目录
一、实验内容:跟踪分析Linux内核的启动过程
实验楼进行实验
1.启动linux内核
$ cd ~/LinuxKernel/
$ qemu -kernel linux-3.18.6/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.img -s -S
# 关于-s和-S选项的说明:
# 1. -S
# -S freeze CPU at startup (use ’c’ to start execution)
# 2. -s
# -s shorthand for -gdb tcp::1234
# 若不想使用1234端口,则可以使用-gdb tcp:xxxx来取代-s选项
2.另开一个shell窗口调试
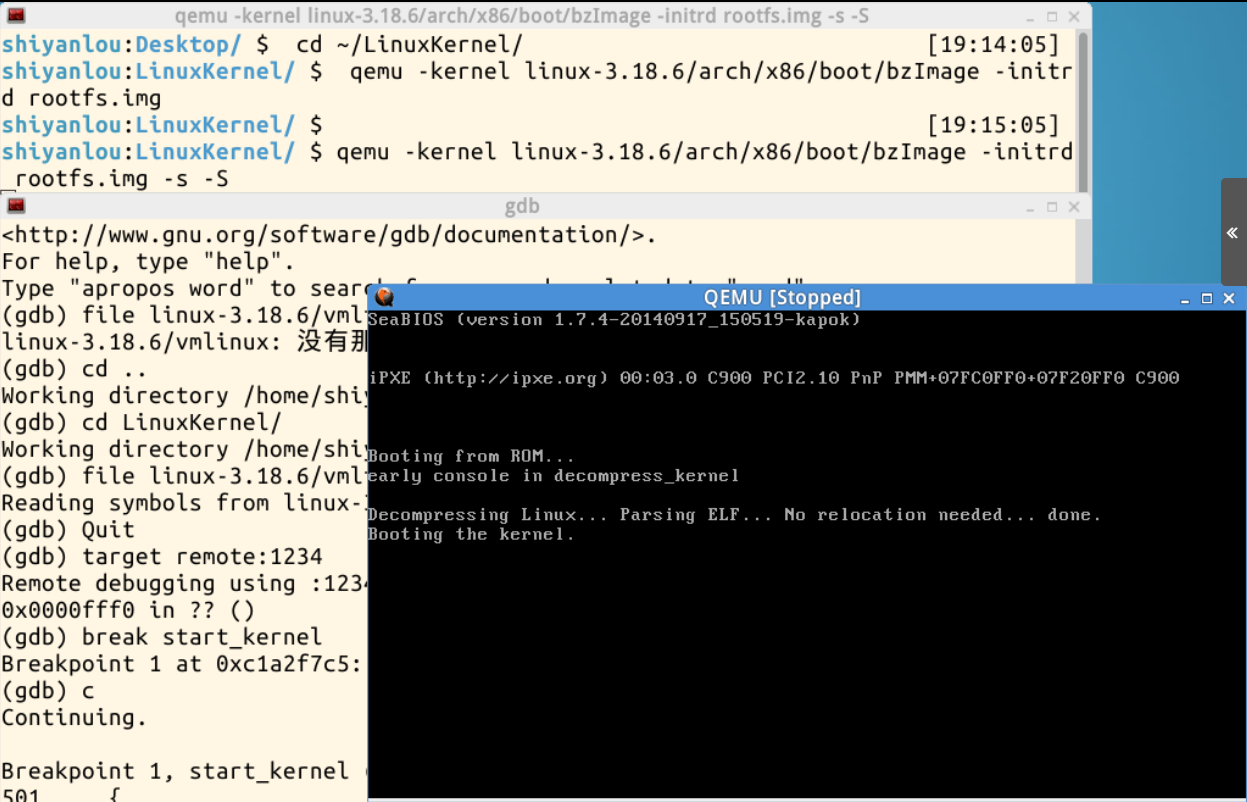
# 打开 GDB 调试器
$ gdb
# 在 GDB 中输入以下命令:
# 在gdb界面中targe remote之前加载符号表
(gdb)file linux-3.18.6/vmlinux
# 建立gdb和gdbserver之间的连接,按c 让qemu上的Linux继续运行
(gdb)target remote:1234
# 断点的设置可以在target remote之前,也可以在之后
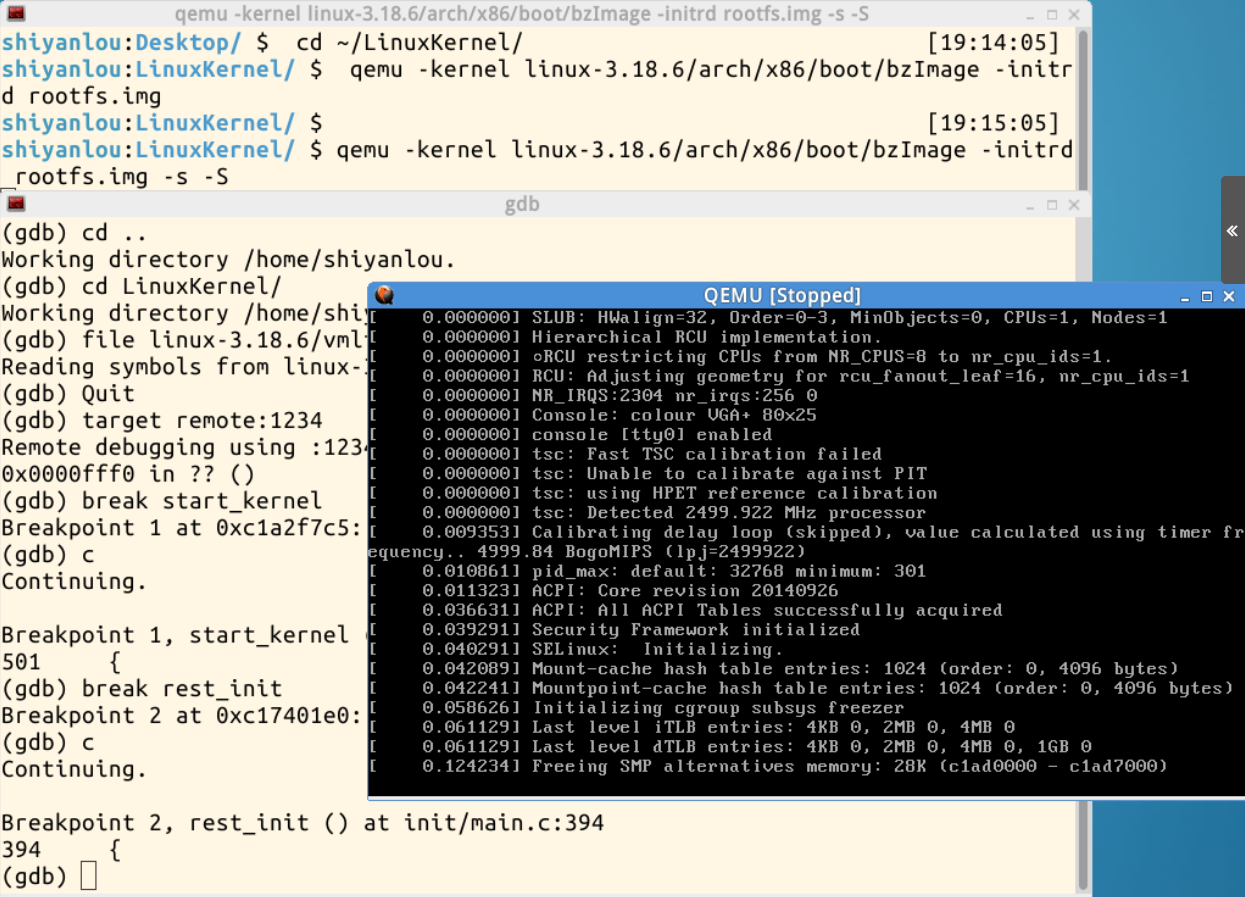
(gdb)break start_kernel
3.函数分析
①.start_kernel函数代码
asmlinkage __visible void __init start_kernel(void)
{
char *command_line;
char *after_dashes;
/*
* Need to run as early as possible, to initialize the
* lockdep hash:
*/
lockdep_init();
set_task_stack_end_magic(&init_task);
smp_setup_processor_id();
debug_objects_early_init();
/*
* Set up the the initial canary ASAP:
*/
boot_init_stack_canary();
cgroup_init_early();
local_irq_disable();
early_boot_irqs_disabled = true;
/*
* Interrupts are still disabled. Do necessary setups, then
* enable them
*/
boot_cpu_init();
page_address_init();
pr_notice("%s", linux_banner);
setup_arch(&command_line);
mm_init_cpumask(&init_mm);
setup_command_line(command_line);
setup_nr_cpu_ids();
setup_per_cpu_areas();
smp_prepare_boot_cpu(); /* arch-specific boot-cpu hooks */
build_all_zonelists(NULL, NULL);
page_alloc_init();
pr_notice("Kernel command line: %s
", boot_command_line);
parse_early_param();
after_dashes = parse_args("Booting kernel",
static_command_line, __start___param,
__stop___param - __start___param,
-1, -1, &unknown_bootoption);
if (!IS_ERR_OR_NULL(after_dashes))
parse_args("Setting init args", after_dashes, NULL, 0, -1, -1,
set_init_arg);
jump_label_init();
/*
* These use large bootmem allocations and must precede
* kmem_cache_init()
*/
setup_log_buf(0);
pidhash_init();
vfs_caches_init_early();
sort_main_extable();
trap_init();
mm_init();
/*
* Set up the scheduler prior starting any interrupts (such as the
* timer interrupt). Full topology setup happens at smp_init()
* time - but meanwhile we still have a functioning scheduler.
*/
sched_init();
/*
* Disable preemption - early bootup scheduling is extremely
* fragile until we cpu_idle() for the first time.
*/
preempt_disable();
if (WARN(!irqs_disabled(),
"Interrupts were enabled *very* early, fixing it
"))
local_irq_disable();
idr_init_cache();
rcu_init();
context_tracking_init();
radix_tree_init();
/* init some links before init_ISA_irqs() */
early_irq_init();
init_IRQ();
tick_init();
rcu_init_nohz();
init_timers();
hrtimers_init();
softirq_init();
timekeeping_init();
time_init();
sched_clock_postinit();
perf_event_init();
profile_init();
call_function_init();
WARN(!irqs_disabled(), "Interrupts were enabled early
");
early_boot_irqs_disabled = false;
local_irq_enable();
kmem_cache_init_late();
/*
* HACK ALERT! This is early. We're enabling the console before
* we've done PCI setups etc, and console_init() must be aware of
* this. But we do want output early, in case something goes wrong.
*/
console_init();
if (panic_later)
panic("Too many boot %s vars at `%s'", panic_later,
panic_param);
lockdep_info();
/*
* Need to run this when irqs are enabled, because it wants
* to self-test [hard/soft]-irqs on/off lock inversion bugs
* too:
*/
locking_selftest();
#ifdef CONFIG_BLK_DEV_INITRD
if (initrd_start && !initrd_below_start_ok &&
page_to_pfn(virt_to_page((void *)initrd_start)) < min_low_pfn) {
pr_crit("initrd overwritten (0x%08lx < 0x%08lx) - disabling it.
",
page_to_pfn(virt_to_page((void *)initrd_start)),
min_low_pfn);
initrd_start = 0;
}
#endif
page_cgroup_init();
debug_objects_mem_init();
kmemleak_init();
setup_per_cpu_pageset();
numa_policy_init();
if (late_time_init)
late_time_init();
sched_clock_init();
calibrate_delay();
pidmap_init();
anon_vma_init();
acpi_early_init();
#ifdef CONFIG_X86
if (efi_enabled(EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES))
efi_enter_virtual_mode();
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_X86_ESPFIX64
/* Should be run before the first non-init thread is created */
init_espfix_bsp();
#endif
thread_info_cache_init();
cred_init();
fork_init(totalram_pages);
proc_caches_init();
buffer_init();
key_init();
security_init();
dbg_late_init();
vfs_caches_init(totalram_pages);
signals_init();
/* rootfs populating might need page-writeback */
page_writeback_init();
proc_root_init();
cgroup_init();
cpuset_init();
taskstats_init_early();
delayacct_init();
check_bugs();
sfi_init_late();
if (efi_enabled(EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES)) {
efi_late_init();
efi_free_boot_services();
}
ftrace_init();
/* Do the rest non-__init'ed, we're now alive */
rest_init();
}
②.代码分析
init_task相当于第一个进程的PCB,在start_kernel函数中进行初始化;
trap_init初始化中断向量;
mm_init内存管理模块的初始化;
sched_init调度模块的初始化;
rest_init是0号进程,它创建了1号进程init和其他一些服务进程。
参照课本使用自己的Linux系统搭建MenuOS的过程
1.下载内核源码(Linux-3.18.6),解压并编译
mkdir LinuxKernel
cd LinuxKernel
wget https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v3.x/linux-3.18.6.tar.xz
ll
xz -d linux-3.18.6.tar.xz
tar -xvf linux-3.18.6.tar
cd linux-3.18.6
make i386_defconfig
make
wget https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v3.x/linux-3.18.6.tar.xz 遇到问题

域名解析失败,参照博客,DNS的设置没有问题,是主机名解析失败,在hosts里配置一下即可解决:
vim /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 8.8.8.8 #google域名服务器
nameserver 8.8.4.4 #google域名服务器
make时遇到compile-gcc的版本问题
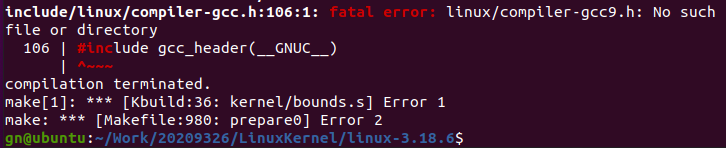
参照同学的解决方法将compiler-gcc5.h重命名为compiler-gcc9.h,编译通过
2.制作根文件系统
mkdir rootfs
git clone https://github.com/mengning/menu.git
cd menu
gcc -pthread -o init linktable.c menu.c test.c -m32 -static
cd ../rootfs
cp ../menu/init ./
find . | cpio -o -Hnewc |gzip -9 > ../rootfs.img
gcc -pthread -o init linktable.c menu.c test.c -m32 -static 时遇到问题:
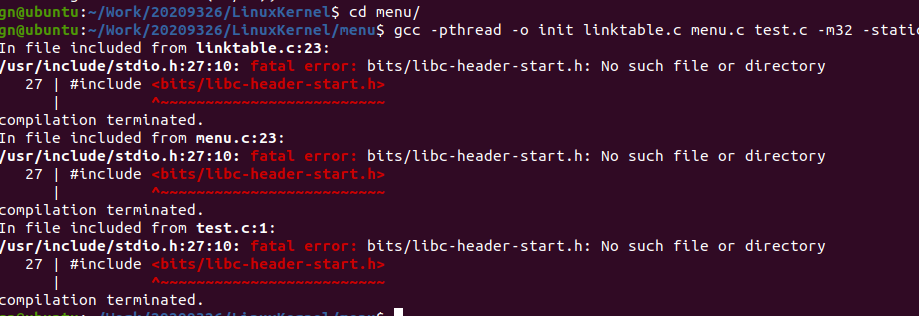
参照博客,环境没有完善
sudo apt-get install gcc-multilib
3.对内核进行跟踪调试
sudo apt-get install libncurses5-dev
make menuconfig
make
4.跟踪调试Linux内核的启动过程
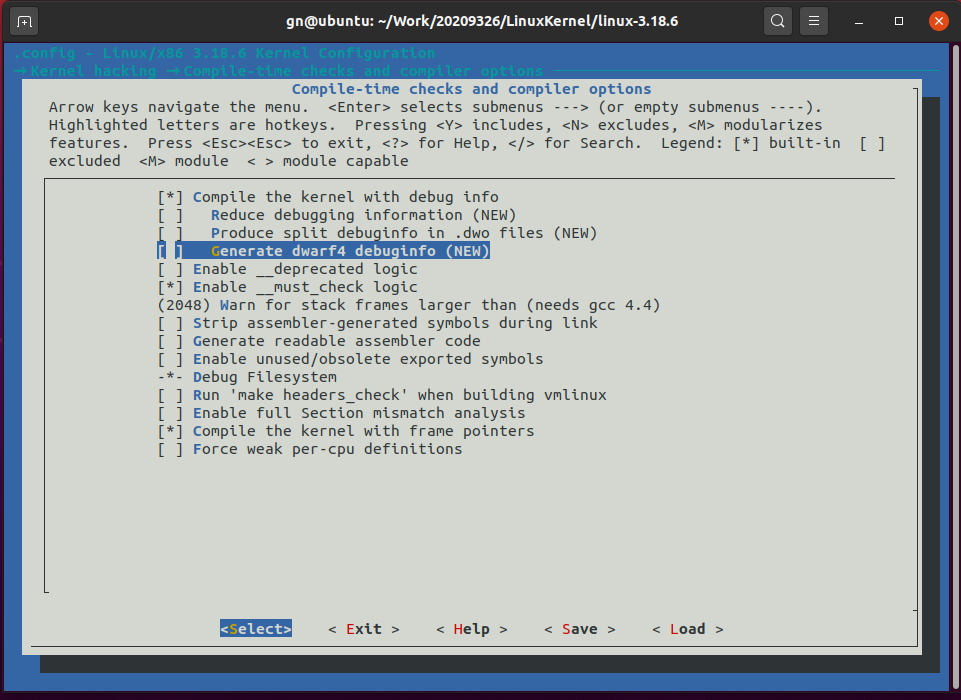
下载安装qemu虚拟机
sudo apt-get install qemu
出现错误,参考马铸鸿、李志成同学的博客,安装qemu-system-i386,使用qemu-system-i386指令替换qemu指令,或者建立一条软链接使用qemu
sudo apt-get install qemu-system-i386
sudo ln -s /usr/bin/qemu-system-i386 /usr/bin/qemu
启动内核
qemu -kernel linux-3.18.6/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.img -S -s//-S:CPU初始化之前冻结起来;-s:在1234端口上创建了一个gdb-server
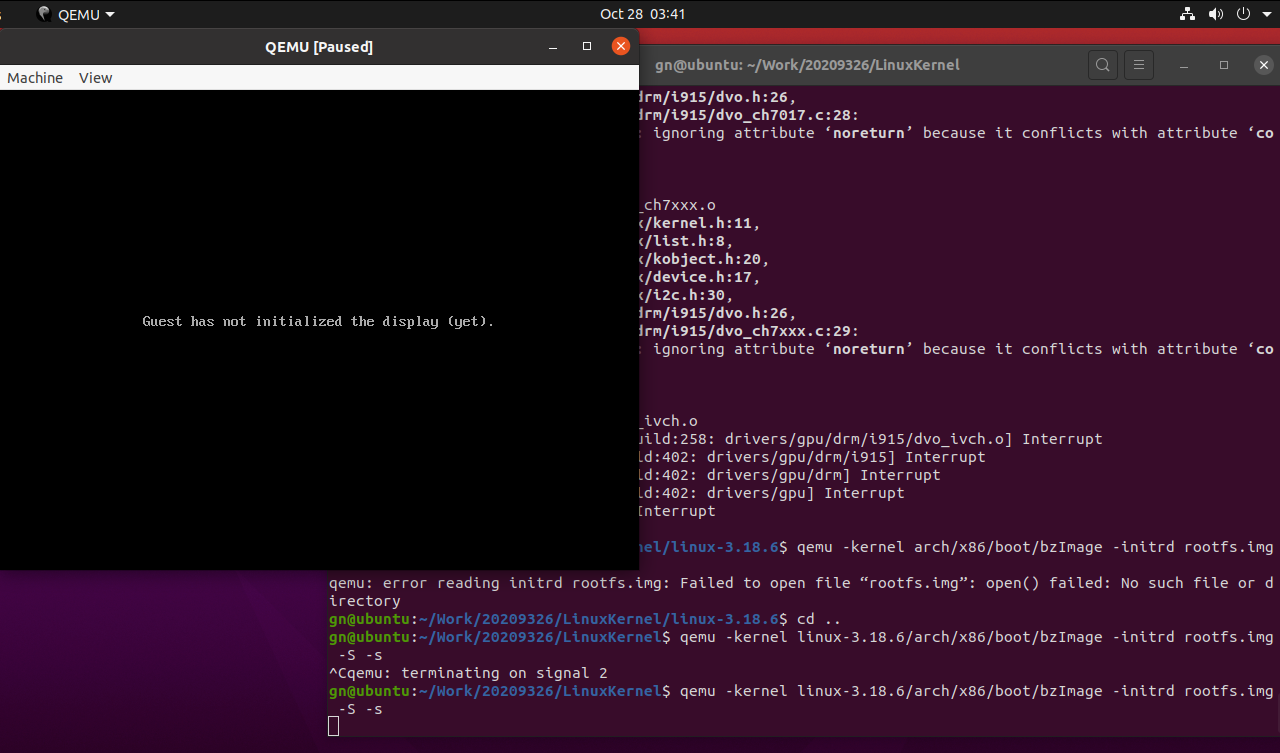
再打开一个窗口,启动gdb,把内核加载进来,建立连接。
file linux-3.18.6/vmlinux
target remote:1234 //用1234这个端口进行连接
在start_kernel处设置断点break start_kernel
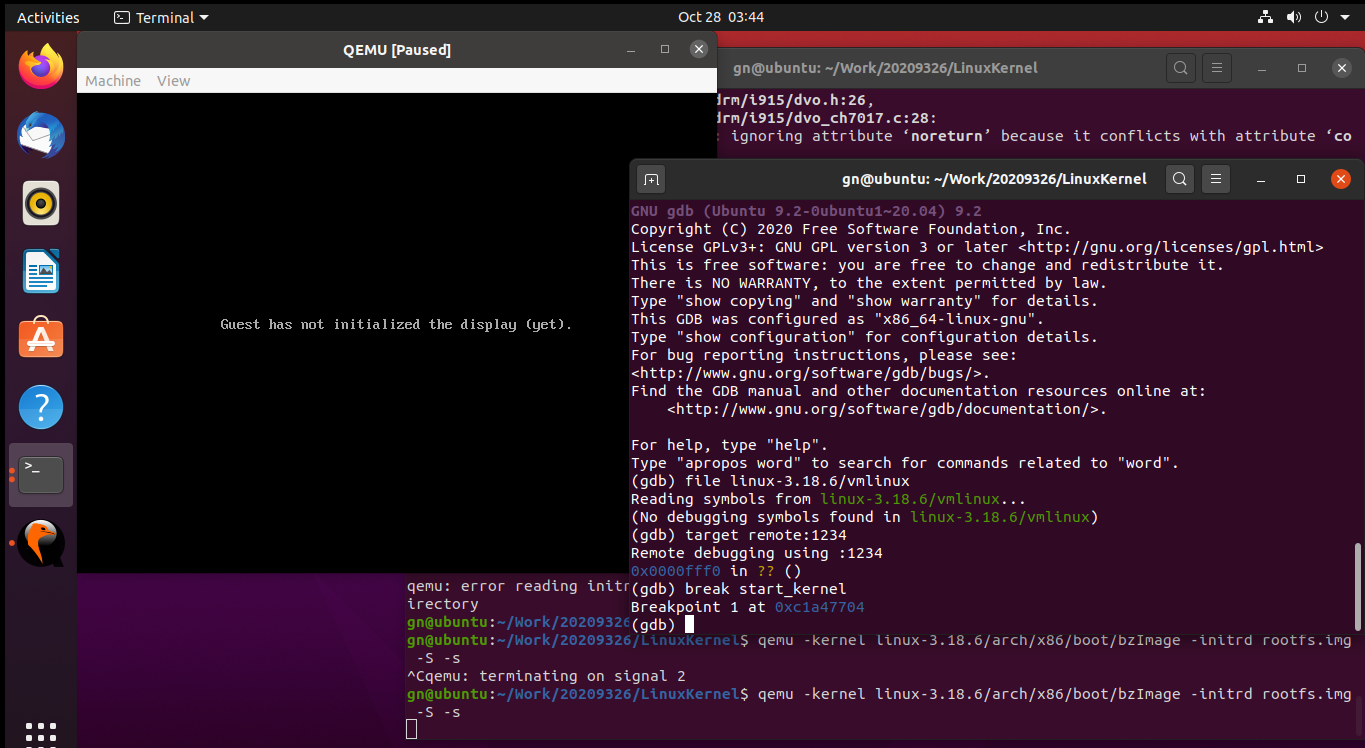
c继续执行
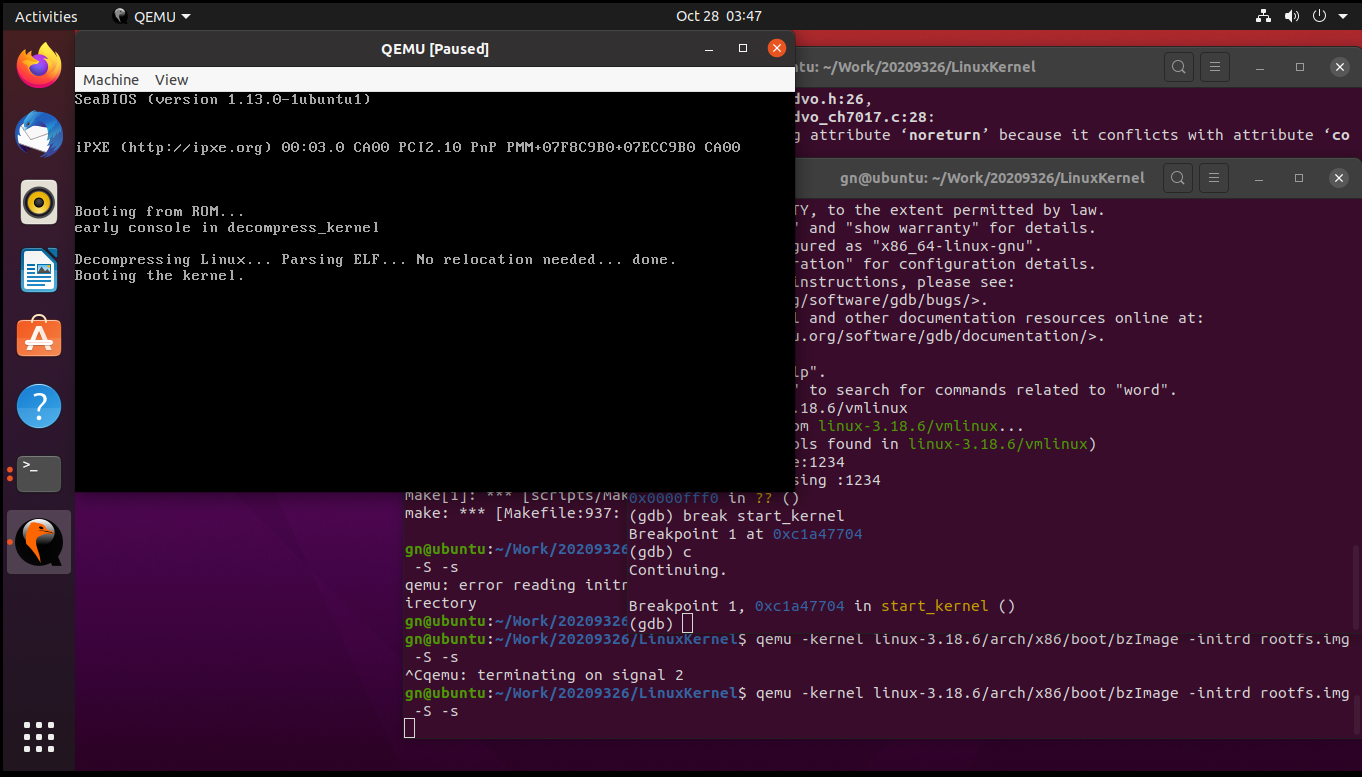
在rest_init处设置断点,后执行
break rest_init
c

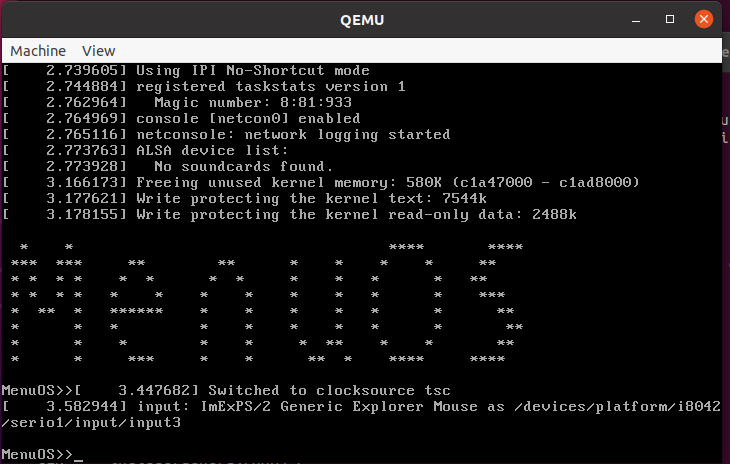
二总结
1.操作系统的两把宝剑:中断上下文的切换——保存现场和恢复现场;进程上下文的切换。
2.linux目录结构:
arch:与体系结构相关的子目录列表,存放CPU体系结构的相关代码;
block:存放Linux存储系统中关于块设备管理的代码;
crypto:存放常见的加密算法的C语言代码;
Documentation:存放文档;
drivers:驱动目录,分门别类的存放Linux内核支持的所有硬件设备的驱动源代码;
firmware:固件;
fs:文件系统,列出Linux支持的各种文件系统的实现;
init:存放Linux内核启动时的初始化代码;
ipc:进程间通信;
kernel:内核,存放内核本身需要的核心代码;
lib:公用的库文件;
mm:内存管理;
net:网络相关的代码;
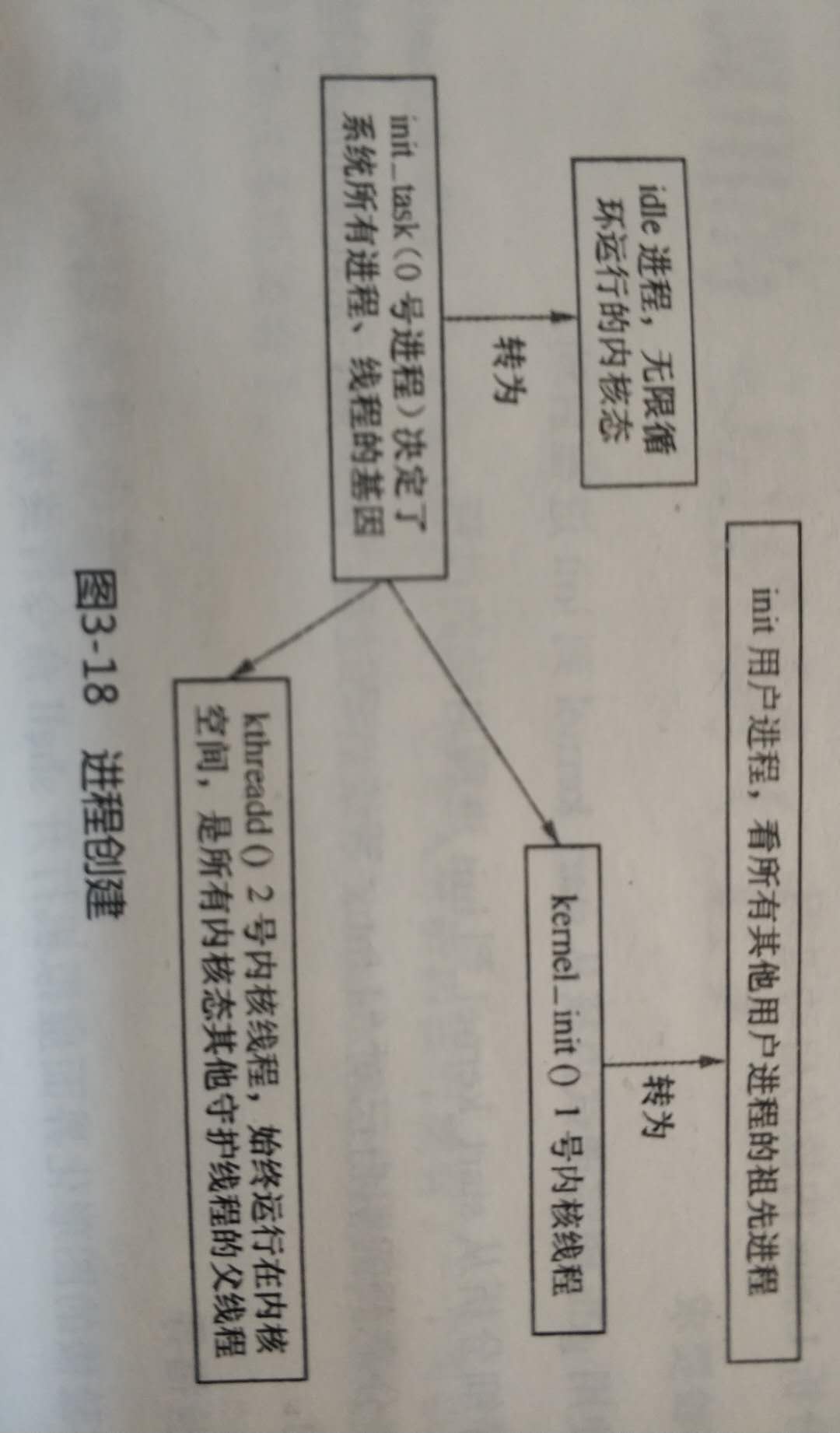
3.Linux系统0号进程,1号进程,2号进程的产生及作用:
0号进程:init_task()在创建init进程后,调用cpu_idle()演变成了idle进程,执行1次调度后,init进程运行。init进程是唯一一个没有通过fork()产生的进程。
1号进程:1号内核进程kernel_init(),由0号进程创建,负责执行内核的部分初始化工作及进行系统配置,最后调用do_execve加载init程序,演变为init进程(用户态1号进程),该进程是其他所有用户进程的祖先进程。
2号进程:kthreadd进程由0号进程创建,始终运行在内核空间,负责所有内核线程的调度和管理。