Ready:
VScode + glslCanvas + glslLinter + Shadering languages support + glslang
Ref:
>>tutorial
>>2dboxsdf
NDC:
uniform vec2 u_resolution;
vec2 P = (gl_FragCoord.xy / u_resolution - vec2(0.5)) * 2.0;
1:sphere

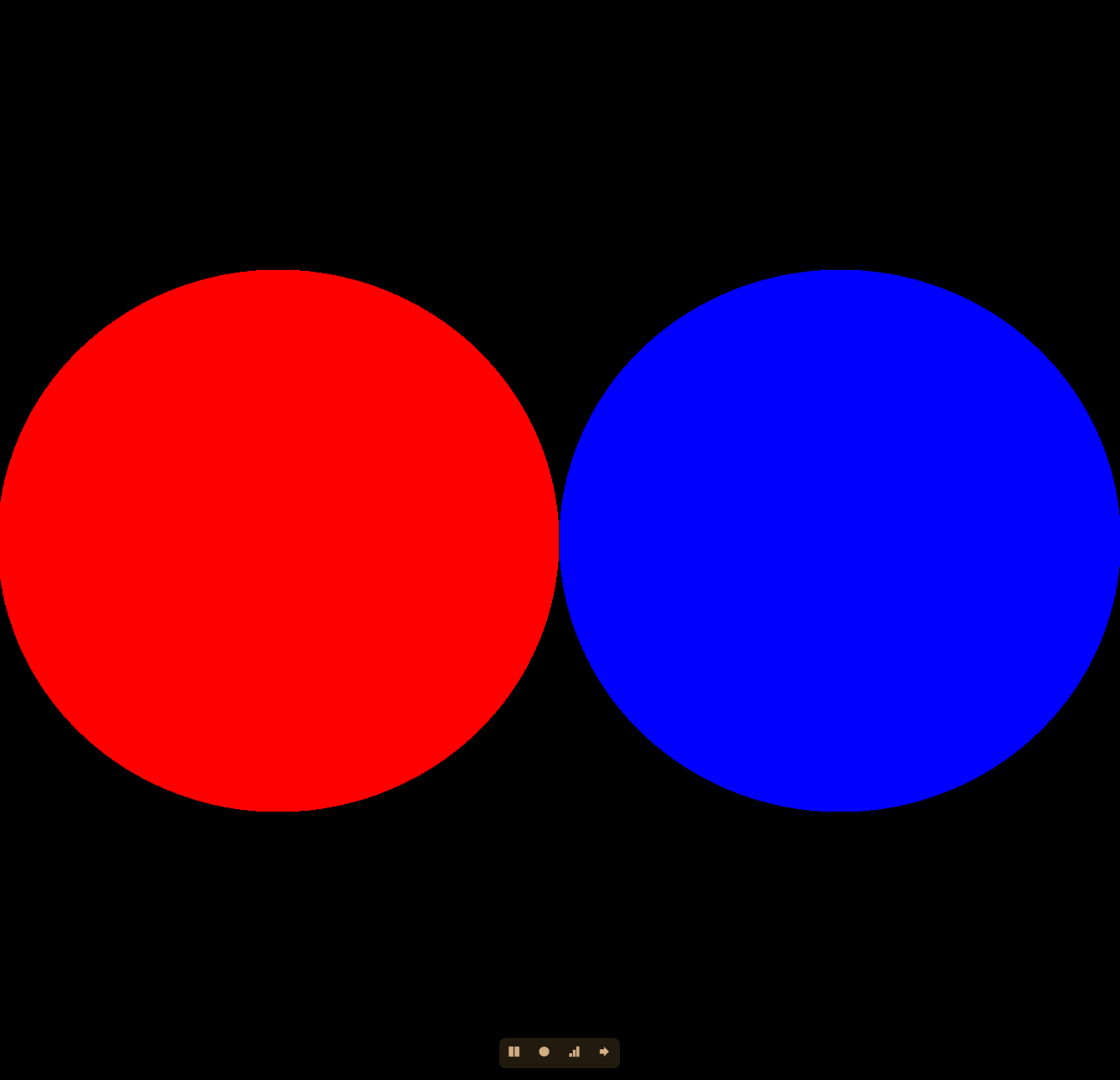
#ifdef GL_ES precision mediump float; #endif uniform vec2 u_resolution; const float e = 1e-8; struct Shape{ float sdf; vec3 color; }; Shape combine_sdf(Shape a, Shape b){ Shape temp; temp.sdf = min(a.sdf,b.sdf); temp.color = a.color * float(a.sdf<=0.0) + b.color * float(b.sdf<=0.0) ; return temp; } float circle_sdf (vec2 pos,vec2 center,float radius) { return length(pos-center) - radius; } void main() { float radius = 0.5; vec2 P = (gl_FragCoord.xy / u_resolution - vec2(0.5)) * 2.0; Shape cle01= Shape(circle_sdf(P,vec2(-0.5, 0.0), radius), vec3(1,0,0)); Shape cle02= Shape(circle_sdf(P,vec2(0.5, 0.0), radius), vec3(0,0,1)); Shape scene = combine_sdf(cle01,cle02); vec3 color = float(scene.sdf <=0.0) * scene.color; gl_FragColor = vec4(color, 1.0); }
2:rectangle

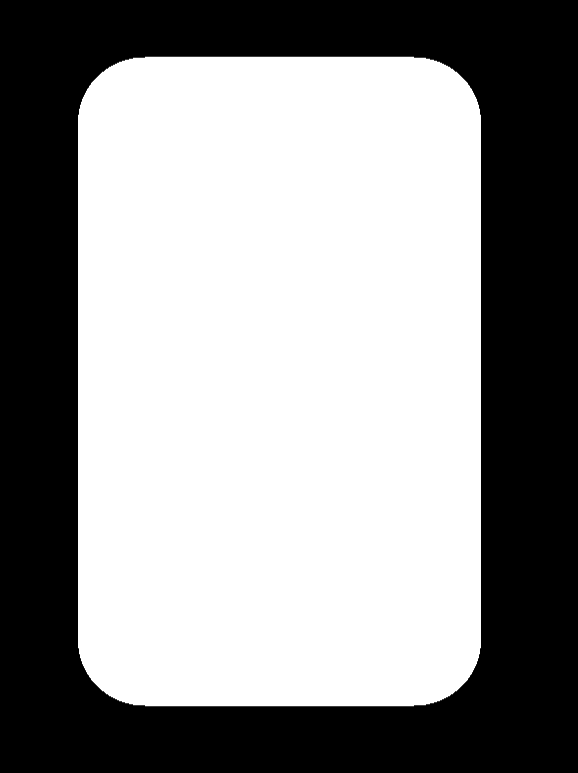
#ifdef GL_ES precision mediump float; #endif uniform vec2 u_resolution; const float e = 1e-8; float Rectangle(vec2 p, vec2 rec, float radius){ vec2 q = abs(p) - rec; float outDis = length(max(q,0.0)); float inDis = min(max(q.x,q.y),0.0); return outDis + inDis - radius; } void main() { float radius = 0.5; vec2 P = (gl_FragCoord.xy / u_resolution - vec2(0.5)) * 2.0; float box = Rectangle(P, vec2(0.2,0.4), 0.1); vec3 L = vec3( float(box<=0.0)); gl_FragColor = vec4(L, 1.0); }
3:polygonShape:

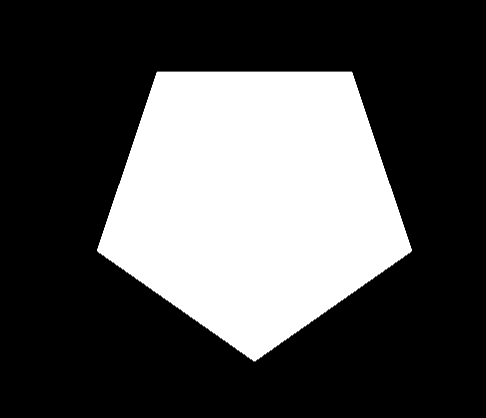
#ifdef GL_ES precision mediump float; #endif uniform vec2 u_resolution; const float e = 1e-8; const float PI = 3.1415926535; float polygonShape(vec2 p,float radius, float sides){ float angle = atan(p.x, p.y); float slice = PI*2.0 / sides; return cos(floor(0.5+angle/slice)*slice - angle) * length(p)- radius; } void main() { float radius = 0.2; vec2 P = (gl_FragCoord.xy / u_resolution - vec2(0.5))*2.0; // Render Simple scene //vec3 L = float(scene.sdf <=0.0) * scene.Cd; float sdf = polygonShape(P,0.2,5.0); vec3 L = vec3( float(sdf<=.0) ); // Out Radiance gl_FragColor = vec4(L,1.0); }
4,u_time:

#ifdef GL_ES precision mediump float; #endif uniform vec2 u_resolution; uniform float u_time; const float e = 1e-8; const float PI = 3.1415926535; float polygonShape(vec2 p,float radius, float sides){ float angle = atan(p.x, p.y); float slice = PI*2.0 / sides; return cos(floor(0.5+angle/slice)*slice - angle) * length(p)- radius; } void main() { float radius = 0.2; vec2 P = gl_FragCoord.xy / u_resolution - vec2(0.5); // Render Simple scene //vec3 L = float(scene.sdf <=0.0) * scene.Cd; float ofx = cos(u_time*5.0)*0.2; float ofy = sin(u_time*5.0)*0.2; vec2 offset = vec2(ofx,ofy); float sdf = polygonShape(P+offset,0.2,6.0); vec3 L = vec3( float(sdf<=.0) ); // Out Radiance gl_FragColor = vec4(L,1.0); }
simple cos sin offset the position by time:
float ofx = cos(u_time*5.0)*0.2; float ofy = sin(u_time*5.0)*0.2; vec2 offset = vec2(ofx,ofy); float sdf = polygonShape(P+offset,0.2,6.0);
GLSL是列向量为主
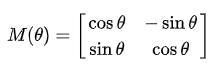

#ifdef GL_ES precision mediump float; #endif uniform vec2 u_resolution; uniform float u_time; const float e = 1e-8; const float PI = 3.1415926535; float polygonShape(vec2 p,float radius, float sides){ float angle = atan(p.x, p.y); float slice = PI*2.0 / sides; return cos(floor(0.5+angle/slice)*slice - angle) * length(p)- radius; } float combineSDF(float s1,float s2){ return min(s1,s2); } // column major mat2 rotate(float angle){ return mat2(vec2(cos(angle),sin(angle)),vec2(-sin(angle),cos(angle))); } // same as above mat2 rotate2(float angle){ return mat2(cos(angle),sin(angle),-sin(angle),cos(angle)); } void main() { float radius = 0.2; vec2 P = (gl_FragCoord.xy / u_resolution - vec2(0.5)) * 2.0; float angle = 45.0; // Red Rectangle vec2 offset1 = vec2(0.5,0.0); // move to left mat2 rot1 = rotate(PI/180.0 * angle); // method 1 vec3 Cd1 = vec3(1,0,0); float sdf1 = polygonShape(rot1* (P + offset1),0.2,4.0); // Green Rectangle vec2 offset2 = vec2(-0.5,0.0); // move to right vec3 Cd2 = vec3(0,1,0); mat2 rot2 = rotate2(PI/180.0 * angle); // In this case, use rotate method 2 same method 1 float sdf2 = polygonShape(rot2*(P + offset2),0.2,4.0); // combie sdf & color float sdf = combineSDF(sdf1,sdf2); vec3 color = Cd1 * float(sdf1<=0.0) + Cd2 * float(sdf2<=0.0); vec3 L = vec3( color * float(sdf<=0.0) ); // Out Radiance gl_FragColor = vec4(L,1.0); }
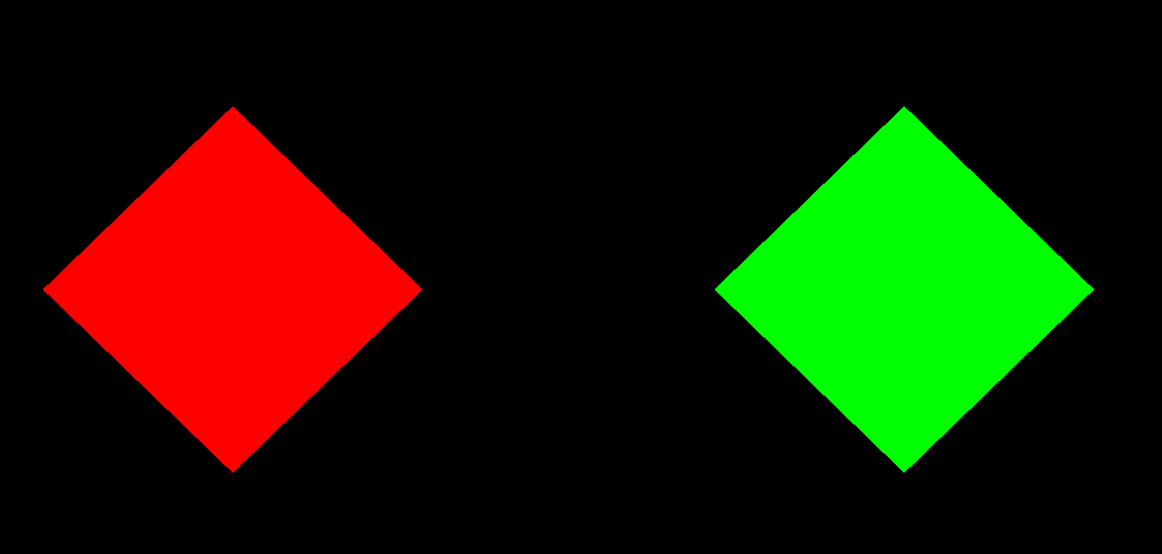
理解其中的变换:
注意其中的mat2*(P + offset),因为P是sdf sample point,相当于基坐标。
再3D 软件都是RST or SRT 这样的顺序,在这里一定要搞清楚是变换的采样基所以先在基坐标系P+offset下绘制出来Rectangle,然后再旋转,顺序是TR
加强理解变换:
还有以中简单的理解你加的offset 是世界空间加的,如果用下面代码:
float sdf2 = polygonShape(rot2*P + rot2*offset2,0.2,4.0);
把P转换到rot2的空间,把offset2转换到rot2空间,空间一致相加没问题。
6,用uv空间做floor效果:

#ifdef GL_ES precision mediump float; #endif uniform vec2 u_resolution; uniform float u_time; const float e = 1e-8; const float PI = 3.1415926535; const float speed = 3.0; void main() { float radius = 0.2; //vec2 P = (gl_FragCoord.xy / u_resolution - vec2(0.5)) * 2.0; vec2 P = gl_FragCoord.xy / u_resolution ; float data = sin(floor(P.x*4.0) + u_time*speed); //data = clamp(data,0.0,1.0); vec3 L = vec3( data ); // Out Radiance gl_FragColor = vec4(L,1.0); }
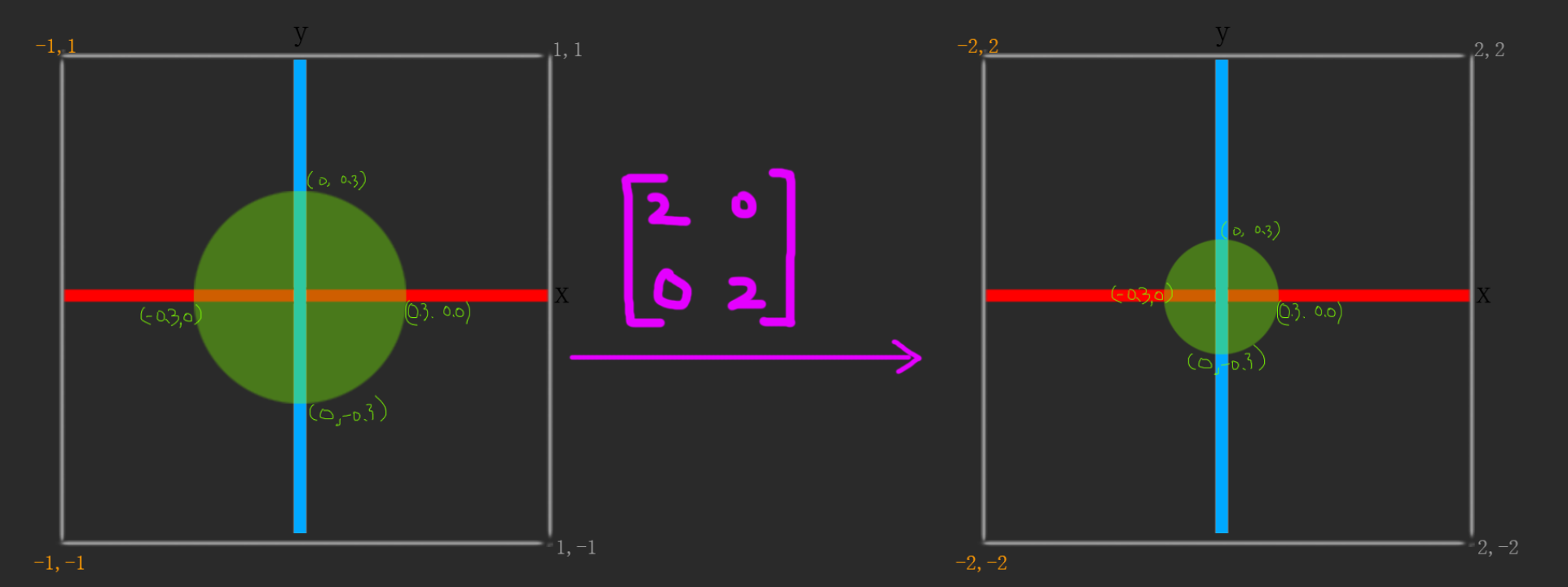
7,理解在这种模式下得缩放:

#ifdef GL_ES precision mediump float; #endif uniform vec2 u_resolution; uniform float u_time; const float e = 1e-8; const float PI = 3.1415926535; const float speed = 3.0; float circle_sdf (vec2 pos,vec2 center,float radius) { return length(pos-center) - radius; } mat2 scale(float sx ,float sy){ return mat2(sx,0.0,0.0,sy); } void main() { float radius = 0.2; vec2 P = (gl_FragCoord.xy / u_resolution - vec2(0.5)) * 2.0; //vec2 P = gl_FragCoord.xy / u_resolution ; mat2 scaleMat = scale(2.0,2.0); P = scaleMat * P; float sdf = circle_sdf( P,vec2(0),0.5); float data = float(sdf<=e); vec3 L = vec3( data ); // Out Radiance gl_FragColor = vec4(L,1.0); }
mat2 scaleMat = scale(2.0,2.0);
按理说用上面得矩阵,图像应该是放大。为什么会呈现出缩放效果:
原因跟rotate一样,因为变换得基坐标,所以就会导致在基坐标放大了,画得图就会变小:
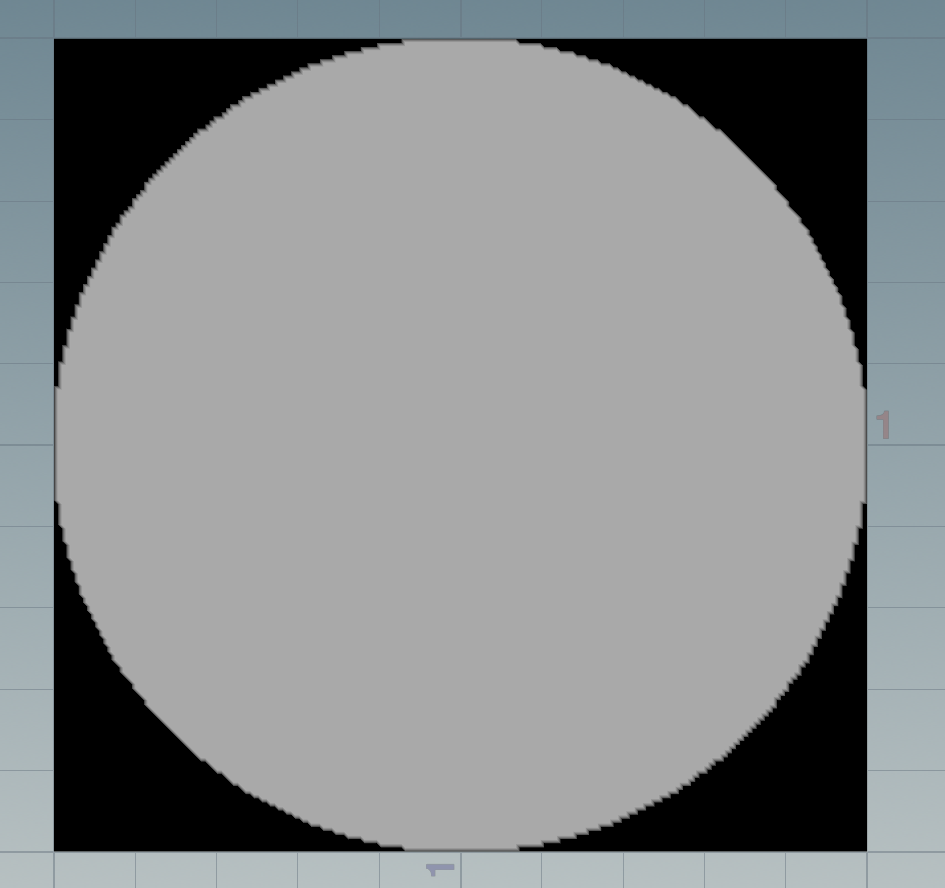
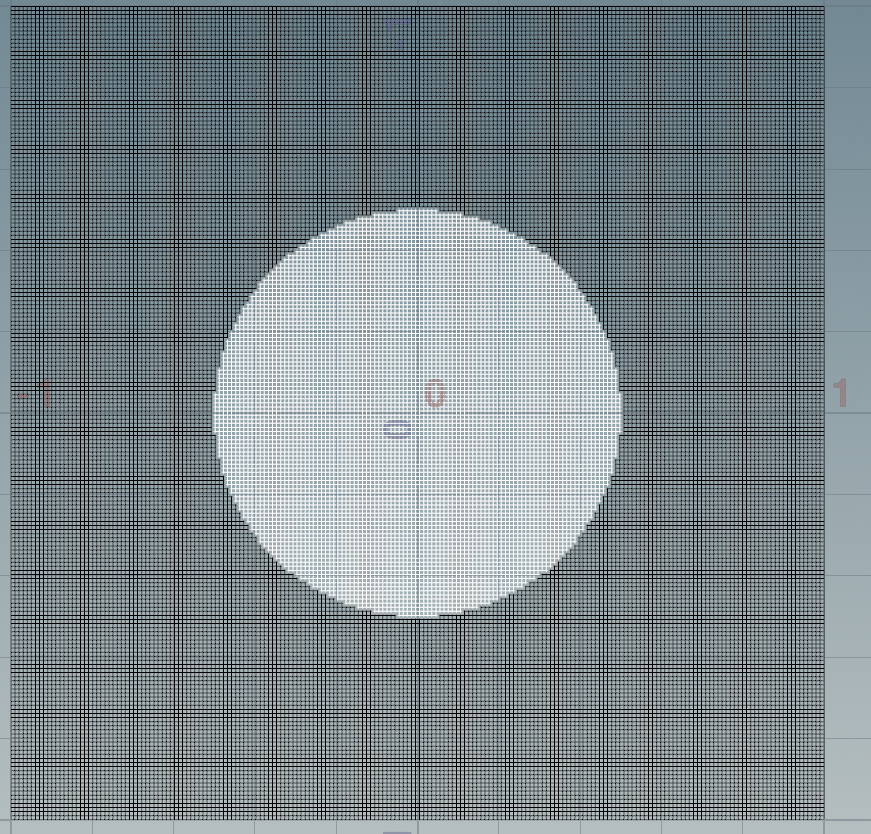
Houdini理解一样:
不应用矩阵时候:
应用后:
8:

#ifdef GL_ES precision mediump float; #endif uniform vec2 u_resolution; uniform float u_time; const float expvalue =4.0; const float light_intensity = 0.1; const int numpoints = 3; void main(){ vec2 uv = gl_FragCoord.xy / u_resolution; // uv pos vec2 P = (uv - vec2(0.5) ) * 2.0; vec3 L = vec3(0.0); for(int i = 0; i <numpoints ; i++){ float per_angle = float(360) / float(numpoints) ; float angle = per_angle * float(i) + u_time * 40.0; float lg_x = sin( radians(angle) )*0.5; float lg_y = cos( radians(angle ) )*0.6; vec2 newpos = vec2(lg_x,lg_y); float data = light_intensity*light_intensity / pow(length(P + newpos),expvalue); L += vec3(data); } gl_FragColor = vec4(L,1.0); }

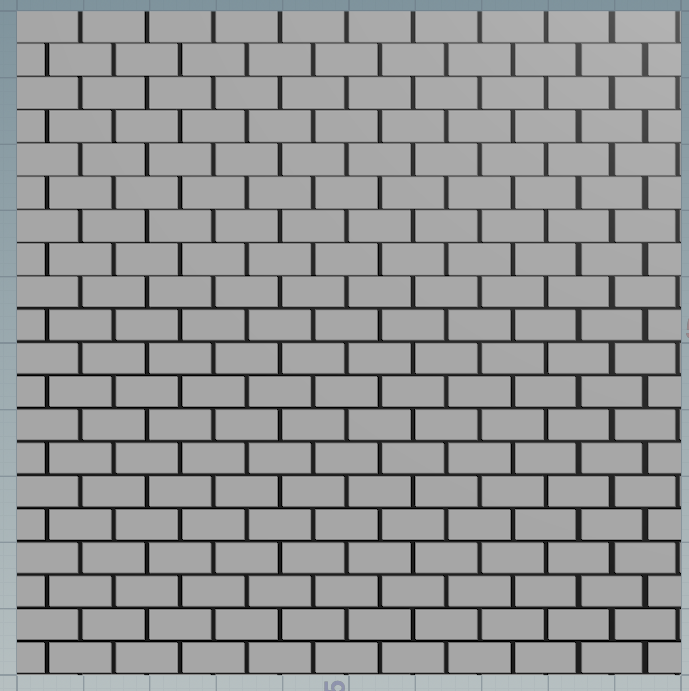
9,下面可能用houdini测试。

float fract(float x){ return x - floor(x); } float step(float edge;float x){ if(x < edge){ return 0; } return 1; } float bsize = chf("bricksize"); float bpct = chf("brickPct"); float xscale = chf("xscale"); float yscale = chf("yscale"); vector2 P = set(@P.x, @P.z); // gen plane at x z , so we assume and translate to x y plane P.x /= xscale; P.y /= yscale; P/= bsize; if (fract(P.y * 0.5) > 0.5) P.x += .5; P.x = fract(P.x); P.y = fract(P.y); P.x = step(P.x , bpct); P.y = step(P.y , bpct); @Cd = P.x * P.y;