数据结构(一) 单链表的实现
一. 单链表的简单介绍
单链表在整个数据结构中可以说是相对比较简单的,但是它的作用却不可忽视,许多相对复杂的数据结构都是基于单链表实现的。在这里我们简单介绍一下单链表。
单链表有节点构成,每个节点封装了数据和下一个节点的地址,最后一个节点指向null。

二. 单链表的java实现
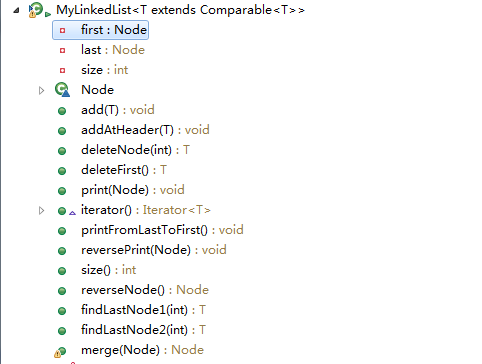
(一)API
该实现单链表可以适合用于存储实现了Comparable接口的任意对象,因此可以对不同节点进行比较,链表内部维护了一个first 和last指针,分别指向链表的头结点和尾节点,size变量存储的是链表的长度。
内部为了了一个Node类,它的实例用于表示节点对象,存储相应的数据和下一个节点的地址。
该实现可以用来添加节点、删除节点、遍历节点、反转链表等,具体介绍参见具体实现。
(二)具体实现
- 添加节点
1. 插入节点(默认从尾部插入)
/** * 向链表中添加节点(从链表尾部添加节点) * 如果链表为空,则链表的第一个节点的最后一个节点都指向新添加的节点 * 如果链表不为空,将最后一个节点的next指向新产生的节点,并将新节点设为最后一个节点 * 节点数加1 * @param data */ public void add(T data) { Node newNode = new Node(data); if(first == null) {//链表为空 first = newNode; last = first; }else {//链表不为空 last.next = newNode; last = newNode; } size++;//节点数加1 }
2. 从链表头部插入节点
/** * 从链表头部添加元素 * @param data */ public void addAtHeader(T data) { Node newNode = new Node(data); if(first == null) { first = newNode; last = first; }else { newNode.next = first; first = newNode; } size++; }
- 删除节点
1. 删除头部节点/** * 删除头结点
* @return */ public T deleteFirst() {
if(first == null)
return null;
T data = first.data; first = first.next; size--; return data; }
2. 删除指定位置节点
/** * 删除指定位置的节点 * @param index * @return */ public T deleteNode(int index) { Node preCurrent = null; Node current = first; if(index == 0) { return deleteFirst(); } int i = 0; while(i < index) { preCurrent = current; current = current.next; i++; } preCurrent.next = current.next; size--; return current.data; }
- 遍历节点
1. 遍历节点
/** * 遍历打印所有节点 */ public void print(Node node) { Node current = node; int i = 0; while(current != null) { System.out.println("This is the "+i+"th Node:"+current.data); current = current.next; i++; } }
2. Iterable实现节点遍历
/** * 遍历方法2: 链表实现Iterable接口,返回一个Iterator对象 * */ @Override public Iterator<T> iterator() { return new Iterator<T>() { Node current = first;//内部维护一个当前节点对象 @Override public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; } @Override public T next() { Node returnNode = current; current = current.next;//小心 return returnNode.data; } }; }
- 反向遍历节点
/** * * 从为到头遍历链表:递归实现 * 也可采用栈,正向遍历压栈,循环完毕,弹栈输出 */ public void printFromLastToFirst() { reversePrint(first); } public void reversePrint(Node n) { if(n == null) { return; } reversePrint(n.next); System.out.println("Node: "+n.data); }
- 链表反转
/** * 链表反转:遍历实现 * 返回反转后链表的头结点 */ public Node reverseNode(Node head) { Node pre = null; while(head != null) { Node temp = head.next;//保留当前头结点的下一个节点 head.next = pre; pre = head; head = temp; } return pre; }
/** * 链表反转:遍历实现 * 思想:翻转head->为首的链表, 然后head变为尾部节点 */ public Node reverseNode(Node head) { if(head == null || head.next == null) { return head; } Node pre = reverseNode(head.next); head.next.next = head; head.next = null; return prev; }
- 返回链表第k个元素
1. 实现1
/** * 返回链表倒数第k个节点(实现1) * 1. 返回链表总长度,计算倒数第k个节点的索引 * 2. 遍历并返回倒数第k个节点 * @param index * @return */ public T findLastNode1(int index) { Node returnNode = first; int k = size()-index;//k为要返回节点的索引 if(k < 0) { throw new NullPointerException("链表长度越界 "); } for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) { returnNode = returnNode.next; } return returnNode.data; }
2. 实现2
/** * 返回链表倒数第k个元素(实现2) * 倒数第k个元素和最后一个元素相差k-1,所以可以选择两个指针 * 1. 将第一个指针从头结点移动k-1次,使头结点和这个节点相差k-1 * 2. 同时移动两个节点,当该节点是最后一个节点时,头结点为倒数第k个节点 * @param index * @return */ public T findLastNode2(int index) { Node firstNode = first; Node lastNode = first; //lastNode向后移动k-1次 for(int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) { if(lastNode == null) { throw new NullPointerException("链表长度越界"); } lastNode = lastNode.next; } //同时移动,指针lastNode为最后一个节点 while(lastNode.next != null) { firstNode = firstNode.next; lastNode = lastNode.next; } return firstNode.data; }
- 合并两个有序链表
/** * 合并两个有序链表 * @param head2 要合并的链表的头结点 * @return 合并后的有序链表的头结点 */ public Node merge(Node head2) { Node head1 = this.first;//当前链表的头结点 if(head1 == null && head1 == null) return null; if(head1 == null) return head2; if(head2 == null) return head1; Node head = null;//新生成链表的头结点 Node current = null;//新生成链表的当前节点 while(head1 != null || head2 != null) {//至少一个链表没有循环完 //1.为新生成的链表添加第一个节点 if(head == null) { if(head1.data.compareTo(head2.data) < 0) { head = head1; current = head; head1 = head1.next; }else { head = head2; current = head; head2 = head2.next; } } //2.为生成的节点添加后续节点 //如果head1为空,直接将当前节点指向head2,返回head即可 if(head1 == null) { current.next = head2; return head; } //如果head2为空,直接将当前节点指向head1,返回即可 if(head2 == null) { current.next = head1; return head; } //如果两个节点都不为空,进行比较,比较后继续循环 if(head1.data.compareTo(head2.data) < 0) { current.next = head1; current = head1; head1 = head1.next; }else { current.next = head2; current = head2; head2 = head2.next; } } return head; }
- 判断链表是否有环
/** * 判断单链表是否有环 * 使用两个指针,first指针每次移动一步,second指针每次移动2步 * @return */ public boolean hasCycle() { Node first = this.first; Node second = this.first; while(second != null) { first = first.next;//每次移动一次 second = second.next.next;//每次移动两次 if(first == second) { return true; } } return false; }