Spring Boot 默认集成了Spring MVC,下面为Spring MVC一些常用注解。
开发环境:IntelliJ IDEA 2019.2.2
Spring Boot版本:2.1.8
新建一个名称为demo的Spring Boot项目。
一、Controller注解
Controller注解用于修饰Java类,被修饰的类充当MVC中的控制器角色。
Controller注解使用了@Component修饰,使用Controller注解修饰的类,会被@ComponentScan检测,并且会作为Spring的bean被放到容器
中。
package com.example.demo; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; @Controller public class DemoController { @RequestMapping("/index") @ResponseBody public String index(){ return "index"; } }
运行项目后,浏览器访问:http://localhost:8080/index,页面显示:
index
二、RestController注解
RestController注解是为了更方便使用@Controller和@ResponseBody。
@ResponseBody修饰控制器方法,方法的返回值将会被写到HTTP的响应体中,所返回的内容不放到模型中,也不会被解释为视图的名称。
下面例子等同于上面例子。
package com.example.demo; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class DemoController { @RequestMapping("/index") public String index(){ return "index"; } }
三、RequestMapping注解
RequestMapping注解可修饰类或方法,主要用于映射请求与处理方法。
当用于修饰类并设置了URL时,表示为各个请求设置了URL前缀。
RequestMapping注解主要有以下属性:
(1)path与value:用于配置映射的url;
(2)method:映射的HTTP方法,如GET、POST、PUT、DELETE;
也可以使用默认配置了@RequestMapping的method属性的几个注解:
@GetMapping等同于RequestMapping(method="RequestMethod.GET")
@PostMapping、@PutMapping、@DeleteMapping类似。
(3)params:为映射的请求配置参数标识;
(4)consumes:配置请求的数据类型,如XML或JSON等;
(5)produces:配置响应的数据类型,如“application/json”返回json数据;
package com.example.demo; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @RequestMapping("/oa") public class DemoController { @RequestMapping(value = "/index1") public String index1(){ return "index1"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/index2", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String index2(){ return "index2"; } @GetMapping(value = "/index3") public String index3(){ return "index3"; } }
浏览器分别访问:
http://localhost:8080/oa/index1
http://localhost:8080/oa/index2
http://localhost:8080/oa/index3
页面分别显示:
index1
index2
index3
四、PathVariable注解
PathVariable注解主要用于修饰方法参数,表示该方法参数是请求URL的变量。
package com.example.demo; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class DemoController { @GetMapping("/index1/{name}") public String index1(@PathVariable String name){ return "index1: " + name; } //可以为@PathVariable配置属性值,显式绑定方法参数与URL变量的值 @GetMapping("/index2/{name}") public String index2(@PathVariable("name") String lc){ return "index2: " + lc; } }
浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/index1/a
页面显示:
a
访问http://localhost:8080/index1/b
页面显示:
b
五、RequestParam注解
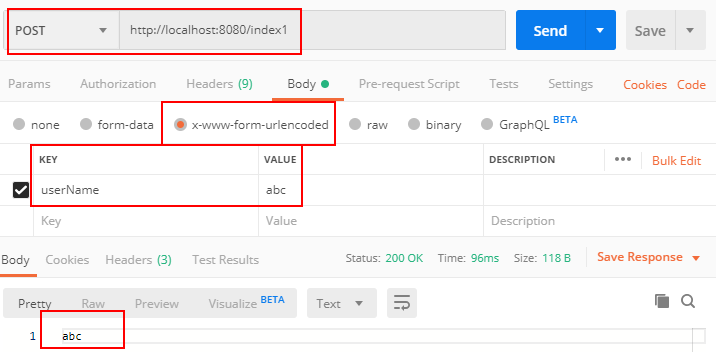
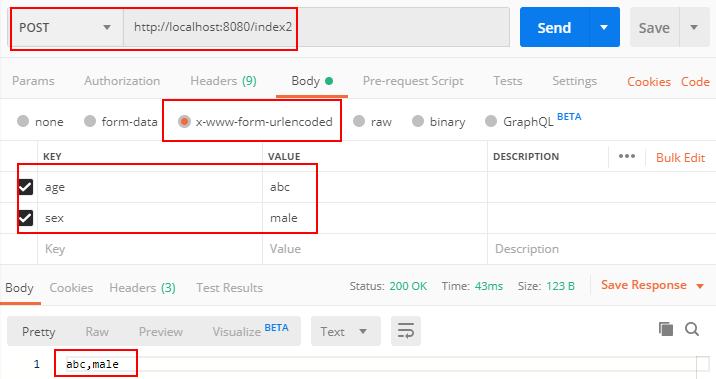
RequestParam注解用于获取请求体中的请求参数,如表单提交后获取页面控件name值。
package com.example.demo; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import java.util.Map; @RestController public class DemoController { @PostMapping("/index1") public String index1(@RequestParam String userName){ return userName; } //map存放所有请求参数 @PostMapping("/index2") public String index2(@RequestParam Map<String,String> map){ String age = map.get("age"); String sex = map.get("sex"); return age + "," + sex; } }
随便在电脑中如桌面新建一个html文件:
<html> <body> <form method="post" action="http://localhost:8080/index1"> <input type="text" name="userName" value="abc" /> <input type="submit" value="提交1" /> </form> <form method="post" action="http://localhost:8080/index2"> <input type="text" name="age" value="22" /> <input type="password" name="sex" value="male" /> <input type="submit" value="提交2" /> </form> </body> </html>
浏览器打开后,如果点击“提交1”按钮后,页面跳到http://localhost:8080/index1,显示abc。
如果点击“提交2”按钮后,页面跳到http://localhost:8080/index2,显示22,male。
用Postman测试:
六、RequestBody注解
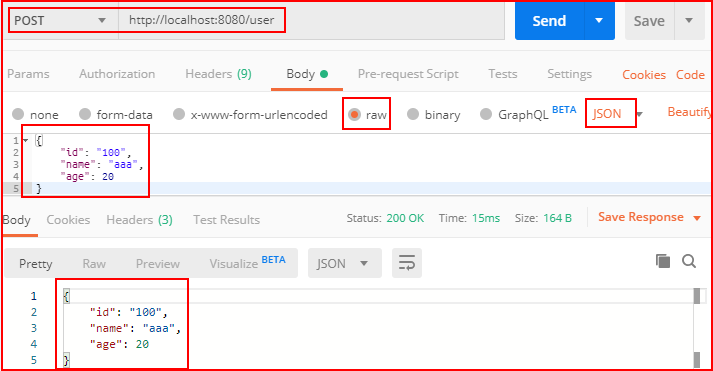
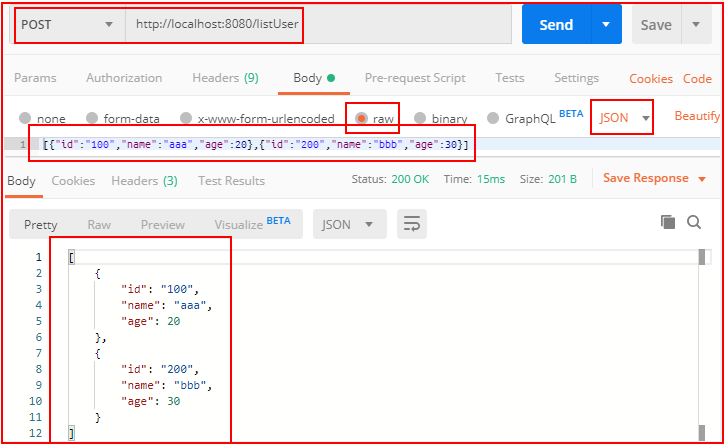
注解@RequestBody接收的参数是来自requestBody中,即请求体。
一般用于处理application/json、application/xml等类型的数据。
GET方式无请求体,所以使用@RequestBody接收数据时,前端只能用POST方式进行提交。
package com.example.demo; import com.example.demo.entity.User; import com.example.demo.service.UserService; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; import javax.annotation.Resource; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; @RestController public class DemoController { @Resource UserService userService; //前端json数据传递到实体中 @PostMapping("/user") @ResponseBody public User user(@RequestBody User user){ return user; } //前端json数据传递到实体集合中 @PostMapping("/listUser") @ResponseBody public List<User> listUser(@RequestBody List<User> list){ return list; } //前端json数据传递到非实体中 @PostMapping("/map") @ResponseBody public String map(@RequestBody Map<String,Object> map){ return map.get("id").toString() + "," + map.get("name").toString() + "," + map.get("age").toString(); } }
用Postman测试:
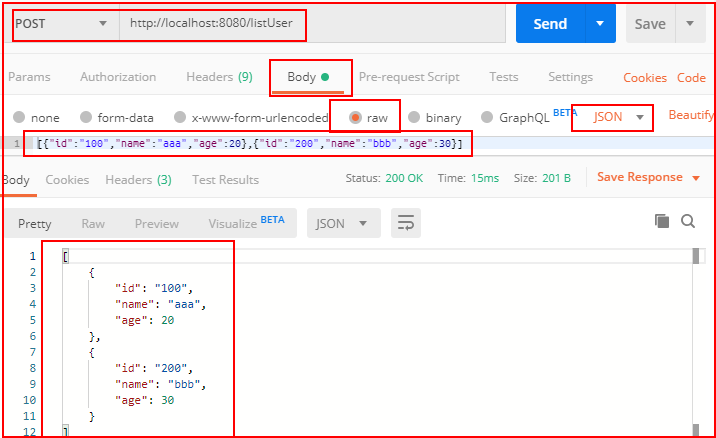
七、文件上传
使用RequestParam注解可以实现文件上传。
package com.example.demo; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; @RestController public class DemoController { @PostMapping("/upload") public String upload(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) throws IOException { String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename(); String filePath = "D:/"; File dest = new File(filePath + fileName); file.transferTo(dest); return "上传成功"; } }
随便新建一个html文件
<html> <body> <form method="post" action="http://localhost:8080/upload" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="file" name="file" /> <input type="submit" value="提交" /> </form> </body> </html>
浏览器打开后,选择一个文件,点击提交后,文件保存到了D盘。