图
要点
重点在于掌握图的基本概念和存储,以及求关键路径、最短路径、拓扑排序的方法。
概念
图G由两个集合V和E组成,记为G=(V,E),其中V是顶点的有穷非空集合,E是V中顶点偶对 (称为边)的有穷集合。通常,也将图G的顶点集和边集分别记为V(G)和E(G)。E(G)可以是 空集。若E(G)为空,则图G只有顶点而没有边。
图的存储结构
邻接矩阵
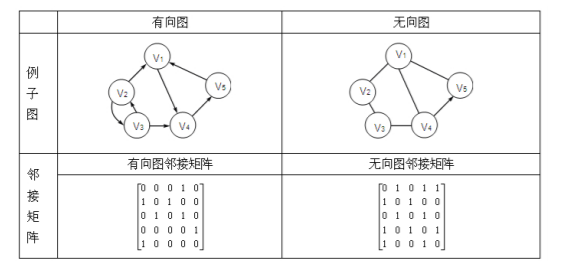
邻接矩阵
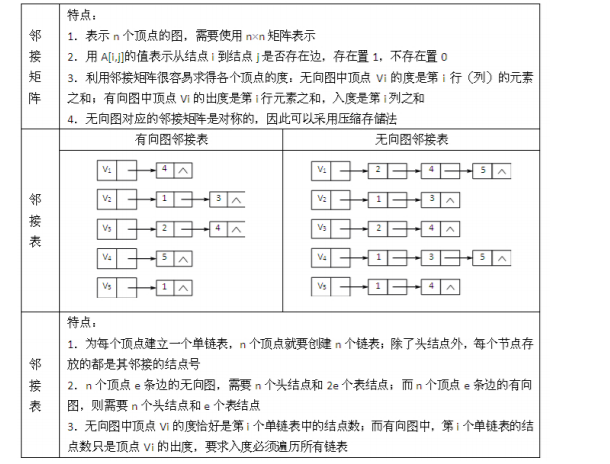
图的遍历
图的遍历也是从某个顶点出发,沿着某条搜索路径对图中每个顶点各做一次且仅做一次访问, 常用的遍历算法包括以下深度优先和广度优先两种

代码实现
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<queue> 3 #include<string.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 #define MaxInt 10000 6 #define Max_V 100 7 typedef char Vtype;//顶点数据类型是字符型 8 typedef int Arctype;//边的权值是整形 9 bool visited[MaxInt]; 10 //图的邻接矩阵存储方式 11 typedef struct 12 { 13 Vtype Vdata[Max_V]; //顶点数据 14 Arctype arcs[Max_V][Max_V]; //邻接矩阵 15 int vexnum,arcnum; //顶点数和边数 16 }AMGraph; 17 18 19 //邻接矩阵创建无向网 20 int LocateVex(AMGraph G,Vtype v); 21 void CreateGraph(AMGraph &G) 22 { 23 cout<<"请输入无向网的顶点个数和边的条数:"<<endl; 24 cin>>G.vexnum>>G.arcnum; 25 cout<<"请依次输入顶点的信息:"<<endl; 26 for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++) 27 cin>>G.Vdata[i]; //此处存放v1 v2 等等节点的名字 28 for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++) 29 for(int j=0;j<G.vexnum;j++) 30 G.arcs[i][j] = MaxInt; 31 32 cout<<"请依次输入边的俩个顶点信息和边的权值:"<<endl; 33 for(int k=0;k<=G.vexnum;k++) 34 { 35 int i,j; 36 char v1,v2; 37 Arctype w; 38 39 cin>>v1>>v2>>w; 40 i = LocateVex(G,v1); 41 j = LocateVex(G,v2); 42 G.arcs[i][j] = w; 43 G.arcs[j][i] = G.arcs[i][j]; 44 } 45 } 46 void Initvisited(AMGraph G,bool v[]) 47 { 48 for(int i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++) 49 v[i] = false; 50 } 51 //深度遍历无向网 52 void DFS_AM(AMGraph G,int v) 53 { 54 int j; 55 if(!visited[v]){ 56 cout<<G.Vdata[v]<<"->"; 57 visited[v] = true; 58 } 59 for(j=0;j<G.vexnum;j++) 60 { 61 if(G.arcs[v][j]!=MaxInt&&!visited[j]) 62 { 63 DFS_AM(G,j); 64 } 65 } 66 } 67 68 //广度优先遍历无向网 69 void BFS(AMGraph G,int v) 70 { 71 queue<Vtype> q; 72 int i; 73 if(!visited[v]) 74 { 75 cout<<G.Vdata[v]<<"->"; 76 q.push(v); 77 visited[v] = true; 78 } 79 while(!q.empty()) 80 { 81 i = q.front(); 82 q.pop(); 83 for(int j=0;j<G.vexnum;j++) 84 { 85 if(G.arcs[i][j]!=MaxInt&&!visited[j]) 86 { 87 cout<<G.Vdata[j]<<"->"; 88 q.push(j); 89 visited[j] = true; 90 } 91 } 92 } 93 } 94 95 int LocateVex(AMGraph G,Vtype v) 96 { 97 int i; 98 for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++) 99 { 100 if(G.Vdata[i] ==v) 101 return i; 102 } 103 return -1; 104 } 105 106 int main() 107 { 108 AMGraph m; 109 CreateGraph(m); 110 Initvisited(m,visited); 111 cout<<"深度优先遍历:"<<endl; 112 DFS_AM(m,0); 113 Initvisited(m,visited); 114 //memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited)); 115 cout<<endl; 116 cout<<"广度优先遍历:"<<endl; 117 BFS(m,0); 118 return 0; 119 }
总结
深度遍历的思想是递归,类似于先序遍历输出,广度优先遍历涉及到了栈的知识,一个节点入栈之后接下来入栈的便是上一个入栈节点的子节点(孩子),这样就实现了广度优先。