Django基本配置
Python的WEB框架有Django、Tornado、Flask 等多种,Django相较与其他WEB框架其优势为:大而全,框架本身集成了ORM、模型绑定、模板引擎、缓存、Session等诸多功能
1.安装
# windows 直接用pip进行安装
pip install django
# 生成的django文件加入到系统环境变量
2.创建并启动
创建 django-admin startproject mysite 运行 python manage.py runserver 127.0.0.1:8001
浏览器访问:
http://127.0.0.1:8001/
3.mysite目录结构
mysite #目录 - mysite # 对整个程序进行配置 - init - settings # 配置文件 - urls # URL对应关系 - wsgi # 遵循WSIG规范,uwsgi + nginx - manage.py # 管理Django程序:
Django业务配置
1.创建app
python manage.py startapp cmdb -->Terminal里面运行
2.app目录结构
# 目录结构 - cmdb - migrations #数据库操作记录(只是修改表结构的记录) - init #表示python数据包(python3中有无均可) - admin #Django为我们提供的后台管理 - apps #配置当前app - models #创建数据库表结构,写指定的类,通过命令可以创建数据库结构 - tests #单元测试 - views #写业务逻辑代码,最重要的就是这个文件了
3.templates模板
(1)在templates目录下生成要给用户显示的登录页面

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> label{ width: 80px; text-align: right; display: inline-block; } </style> </head> <body> <form action="/login" method="post"> <p> <label for="username">用户名:</label> <input id="username" name="user" type="text" /> </p> <p> <label for="password">密码:</label> <input id="password" name="pwd" type="password" /> <input type="submit" value="提交" /> </p> </form> </body> </html>
(2)修改urls文件增加login路径
from django.conf.urls import url from django.contrib import admin from cmdb import views #导入views模块 urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), url(r'^login', views.login), #添加login.html的url,后面要加逗号 ]
(3)修改view文件,对数据进行处理
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse from django.shortcuts import render def login(request): return render(request,'login.html') # 上面代码等同于这个 # f = open('templates/login.html','r',encoding='utf-8') # data = f.read() # f.close() # return HttpResponse(data)
(4)配置静态文件static路径
静态文件static里面是存放css和js文件的,要想显示相应的样式,必须先修改settings文件配置
# settings.py文件里增加下面内容
STATIC_URL = '/static/'
STATICFILES_DIRS = (
os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'static'),
)
配置完路劲后就可以用css和js文件了
Django表单交互
1.获取表单提交类型做相应处理,用户名密码输正确跳转到页面,输入错误有提示信息

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/commons.css" /> <style> label{ width: 80px; text-align: right; display: inline-block; } </style> </head> <body> <form action="/login/" method="post"> <p> <label for="username">用户名:</label> <input id="username" name="user" type="text" /> </p> <p> <label for="password">密码:</label> <input id="password" name="pwd" type="password" /> <input type="submit" value="提交" /> <span style="color: red;">{{ error_msg }}</span> </p> </form> </body> </html>
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse from django.shortcuts import render from django.shortcuts import redirect def login(request): # request 包含了用户提交的所有信息 # print(request.method) error_msg = '' if request.method == 'POST': user = request.POST.get('user', None) pwd = request.POST.get('pwd', None) if user == 'root' and pwd == '123': # 去跳转 return redirect('http://www.baidu.com') else: error_msg = '用户名或密码错误' return render(request, 'login.html', {'error_msg': error_msg})
2.模拟数据库交互
访问login界面,用户输入用户名跳转到home页面
(1)登陆页面

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/commons.css" /> <style> label{ width: 80px; text-align: right; display: inline-block; } </style> </head> <body> <form action="/login/" method="post"> <p> <label for="username">用户名:</label> <input id="username" name="user" type="text" /> </p> <p> <label for="password">密码:</label> <input id="password" name="pwd" type="password" /> <input type="submit" value="提交" /> <span style="color: red;">{{ error_msg }}</span> </p> </form> </body> </html>
(2)home页面

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body style="margin: 0"> <div style="height: 48px;background-color: #dddddd"></div> <div> <form action="/home/" method="post"> <input type="text" name="username" placeholder="用户名" /> <input type="text" name="email" placeholder="邮箱"/> <input type="text" name="gender" placeholder="性别"/> <input type="submit" value="添加" /> </form> </div> <div> <table> {% for row in user_list %} <tr> <td>{{ row.username }}</td> <td>{{ row.gender }}</td> <td>{{ row.email }}</td> </tr> {% endfor %} </table> </div> </body> </html>
(3)修改view文件,对输入的内容进行处理
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse from django.shortcuts import render from django.shortcuts import redirect def login(request): # request 包含了用户提交的所有信息 # print(request.method) error_msg = '' if request.method == 'POST': user = request.POST.get('user', None) pwd = request.POST.get('pwd', None) if user == 'root' and pwd == '123': # 去跳转 return redirect('/home') else: error_msg = '用户名或密码错误' return render(request, 'login.html', {'error_msg': error_msg}) USER_LIST = [ {'id': 1, 'username': 'derek', 'email': '111', "gender": '男'}, {'id': 2, 'username': 'jack', 'email': '222', "gender": '女'}, {"id": 3, 'username': 'tom', 'email': '333', "gender": '男'}, ] def home(request): if request.method == "POST": # 获取用户提交的数据 POST请求中 u = request.POST.get('username') e = request.POST.get('email') g = request.POST.get('gender') temp = {'username': u, 'email': e, "gender": g} USER_LIST.append(temp) return render(request, 'home.html', {'user_list': USER_LIST})
3.获取checkbox多个值

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <form action="/login/" method="POST" > <p> 111:<input type="checkbox" name="favor" value="11"/> 222:<input type="checkbox" name="favor" value="22"/> 333:<input type="checkbox" name="favor" value="33"/> </p> <input type="submit" value="提交"/> </form> </body> </html>
修改views.py文件对表单处理
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse from django.shortcuts import render from django.shortcuts import redirect def login(request): #checkbox 多选框 if request.method == "POST": favor_list = request.POST.getlist("favor") #getlist获取多个值 print(favor_list) #多选框获取到的是列表格式 #['11', '22', '33'] return render(request,"login.html") elif request.method == "GET": return render(request,"login.html") else: print("other")
当用户提交之后,在后台上可以获取用户提交的信息,如下图
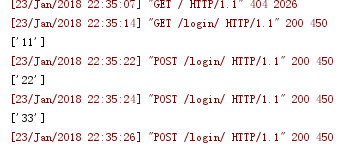
4.上传文件file

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <form action="/login" method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <p> <input type="file" name="files"/> </p> <input type="submit" value="提交"/> </form> </body> </html>
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse import os def login(request): #file 上传文件 if request.method == "POST": obj = request.FILES.get('files') #用files获取文件对象 if obj: print(obj, type(obj), obj.name) # test.jpg <class 'django.core.files.uploadedfile.InMemoryUploadedFile'> test.jpg import os file_path = os.path.join('upload', obj.name) #保存用户上传文件的路劲 f = open(file_path, "wb") for item in obj.chunks(): #chunks表示所有的数据块,是个迭代器 f.write(item) f.close() return render(request,"login.html") elif request.method == "GET": return render(request,"login.html") else: print("other")
