1.堆:堆是一种树,由它实现的优先级队列的插入和删除的时间复杂度都是O(logn),用堆实现的优先级队列虽然和数组实现相比较删除慢了些,但插入的时间快的多了。当速度很重要且有很多插入操作时,可以选择堆来实现优先级队列。
2.java的堆和数据结构堆:java的堆是程序员用new能得到的计算机内存的可用部分。而数据结构的堆是一种特殊的二叉树。
3.堆是具有如下特点的二叉树:
3.1.它是完全二叉树,也就是说除了树的最后一层节点不需要是满的,其他的每一层从左到右都必须是满的。
3.1.1.完全二叉树图解: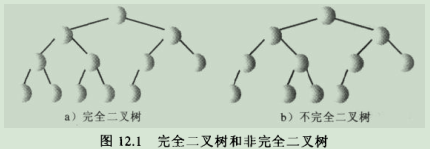
3.2.它常常用数组实现。
3.2.1.数组和堆的对应关系示意图: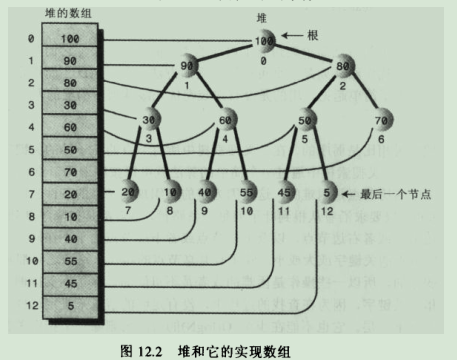
3.3.堆中每一个节点都满足堆的条件,也就是说每一个关键字的值都大于或等于这个节点的子节点的关键字值。
堆是完全二叉树的事实说明了表示堆的数组中没有空项,即从0-->n-1的每个数据单元都有数据项。
4.堆在存储器中的表示是数组,堆只是一个概念上的表示。
5.堆的弱序:堆和二叉搜索树相比是弱序的,在二叉搜索树中,当前节点的值总是比左子节点的值大,却比它的右子节点的值小,因此按序遍历相对容易。而堆的组织规则弱,它只要求从根到叶子节点的每一条路径,节点都是按降序排列的。同一节点的左右子节点都没有规律。因此,堆不支持按序遍历,也不能在堆上便利的查找指定关键字,因为在查找的过程中,没有足够的信息决定选择通过节点的两个那一个走向下一层。它也不能在少于O(logn)的时间内删除一个指定的节点,因为没有办法找到这个节点。因此,堆的这种近乎无序的规则似乎毫无用处,不过对于快速移除最大节点的操作,以及快速插入新节点的操作,这种顺序已经足够了。这些操作是使用堆作为优先级队列所需要的全部操作。
6.移除操作:移除是指删掉关键字值最大的节点,即根节点。移除思路如下:
6.1.移走根,
6.2.把左后一个节点移到根的位置,
6.3.一直向下筛选这个节点,知道它在一个大于它的节点之下,小于它的节点之上为止。
6.4.过程图解: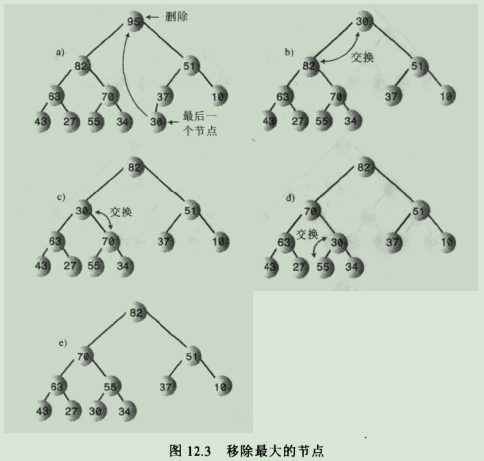
说明:在被筛选节点的每个暂时停留的位置,向下筛选的算法总是要检查那一个子节点更大,然后目标节点和较大的子节点交换位置,如果要把目标节点和较小的子节点交换,那么这个子节点就会变成大子节点的父节点,这就违背了堆的条件。
7.堆的插入:插入使用向上筛选,节点最后插入到数组最后第一个空着的单元中,数组容量大小增加1。
7.1.插入图解: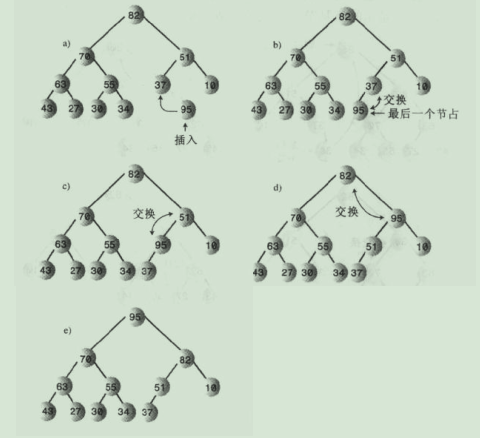
说明:向上筛选的算法比向下筛选的算法相对简单,因为它不需要比较两个子节点关键字值的大小,节点只有一个父节点。目标节点主要和它的父亲节点换位即可。
7.2.不是真的交换: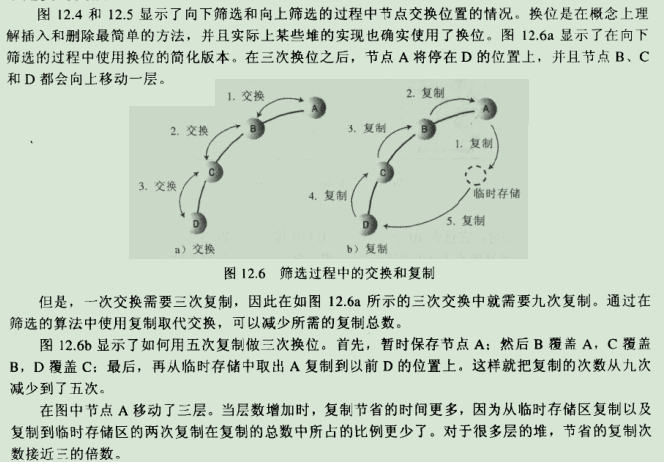
8.用数组表示一棵树时,如果数组中节点的索引位x,则
a.它的父节点的下标是:(x-1)/2;
b.它的左子节点的下标为2*x + 1;
c.它的右子节点的下标是2*x + 2;
9.堆的代码:
9.1.Node.java

1 package com.cn.heap; 2 /** 3 * 堆的节点类 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class Node { 8 private int iData; 9 public Node(int id){ 10 iData = id; 11 } 12 public int getkey(){ 13 return iData; 14 } 15 public void setkey(int id){ 16 iData = id; 17 } 18 }
9.2.Heap.java

1 package com.cn.heap; 2 /** 3 * 堆的实现类 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class Heap { 8 private Node[] heapArray; 9 private int maxSize; 10 private int currentSize; 11 public Heap(int mx){ 12 maxSize = mx; 13 heapArray = new Node[maxSize]; 14 currentSize = 0; 15 } 16 public boolean isEmpty(){ 17 return currentSize == 0 ; 18 } 19 public boolean insert(int key){ 20 if (currentSize == maxSize) 21 return false; 22 Node thenode = new Node(key); 23 heapArray[currentSize] = thenode; 24 trickleUp(currentSize ++); 25 return true; 26 } 27 public void trickleUp(int index){ 28 int parent = (index - 1) / 2; 29 Node bottom = heapArray[index]; 30 while (index > 0 && heapArray[parent].getkey() < bottom.getkey()){ 31 heapArray[index] = heapArray[parent]; 32 index = parent; 33 parent = (parent - 1) / 2; 34 } 35 heapArray[index] = bottom; 36 } 37 public Node remove(){ 38 Node root = heapArray[0]; 39 heapArray[0] = heapArray[-- currentSize]; 40 trickleDown(0); 41 return root; 42 } 43 public void trickleDown(int index){ 44 int largeChild; 45 Node top = heapArray[index]; 46 while (index < currentSize / 2){ 47 int leftChild = 2 * index + 1; 48 int rightChild = 2 * index + 2; 49 if (rightChild < currentSize && heapArray[leftChild].getkey() < heapArray[rightChild].getkey()) 50 largeChild = rightChild; 51 else 52 largeChild = leftChild; 53 if (top.getkey() >= heapArray[largeChild].getkey()) 54 break; 55 heapArray[index] = heapArray[largeChild]; 56 index = largeChild; 57 } 58 heapArray[index] = top; 59 } 60 public boolean change(int index,int newvalue){ 61 if (index < 0 || index >=currentSize) 62 return false; 63 int oldvalue = heapArray[index].getkey(); 64 heapArray[index].setkey(newvalue); 65 if (oldvalue < newvalue) 66 trickleUp(index); 67 else 68 trickleDown(index); 69 return true; 70 } 71 public void displayHeap(){ 72 System.out.print("heapArray:"); 73 for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) { 74 if (heapArray[i] != null) 75 System.out.print(heapArray[i].getkey()+" "); 76 else 77 System.out.print("--"); 78 } 79 System.out.println(""); 80 int nBlanks = 32; 81 int itemsPerrow = 1; 82 int column = 0; 83 int j = 0; 84 String dots = "........................"; 85 System.out.println(dots + dots); 86 while (currentSize > 0){ 87 if (column == 0) 88 for (int i = 0; i < nBlanks; i++) { 89 System.out.print(" "); 90 } 91 System.out.print(heapArray[j].getkey()); 92 if (++ j == currentSize) 93 break; 94 if (++ column == itemsPerrow){ 95 nBlanks /= 2; 96 itemsPerrow *= 2; 97 column = 0; 98 System.out.println(); 99 } 100 else 101 for (int i = 0; i < nBlanks * 2 - 2; i++) 102 System.out.print(' '); 103 } 104 System.out.println(" "+dots + dots); 105 } 106 }
9.3.HTest.java

1 package com.cn.heap; 2 /** 3 * heap类的测试 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class HTest { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 Heap h = new Heap(10); 10 h.insert(10); 11 h.insert(30); 12 h.insert(20); 13 h.insert(18); 14 h.insert(12); 15 h.displayHeap(); 16 h.remove(); 17 h.displayHeap(); 18 } 19 }
10.堆的效率:上述操作的时间复杂度是:O(logn)。
11.堆排序实现思路:使用insert()向堆中插入所有无序的数据项,然后重复使用remove()方法,就可以按序移除所有数据项,它的效率和快速排序类似,都是O(NlogN),但快排稍微快些,因为堆插入时的向下筛选多出的比较所占用的时间。
11.1.Node.java

1 package com.cn.heap; 2 /** 3 * 堆的节点类 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class Node { 8 private int iData; 9 public Node(int id){ 10 iData = id; 11 } 12 public int getkey(){ 13 return iData; 14 } 15 public void setkey(int id){ 16 iData = id; 17 } 18 }
11.2.Heap.java

1 package com.cn.heap; 2 /** 3 * 堆的实现类 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class Heap { 8 private Node[] heapArray; 9 private int maxSize; 10 private int currentSize; 11 public Heap(int mx){ 12 maxSize = mx; 13 heapArray = new Node[maxSize]; 14 currentSize = 0; 15 } 16 public boolean isEmpty(){ 17 return currentSize == 0 ; 18 } 19 public boolean insert(int key){ 20 if (currentSize == maxSize) 21 return false; 22 Node thenode = new Node(key); 23 heapArray[currentSize] = thenode; 24 trickleUp(currentSize ++); 25 return true; 26 } 27 public void trickleUp(int index){ 28 int parent = (index - 1) / 2; 29 Node bottom = heapArray[index]; 30 while (index > 0 && heapArray[parent].getkey() < bottom.getkey()){ 31 heapArray[index] = heapArray[parent]; 32 index = parent; 33 parent = (parent - 1) / 2; 34 } 35 heapArray[index] = bottom; 36 } 37 public Node remove(){ 38 Node root = heapArray[0]; 39 heapArray[0] = heapArray[-- currentSize]; 40 trickleDown(0); 41 return root; 42 } 43 public void trickleDown(int index){ 44 int largeChild; 45 Node top = heapArray[index]; 46 while (index < currentSize / 2){ 47 int leftChild = 2 * index + 1; 48 int rightChild = 2 * index + 2; 49 if (rightChild < currentSize && heapArray[leftChild].getkey() < heapArray[rightChild].getkey()) 50 largeChild = rightChild; 51 else 52 largeChild = leftChild; 53 if (top.getkey() >= heapArray[largeChild].getkey()) 54 break; 55 heapArray[index] = heapArray[largeChild]; 56 index = largeChild; 57 } 58 heapArray[index] = top; 59 } 60 public boolean change(int index,int newvalue){ 61 if (index < 0 || index >=currentSize) 62 return false; 63 int oldvalue = heapArray[index].getkey(); 64 heapArray[index].setkey(newvalue); 65 if (oldvalue < newvalue) 66 trickleUp(index); 67 else 68 trickleDown(index); 69 return true; 70 } 71 public void displayHeap(){ 72 System.out.print("heapArray:"); 73 for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) { 74 if (heapArray[i] != null) 75 System.out.print(heapArray[i].getkey()+" "); 76 else 77 System.out.print("--"); 78 } 79 System.out.println(""); 80 int nBlanks = 32; 81 int itemsPerrow = 1; 82 int column = 0; 83 int j = 0; 84 String dots = "........................"; 85 System.out.println(dots + dots); 86 while (currentSize > 0){ 87 if (column == 0) 88 for (int i = 0; i < nBlanks; i++) { 89 System.out.print(" "); 90 } 91 System.out.print(heapArray[j].getkey()); 92 if (++ j == currentSize) 93 break; 94 if (++ column == itemsPerrow){ 95 nBlanks /= 2; 96 itemsPerrow *= 2; 97 column = 0; 98 System.out.println(); 99 } 100 else 101 for (int i = 0; i < nBlanks * 2 - 2; i++) 102 System.out.print(' '); 103 } 104 System.out.println(" "+dots + dots); 105 } 106 public void displayArray(){ 107 for (int i = 0; i < maxSize; i++) 108 System.out.print(heapArray[i].getkey()+" "); 109 System.out.println(); 110 } 111 public void insertAt(int index,Node newnode){ 112 heapArray[index] = newnode; 113 } 114 public void incrementSize(){ 115 currentSize ++; 116 } 117 }
11.3.HeapSort.java

1 package com.cn.heap; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 /** 6 * 基于堆的排序----堆排序 7 * @author Administrator 8 * 9 */ 10 public class HeapSort { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 int size,j; 13 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 14 System.out.print("Enter number of items: "); 15 size = in.nextInt(); 16 Heap theheap = new Heap(size); 17 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { 18 int random = (int)(Math.random()*100); 19 Node node = new Node(random); 20 theheap.insertAt(i, node); 21 theheap.incrementSize(); 22 } 23 System.out.print("random: "); 24 theheap.displayArray(); 25 for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i --) { 26 theheap.trickleDown(i); 27 } 28 System.out.print("heap: "); 29 theheap.displayArray(); 30 theheap.displayHeap(); 31 for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i --) { 32 Node node = theheap.remove(); 33 theheap.insertAt(i,node); 34 } 35 System.out.print("sorted: "); 36 theheap.displayArray(); 37 } 38 }
