负载均衡
Dubbo支持的负载均衡有如下策略:默认是随机
- 权重随机(random),实现类RandomLoadBalance
- 权重轮询(roundrobin),实现类RoundRobinLoadBalance
- 最少活跃(leastactive)负载策略,实现类LeastActiveLoadBalance
- 一致性hash(consistenthash) 实现类ConsistentHashLoadBalance
在AbstractClusterInvoker#invoke => AbstractClusterInvoker#initLoadBalance
protected LoadBalance initLoadBalance(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, Invocation invocation) { if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(invokers)) { //从url通过key "loadbalance" 取不到值,就取默认random随机策略 return ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(invokers.get(0).getUrl() .getMethodParameter(RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation), Constants.LOADBALANCE_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE)); } else { return ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE); } }
FailoverClusterInvoker.doInvoke =>
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyInvokers, invoked); =>
Invoker<T> invoker = doSelect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected) =>
Invoker<T> invoker = loadbalance.select(invokers, getUrl(), invocation);
到这边就进入了具体的负载策略逻辑了,下面以最小活跃数来介绍
@Override protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) { // Number of invokers 总个数 int length = invokers.size(); // The least active value of all invokers int leastActive = -1; // 当前最小活跃数值 // The number of invokers having the same least active value (leastActive) int leastCount = 0; // 相同最小活跃数的个数 // The index of invokers having the same least active value (leastActive) int[] leastIndexes = new int[length]; // 相同最小活跃数的下标 // the weight of every invokers int[] weights = new int[length]; // The sum of the warmup weights of all the least active invokes int totalWeight = 0; // 总权重 // The weight of the first least active invoke int firstWeight = 0; // 第一个权重,用于于计算是否相同 // Every least active invoker has the same weight value? boolean sameWeight = true; // 是否所有权重相同 // Filter out all the least active invokers for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { Invoker<T> invoker = invokers.get(i); // Get the active number of the invoke int active = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName()).getActive(); // Get the weight of the invoke configuration. The default value is 100. int afterWarmup = getWeight(invoker, invocation); // save for later use weights[i] = afterWarmup; // If it is the first invoker or the active number of the invoker is less than the current least active number if (leastActive == -1 || active < leastActive) { // 每次循环到的invoker 得到的最小连接数 小于超过之前invoke的最小连接数 // Reset the active number of the current invoker to the least active number leastActive = active; //把最小的连接数赋值给leastActive // Reset the number of least active invokers leastCount = 1; // 当前相同的最小连接数reset为1个 // Put the first least active invoker first in leastIndexs leastIndexes[0] = i; // Reset totalWeight totalWeight = afterWarmup; // Record the weight the first least active invoker firstWeight = afterWarmup; // Each invoke has the same weight (only one invoker here) sameWeight = true; // If current invoker's active value equals with leaseActive, then accumulating. } else if (active == leastActive) { // 发现当前的invoke最小连接数 与 目前最小连接数相同 // Record the index of the least active invoker in leastIndexs order leastIndexes[leastCount++] = i; // 最小连接数就+1 并保存这个invoker的下标到leastIndexes // Accumulate the total weight of the least active invoker totalWeight += afterWarmup; // If every invoker has the same weight? if (sameWeight && i > 0 && afterWarmup != firstWeight) { sameWeight = false; } } } // Choose an invoker from all the least active invokers if (leastCount == 1) { // 相同最小连接数只有一个的话 直接返回该下标的invoker // If we got exactly one invoker having the least active value, return this invoker directly. return invokers.get(leastIndexes[0]); } if (!sameWeight && totalWeight > 0) { // If (not every invoker has the same weight & at least one invoker's weight>0), select randomly based on // totalWeight. int offsetWeight = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight); // Return a invoker based on the random value. for (int i = 0; i < leastCount; i++) { int leastIndex = leastIndexes[i]; offsetWeight -= weights[leastIndex]; if (offsetWeight < 0) { return invokers.get(leastIndex); } } } // If all invokers have the same weight value or totalWeight=0, return evenly. // 如果权重相同或权重为0则均等随机 return invokers.get(leastIndexes[ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(leastCount)]); }
其他的负载均衡策略相对简单,不过多介绍,读者可以网上查阅相关资料。另外关于加权轮询算法可以参看这篇文章:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1109584
集群容错
这是来自官网上的关于集群容错的示意图
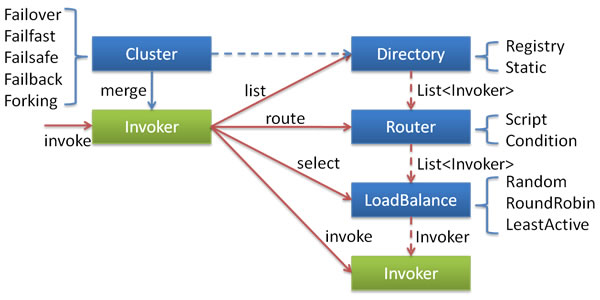
下面对这几种集群容错模式的简单介绍,默认使用
Failfast Cluster
快速失败,只发起一次调用,失败立即报错。通常用于非幂等性的写操作,比如新增记录。
Failsafe Cluster
失败安全,出现异常时,直接忽略。通常用于写入审计日志等操作。
Failback Cluster
失败自动恢复,后台记录失败请求,定时重发。通常用于消息通知操作。
Forking Cluster
并行调用多个服务器,只要一个成功即返回。通常用于实时性要求较高的读操作,但需要浪费更多服务资源。可通过 forks="2" 来设置最大并行数。
Broadcast Cluster
广播调用所有提供者,逐个调用,任意一台报错则报错。通常用于通知所有提供者更新缓存或日志等本地资源信息。
FailoverClusterInvoker(FailoverCluster,dubbo默认策略)
失败后自动选择其他服务提供者进行重试,重试次数由retries属性设置,< dubbo:reference retries = “2”/>设置,默认为2,代表重试2次,最多执行3次。
AvailableClusterInvoker
策略:选择集群第一个可用的服务提供者。
缺点:相当于服务的主备,但同时只有一个服务提供者承载流量,并没有使用集群的负载均衡机制。
这边以一个简单的AvailableClusterInvoker作为一个简单的例子来介绍一下,
AbstractClusterInvoker#invoke -> AvailableClusterInvoker#doInvoke
很简单 就是只要发现有一个invoker可以使用 就选择该invoker
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException { for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) { if (invoker.isAvailable()) { return invoker.invoke(invocation); } } throw new RpcException("No provider available in " + invokers); }