Fox Ciel starts to learn programming. The first task is drawing a fox! However, that turns out to be too hard for a beginner, so she decides to draw a snake instead.
A snake is a pattern on a n by m table. Denote c-th cell of r-th row as (r, c). The tail of the snake is located at (1, 1), then it's body extends to (1, m), then goes down 2 rows to (3, m), then goes left to (3, 1) and so on.
Your task is to draw this snake for Fox Ciel: the empty cells should be represented as dot characters ('.') and the snake cells should be filled with number signs ('#').
Consider sample tests in order to understand the snake pattern.
The only line contains two integers: n and m (3 ≤ n, m ≤ 50).
n is an odd number.
Output n lines. Each line should contain a string consisting of m characters. Do not output spaces.
3 3
###
..#
###
3 4
####
...#
####
5 3
###
..#
###
#..
###
9 9
#########
........#
#########
#........
#########
........#
#########
#........
#########
简单模拟,偶数行打'#',奇数行打'.',再根据奇数整除2后的奇偶性决定是行首还是行尾打'#'。
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef long long ll; 4 char a[55][55]; 5 int main() 6 { 7 int n,m,i,j; 8 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 9 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 10 { 11 if((i&1) == 0)for(j=0;j<m;j++)a[i][j]='#'; 12 else 13 { 14 for(j=0;j<m;j++)a[i][j]='.'; 15 int k=(i>>1); 16 if((k&1) == 0)a[i][m-1]='#';else a[i][0]='#'; 17 } 18 } 19 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 20 { 21 for(j=0;j<m;j++)putchar(a[i][j]); 22 printf(" "); 23 } 24 return 0; 25 }
Fox Ciel is playing a mobile puzzle game called "Two Dots". The basic levels are played on a board of size n × m cells, like this:
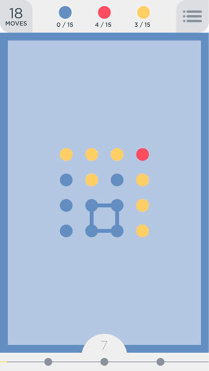
Each cell contains a dot that has some color. We will use different uppercase Latin characters to express different colors.
The key of this game is to find a cycle that contain dots of same color. Consider 4 blue dots on the picture forming a circle as an example. Formally, we call a sequence of dots d1, d2, ..., dk a cycle if and only if it meets the following condition:
- These k dots are different: if i ≠ j then di is different from dj.
- k is at least 4.
- All dots belong to the same color.
- For all 1 ≤ i ≤ k - 1: di and di + 1 are adjacent. Also, dk and d1 should also be adjacent. Cells x and y are called adjacent if they share an edge.
Determine if there exists a cycle on the field.
The first line contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n, m ≤ 50): the number of rows and columns of the board.
Then n lines follow, each line contains a string consisting of m characters, expressing colors of dots in each line. Each character is an uppercase Latin letter.
Output "Yes" if there exists a cycle, and "No" otherwise.
3 4
AAAA
ABCA
AAAA
Yes
3 4
AAAA
ABCA
AADA
No
4 4
YYYR
BYBY
BBBY
BBBY
Yes
7 6
AAAAAB
ABBBAB
ABAAAB
ABABBB
ABAAAB
ABBBAB
AAAAAB
Yes
2 13
ABCDEFGHIJKLM
NOPQRSTUVWXYZ
No
In first sample test all 'A' form a cycle.
In second sample there is no such cycle.
The third sample is displayed on the picture above ('Y' = Yellow, 'B' = Blue, 'R' = Red).
对每个点进行dfs。如果某一步可以走到先前走过的点,且不是上一次刚刚走过的点,则走过的全部或部分点一定可以连成圈。
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef long long ll; 4 char a[55][55]; 5 bool f[55][55]; 6 struct pt 7 { 8 int x,y; 9 bool operator != (const pt& p) 10 { 11 return (x != p.x) || (y != p.y); 12 } 13 }; 14 const int dx[]={-1, 0,+1, 0}; 15 const int dy[]={ 0,+1, 0,-1}; 16 int n,m; 17 bool yes; 18 void dfs(pt pre,pt par) 19 { 20 if(yes)return; 21 int k; 22 pt t; 23 for(k=0;k<4;k++) 24 { 25 t.x = pre.x + dx[k]; 26 t.y = pre.y + dy[k]; 27 if(0 <= t.x && t.x < n && 0 <= t.y && t.y < m && t != par && a[t.x][t.y] == a[par.x][par.y]) 28 { 29 if(f[t.x][t.y]) 30 { 31 yes = true; 32 return; 33 } 34 f[t.x][t.y] = true; 35 dfs(t,pre); 36 if(yes)return; 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 int main() 41 { 42 int i,j; 43 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 44 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 45 { 46 scanf("%s",a[i]); 47 } 48 yes = false; 49 for(i=0;i<n;i++)for(j=0;j<m;j++) 50 { 51 memset(f,0,sizeof f); 52 f[i][j]=true; 53 pt p; 54 p.x = i; 55 p.y = j; 56 dfs(p,p); 57 if(yes) 58 { 59 puts("Yes"); 60 return 0; 61 } 62 } 63 puts("No"); 64 return 0; 65 }
Fox Ciel is going to publish a paper on FOCS (Foxes Operated Computer Systems, pronounce: "Fox"). She heard a rumor: the authors list on the paper is always sorted in the lexicographical order.
After checking some examples, she found out that sometimes it wasn't true. On some papers authors' names weren't sorted inlexicographical order in normal sense. But it was always true that after some modification of the order of letters in alphabet, the order of authors becomes lexicographical!
She wants to know, if there exists an order of letters in Latin alphabet such that the names on the paper she is submitting are following in the lexicographical order. If so, you should find out any such order.
Lexicographical order is defined in following way. When we compare s and t, first we find the leftmost position with differing characters:si ≠ ti. If there is no such position (i. e. s is a prefix of t or vice versa) the shortest string is less. Otherwise, we compare characters siand ti according to their order in alphabet.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100): number of names.
Each of the following n lines contain one string namei (1 ≤ |namei| ≤ 100), the i-th name. Each name contains only lowercase Latin letters. All names are different.
If there exists such order of letters that the given names are sorted lexicographically, output any such order as a permutation of characters 'a'–'z' (i. e. first output the first letter of the modified alphabet, then the second, and so on).
Otherwise output a single word "Impossible" (without quotes).
3
rivest
shamir
adleman
bcdefghijklmnopqrsatuvwxyz
10
tourist
petr
wjmzbmr
yeputons
vepifanov
scottwu
oooooooooooooooo
subscriber
rowdark
tankengineer
Impossible
10
petr
egor
endagorion
feferivan
ilovetanyaromanova
kostka
dmitriyh
maratsnowbear
bredorjaguarturnik
cgyforever
aghjlnopefikdmbcqrstuvwxyz
7
car
care
careful
carefully
becarefuldontforgetsomething
otherwiseyouwillbehacked
goodluck
acbdefhijklmnogpqrstuvwxyz
两两比较字符串。如果前一个串是当前串的前缀则无需重排字母表;如果当前串是前一个串的前缀则发生错误,Impossible;否则就找到最左不同字符,并形成两结点,令前一个字符结点指向当前字符结点,最后再做一次拓扑排序。
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef long long ll; 4 char a[111][111]; 5 int l[111],di[333]; 6 vector<char>G[333],O; 7 bool f[333]; 8 void dg() 9 { 10 int j,i; 11 for(i='a';i<='z';i++){ 12 printf("%c:",i); 13 for(j=0;j<G[i].size();j++) 14 printf("%c ",G[i][j]); 15 printf(" ");} 16 } 17 int main() 18 { 19 int i,j,n; 20 scanf("%d",&n); 21 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 22 { 23 scanf("%s",a[i]); 24 l[i] = strlen(a[i]); 25 } 26 if(n==1) 27 { 28 puts("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"); 29 return 0; 30 } 31 for(i=1;i<n;i++) 32 { 33 j=0; 34 int minl=min(l[i],l[i-1]); 35 while(j<minl && a[i][j]==a[i-1][j])j++; 36 if(j==minl && l[i]<l[i-1]) 37 { 38 puts("Impossible"); 39 return 0; 40 } 41 else if(j==minl && l[i]>=l[i-1])continue; 42 G[a[i-1][j]].push_back(a[i][j]); 43 di[a[i][j]]++; 44 }//dg(); 45 int N=26; 46 while(N) 47 { 48 for(i='a';i<='z';i++)if(di[i]==0)break; 49 if(i>'z')break; 50 O.push_back(i); 51 di[i]=-1; 52 N--; 53 for(j=0;j<G[i].size();j++)di[G[i][j]]--; 54 } 55 if(N==0) 56 { 57 for(i=0;i<26;i++)putchar(O[i]); 58 printf(" "); 59 } 60 else 61 puts("Impossible"); 62 return 0; 63 }