一、什么是plist文件
1>将数据直接写在代码里面,不是一种合理的做法。如果数据经常修改,就要经常翻开对应的代码进行修改,造成代码扩展性低
2>因此,可以考虑将经常变得数据放在文件中进行存储,程序启动后从文件中读取最新的数据。如果要变动数据,直接修改数据文件即可,不用修改代码
3>一般可以使用属性列表文件存储NSArray或者NSDictionary之类的数据,这种“属性列表文件”的扩展名是plist,因此也成为“plist文件”
二、创建plist文件
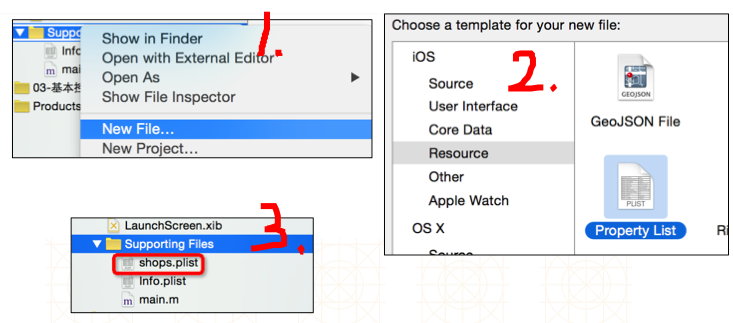
三、解析plist文件
代码实例:
1 // 一个NSBundle对象对应一个资源包(图片、音频、视频、plis等文件) 2 // NSBundle的作用:用来访问与之对应的资源包内部的文件,可以用来获得文件的全路径 3 // 项目中添加的资源都会被添加到主资源包中 4 // [NSBundle mainBundle]关联的就是项目的主资源包 5 NSBundle *bundle = [NSBundle mainBundle]; 6 NSString *file = [bundle pathForResource:@"things" ofType:@"plist"]; 7 self.things = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:file];
四、plist文件的使用注意
1>plist的文件名不能叫做"info"、"Info"之类的
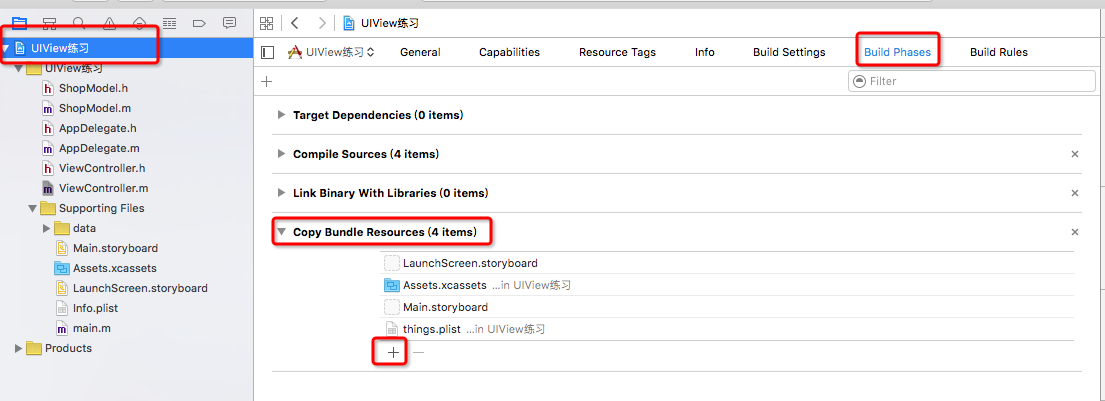
2>添加plist等文件资源的时候,一定要勾选下面的选项

如果遇到忘了勾选的情况,可以用一下方式解决
五、懒加载
1>为什么用到懒加载
加载plist等文件数据,加载数据用懒加载,如果一上来就将所有数据都加载,第一影像程序性能,第二,加载的数据本次操作不一定能用上,浪费内存--懒加载的本质就是重写getter方法,也就是使用数据的时候才进行加载!
2>代码实例--之前是在viewDidLoad方法中获取的数据,不管用不用到都要加载。以下方法是在用到时再加载
1 @property (strong, nonatomic) NSArray *things; // 重写get方法,实现懒加载
1 // 重写things的get方法,实现懒加载 2 - (NSArray *)things 3 { 4 if (_things == NULL) { 5 // 加载主资源包 6 NSBundle *bundle = [NSBundle mainBundle]; 7 // 通过主资源包获取things.plist的全路径 8 NSString *file = [bundle pathForResource:@"things" ofType:@"plist"]; 9 // 通过全路径获取数据 10 _things = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:file]; 11 } 12 return _things; 13 }
六、模型--模型取代字典
1>模型的本质就是直接继承NSObject的类文件
2>字典转模型的过程最好封装在模型内部,模型中的属性对应字典的哪个key值,模型说的算,外部不要干涉,外部只管调用模型的构造方法获取模型
3>模型应该提供一个可以传入字典参数的构造方法,一个类方法,一个对象方法
1 // ShopModel.h 2 // UIView练习 3 // 4 // Created by admin on 16/3/5. 5 // Copyright © 2016年 admin. All rights reserved. 6 // 商品模型 7 8 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> 9 10 @interface ShopModel : NSObject 11 /** 商品名称 */ 12 @property(nonatomic,strong) NSString *name; 13 /** 商品图片 */ 14 @property(nonatomic,strong) NSString *icon; 15 16 - (instancetype)initWithDic:(NSDictionary *)dic; 17 + (instancetype)shopModelWithDic:(NSDictionary *)dic; 18 @end
模型的实现部分:
1 // ShopModel.m 2 // UIView练习 3 // 4 // Created by admin on 16/3/5. 5 // Copyright © 2016年 admin. All rights reserved. 6 // 7 8 #import "ShopModel.h" 9 10 @implementation ShopModel 11 12 - (instancetype)initWithDic:(NSDictionary *)dic 13 { 14 if (self = [super init]) 15 { 16 self.name = dic[@"name"]; 17 self.icon = dic[@"icon"]; 18 } 19 return self; 20 } 21 22 +(instancetype)shopModelWithDic:(NSDictionary *)dic 23 { 24 return [[self alloc] initWithDic:dic]; 25 } 26 @end
5>懒加载+模型
之前的懒加载代码,得到的数据是字典的集合,下面的代码是在懒加载的过程中实现了字典转换模型
1 // 重写things的get方法,实现懒加载 2 - (NSArray *)things 3 { 4 if (_things == NULL) { 5 // 加载主资源包 6 NSBundle *bundle = [NSBundle mainBundle]; 7 // 通过主资源包获取things.plist的全路径 8 NSString *file = [bundle pathForResource:@"things" ofType:@"plist"]; 9 // 通过全路径获取数据 10 _things = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:file]; 11 12 // 思路:数据的get方法,直接返回模型的集合,遍历字典数组,将字典的数据在懒加载过程中都转化成模型数据 13 NSMutableArray *arrTemp = [NSMutableArray array]; // 定义可变数组 14 for (NSDictionary *dic in _things) { 15 [arrTemp addObject:[ShopModel shopModelWithDic:dic]]; 16 } 17 _things = arrTemp; // 将装有的模型集合赋值给成员变量 18 } 19 return _things; 20 }
七、补充instancetype
1>instancetype在类型表示上,跟id一样,可以表示任何对象类型
2>instancetype只能用在返回值类型上,不能像id一样用在参数类型上
3>instancetype比id多一个好处:编译器会检测instancetype的真实类型