 25 } 26 if ((out = fopen(outfile, "w")) == NULL) 27 { 28 printf("无法打开此文件 "); 29 exit(0); 30 } 31 ch = fgetc(in); 32 while (!feof(in)) 33 { 34 fputc(ch, out); 35 putchar(ch); 36 ch = fgetc(in); 37 } 38 putchar(10); 39 fclose(in); 40 fclose(out); 41 return 0; 42 }
③
要用到的函数:fgets和fputs
1 /* 2 题目: 3 从键盘读入若干个字符串,对它们按字母从小到大的顺序排序, 4 然后把排好序的字符串送到磁盘文件中保存。 5 思路: 6 ①从键盘读入n个字符串,存放在一个二维字符数组中,每一个一维数组存放一个字符串 7 ②对字符数组中的n个字符串按字母顺序排序,排好序的字符串仍然存放在字符数组中 8 ③将字符数组中的字符串顺序输出 9 */ 10 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 11 #include <stdio.h> 12 #include <stdlib.h> 13 #include <string.h> 14 int main() 15 { 16 FILE* fp; 17 char str[3][10], temp[10]; 18 int i, j, k, n = 3; 19 printf("Enter strings: "); 20 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) 21 gets(str[i]); 22 for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) 23 { 24 k = i; 25 for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++) 26 if (strcmp(str[k], str[j]) > 0) k = j; 27 if (k != i) 28 { 29 strcpy(temp, str[i]); 30 strcpy(str[i], str[k]); 31 strcpy(str[k], temp); 32 } 33 } 34 if ((fp = fopen("D:\CC\string.txt", "w")) == NULL) 35 { 36 printf("cannot open the file! "); 37 exit(0); 38 } 39 printf(" The new sequence: "); 40 for (i = 0; i < n;i++) 41 { 42 fputs(str[i], fp); 43 fputs(" ", fp); 44 printf("%s ", str[i]); 45 } 46 return 0; 47 }
1 /* 2 题目: 3 编写程序,从文件string.dat中读回字符串,并在屏幕上显示 4 思路: 5 没有什么卵思路 6 */ 7 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <stdlib.h> 10 #include <string.h> 11 int main() 12 { 13 FILE* fp; 14 char str[3][10]; 15 int i = 0; 16 if ((fp = fopen("D:\CC\string.txt", "r")) == NULL) 17 { 18 printf("cannot open the file "); 19 exit(0); 20 } 21 while (fgets(str[i], 10, fp) != NULL) 22 { 23 printf("%s", str[i]); 24 i++; 25 } 26 fclose(fp); 27 return 0; 28 }
④
要用到的函数:fread和fwrite
1 /* 2 题目: 3 从键盘输入10个学生的有关数据,然后把它们转存到磁盘文件中去。 4 思路: 5 定义一个有10个元素的结构体数组,用来存放10个学生的数据。 6 从main函数输入10个学生的数据。用save函数实现向磁盘输出学生数据。用fwrite函数一次输出一个学生的数据 7 */ 8 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 9 #include <stdio.h> 10 #include <stdlib.h> 11 #include <string.h> 12 #define SIZE 10 13 struct Student_type 14 { 15 char name[10]; 16 char addr[15]; 17 int num; 18 int age; 19 }stud[SIZE]; 20 void save() 21 { 22 FILE* fp; 23 int i; 24 if ((fp = fopen("stu.dat", "wb")) == NULL) 25 { 26 printf("cannot open file "); 27 return; 28 } 29 for (i = 0; i < SIZE;i++) 30 { 31 if (fwrite(&stud[i], sizeof(struct Student_type), 1, fp) != 1) 32 printf("file write error "); 33 } 34 fclose(fp); 35 } 36 int main() 37 { 38 int i; 39 printf("Please enter data of students: "); 40 for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) 41 { 42 scanf("%s%d%d%s",stud[i].name, &stud[i].num, &stud[i].age, stud[i].addr); 43 } 44 save(); 45 return 0; 46 }
1 /* 2 题目: 3 验证上一个程序是否成功,编写程序从stu.dat文件中读入数据,然后在屏幕上输出 4 思路: 5 用fread函数从文件中读数据 6 */ 7 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <stdlib.h> 10 #include <string.h> 11 #define SIZE 10 12 struct Student_type 13 { 14 char name[10]; 15 char addr[15]; 16 int num; 17 int age; 18 }stud[SIZE]; 19 int main() 20 { 21 FILE* fp; 22 int i; 23 if ((fp = fopen("stu.dat", "rb")) == NULL) 24 { 25 printf("cannot open file "); 26 exit(0); 27 } 28 for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) 29 { 30 fread(&stud[i],sizeof(struct Student_type),1,fp); 31 printf("%-10s %4d %4d %-15s ",stud[i].name,stud[i].num,stud[i].age,stud[i].addr); 32 } 33 fclose(fp); 34 return 0; 35 }
四、邓老师给出的一组对比实验:
①程序1:把一个int数组里的大于90的数据用fprintf循环写入E:盘下DATA文件夹下file1.dat;再从文件用fscanf读出来输出到屏幕。
1 /* 2 题目: 3 把一个int数组里的大于90的数据用fprintf循环写入E:盘下DATA文件夹下file1.dat;再从文件用fscanf读出来输出到屏幕。 4 思路: 5 没有什么思路 6 */ 7 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <stdlib.h> 10 #include <string.h> 11 int main() 12 { 13 FILE* fp; 14 int a[15] = {95,56,78,102,96,56,19,20,34,99,89,90,150,620,92}; 15 int b[20]; 16 int flag=0,i; 17 if ((fp = fopen("E:\file1.dat", "w")) == NULL) 18 { 19 printf("cannot open the file! "); 20 exit(0); 21 } 22 for (i = 0; i < 15; i++) 23 { 24 if (a[i] > 90) 25 { 26 fprintf(fp,"%d ",a[i]); 27 flag++; 28 } 29 } 30 fclose(fp);//划重点!!再次使用fp应该释放掉!!不然会出错 31 fp = fopen("E:\file1.dat", "r"); 32 for (i = 0; i < flag; i++) 33 { 34 fscanf(fp,"%d",&b[i]); 35 printf("%d ", b[i]); 36 } 37 fclose(fp); 38 return 0; 39 }
②程序2:把一个结构体数组里的score项小于60分的数据用fwrite一次性写入E:盘下DATA文件夹下file2.dat,再用fread读出来显示到屏幕。
1 /* 2 题目: 3 把一个结构体数组里的score项小于60分的数据用fwrite一次性写入E:盘下DATA文件夹下file2.dat, 4 再用fread读出来显示到屏幕。 5 思路: 6 /*===========================================================================*/ 7 /*题目要求“一次性”,所以就不能一次次地读进去,得一次性把成绩小于60分的人一次性读进去。 8 一个想法:由于读入后再删除不小于60分的数据很麻烦,不如在输入的时候就把分数不小于60分的人过滤掉 9 但这样好像有点违背题意:结构体数组是给定的,转存一下就OK啦!*/ 10 /*===========================================================================*/ 11 /*上面是我对题目的初步理解,是错的,其实代码很简单,题目所要求的“一次性”表示“一次就把一个学生的 12 所有信息写入文件”而不是“把符合要求的所有学生放在一个结构体数组中,一次性把这个数组写入文件,这样 13 是肯定行不通的!”*/ 14 /*===========================================================================*/ 15 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 16 #include <stdio.h> 17 #include <stdlib.h> 18 #include <string.h> 19 typedef struct student 20 { 21 char name[20]; 22 char sex; 23 int score; 24 }student; 25 int main() 26 { 27 int n, i; 28 int scorex; 29 int flag = 0;//统计有多少个学生的成绩小于60 30 char namex[20]; 31 char sexx; 32 student a[100]; 33 FILE* fp; 34 scanf("%d", &n); 35 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) 36 { 37 scanf("%s %c %d", namex, &sexx, &scorex);//筛选掉分数不小于60的人 38 if (scorex < 60) 39 { 40 strcpy(a[flag].name, namex); 41 a[flag].sex = sexx; 42 a[flag].score = scorex; 43 44 flag++; 45 } 46 } 47 if ((fp = fopen("E:\file2.dat", "wb")) == NULL) 48 { 49 printf("cannot open the file! "); 50 exit(0); 51 } 52 for (i = 0; i < flag; i++) 53 { 54 fwrite(&a[i], sizeof(student), 1, fp); 55 } 56 fclose(fp); 57 if ((fp = fopen("E:\file2.dat", "rb")) == NULL) 58 { 59 printf("cannot open the file! "); 60 exit(0); 61 } 62 for (i = 0; i < flag; i++) 63 { 64 fread(&a[i], sizeof(student), 1, fp); 65 printf("%s %c %d ",a[i].name,a[i].sex,a[i].score); 66 } 67 fclose(fp); 68 return 0; 69 }