纯文本描述,时间有限,就不再另行搞图了,以后如果有需要再补充就是,现在本地版的Visual Paradigm还用不熟,processon的话也可以画,到时候看如果说以后需要培训新人或者做技术共享的时候再补充吧
注意:我这边大部分的博客都是为了记录给自己看的,并非为了让大家能一眼看明白,毕竟这玩意不是写几百个字就能说明白的。
说到Spring跳脱不开IOC和AOP。这边MVC主要牵扯到的也就是IOC
在整个IOC的启动过程中,真正用来初始化MVC构建的是一个监听器事件,直接看截图吧,这里是在IOC的refresh方法执行快结束的时候触发(AbstractApplicationContext->refresh->finishRefresh->publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this)))
最终到了下面这个方法:

先看一下类图吧
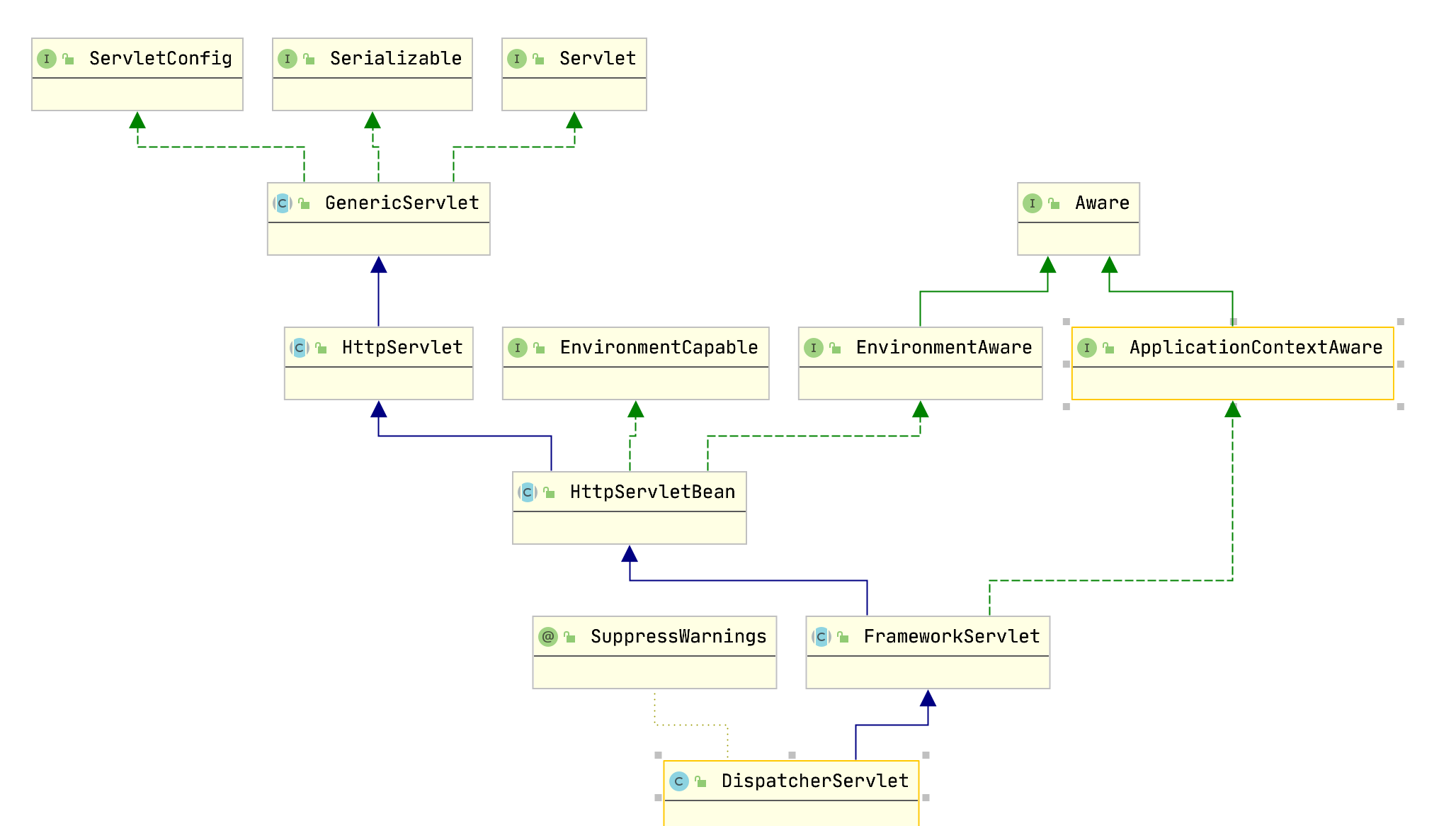
简单来说就是FrameworkServlet是DispatcherServlet(这个类要是不知道,那也不用看Spring MVC了)的父类
继续看里面的方法

大概解释下:
/** * Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses. * <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects. */ protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { // 上传文件用的 initMultipartResolver(context); // 国际化 initLocaleResolver(context); // 主题渲染 initThemeResolver(context); // 请求映射 initHandlerMappings(context); // 处理适配器,连接处理器和视图的,就是View and Action,比如说调用完了action之后将输出转化为视图 initHandlerAdapters(context); // 异常处理解析 initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); // 视图名称转化,看里面的接口,实现的是前后缀组装,比如说传入的是 /index.html,可以转化为 /view/index.ftl initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); // 视图渲染,比如ThymeleafViewResolver和FreeMarkerViewResolver initViewResolvers(context); // 快照Map,这个可以参考RequestMappingHandlerAdapter->getModelAndView里面有个对跳转的处理需要获取FlashMap initFlashMapManager(context); }
这里面的方法点进去执行的逻辑都差不多,就看一个,请求映射的,基本上都是初始化对应的策略、排序,没有的话就从默认取或初始化。
/** * Initialize the HandlerMappings used by this class. * <p>If no HandlerMapping beans are defined in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * we default to BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping. */ private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) { this.handlerMappings = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) { // Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts. Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values()); // We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order. AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings); } } else { try { HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class); this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later. } } // Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering // a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found. if (this.handlerMappings == null) { this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties"); } } }
初始化基本上就是流程
运行的时候
1、入口:HttpServlet(service)->FrameworkServlet(service)->processRequest->DispacherServlet(doService)->dispacher
2、大致流程
/** * Process the actual dispatching to the handler. * <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order. * The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters * to find the first that supports the handler class. * <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers * themselves to decide which methods are acceptable. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure */ protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); // 这层异常处理主要是处理未知的异常 try { ModelAndView mv = null; // 这层异常结合这个变量,可用于后面视图的匹配(尝试从异常视图解析器中匹配) Exception dispatchException = null; try { // 检查是否是上传文件 processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request. // 获取一个处理器,并包裹进一个处理器链,里面主要是Controller对象和一堆拦截器 mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); // 匹配不到处理器的情况 if (mappedHandler == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request. // 获取一个适配器,将上面获取的处理器对应的实际controller包裹进去,适合用于扩展 HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } // 调用前置拦截器 if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // Actually invoke the handler. // 调用适配器的处理,主要业务逻辑也在这里执行,方法比较复杂 mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } // 如果没有视图名称的话,设置一个默认的,一般是请求名 applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); // 调用后置拦截器 mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } catch (Throwable err) { // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); } // 对返回结果进行处理,比如视图的渲染 processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); } // 理资源释放 finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } }
比较复杂的是这行代码:
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
里面涉及了入参的解析获取,实际处理器的方法调用。这个就自己看比较好。