1.树:树通常结合了有序数组和链表的优点,在树中查找数据项的速度和在有序数组中查找一样快,并且插入数据项和删除数据项的速度也和链表一样快。
2.树由边连接的节点而构成。节点一般代表着一些实体,节点间的直线表示关联节点间的路径,java中通常用引用来表示路径(c等一般是指针),
2-1.树的图: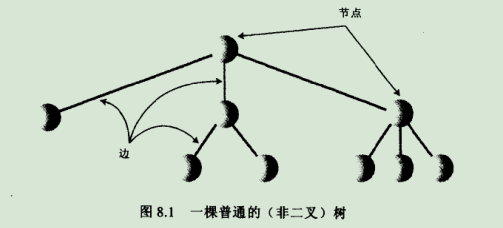
3.树有很多种,这里讨论一种特殊的树---二叉树,二叉树的节点最多有两个子节点。更普遍的树中子节点的个数可以多于两个。这种树称为多路树。
3.1.树的术语: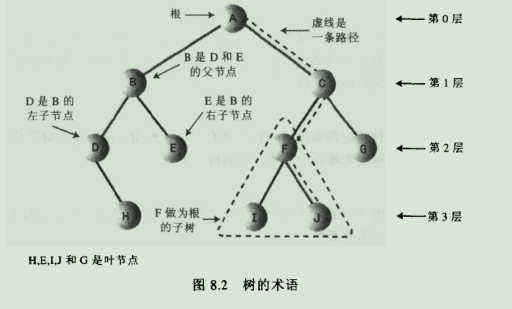
路径:设想一个沿着连接节点的边从一个节点走到另一个节点,所经过个节点的顺序排列就称为‘路径’。
关键字:可以看到,对象中通常有一个数据域被指定位关键字值,这个值通常用于查询或其他操作。在树的图形中,如果用圆来保存数据项的节点,那么一般将这个数据项的关键字值显示在这个圆中。
4.二叉树:如果树中每个节点最多只能有两个子节点,这样的树就称为二叉树。二叉树在学术上称为二叉搜索树(一个节点的左子节点的关键字值小于这个节点,右子节点的关键字值大于或等于这个父节点)。
5.二叉树的遍历(拿8.2图来说)
5.1.前序遍历:A--B--D--H--E--C--F--I--J--G
5.2.中序遍历:最常用,即将二叉搜索树按照关键字值升序访问。D--H--B--E--A--I--F--J--C--G
5.3.后序遍历:H--D--E--B--I--J--F--G--C--A
6.二叉树代码对象引用方式:
6.1.Node.java
1 package com.cn.tree; 2 /** 3 * 树的节点类 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class Node { 8 int iData; 9 double fData; 10 Node leftchild; 11 Node rightchild; 12 public void displayNode(){ 13 System.out.println("当前节点:"+iData+" 左孩子:"+(leftchild == null?null:leftchild.iData)+" 右孩子:"+(rightchild == null?null:rightchild.iData)); 14 } 15 }
6.2.Tree.java
1 package com.cn.tree; 2 /** 3 * 树的代码 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class Tree { 8 private Node root; 9 //查找关键字所在的节点 10 public Node find(int key){ 11 Node current = root; 12 while (current.iData != key){ 13 if (key < current.iData) 14 current = current.leftchild; 15 else 16 current = current.rightchild; 17 if (current == null) 18 return null; 19 } 20 return current; 21 } 22 //中序遍历 23 public void inorder(Node localroot){ 24 if (localroot != null){ 25 inorder(localroot.leftchild); 26 System.out.print(localroot.iData+" "); 27 inorder(localroot.rightchild); 28 }else{ 29 System.out.println(""); 30 } 31 } 32 //插入节点 33 public void insert(int id,double dd){ 34 Node newnode = new Node(); 35 newnode.iData = id; 36 newnode.fData = dd; 37 if (root == null) 38 root = newnode; 39 else{ 40 Node current = root; 41 Node parent; 42 while (true){ 43 parent = current; 44 if (id < current.iData){ 45 current = current.leftchild; 46 if (current == null){ 47 parent.leftchild = newnode; 48 return; 49 } 50 } 51 else{ 52 current = current.rightchild; 53 if (current == null){ 54 parent.rightchild = newnode; 55 return; 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 } 61 //获取树中的最小值节点 62 public Node min(){ 63 Node current,last = null; 64 current = root; 65 while (current != null){ 66 last = current; 67 current = current.leftchild; 68 } 69 return last; 70 } 71 //获取树中的最大值节点 72 public Node max(){ 73 Node current,last = null; 74 current = root; 75 while (current != null){ 76 last = current; 77 current = current.rightchild; 78 } 79 return last; 80 } 81 //删除节点 82 public boolean delete(int key){ 83 Node current = root; 84 Node parent = root; 85 boolean isleftchild = true; 86 //寻找待删除关键字值所在节点 87 while (current.iData != key){ 88 parent = current; 89 if (key < current.iData){ 90 isleftchild = true; 91 current = current.leftchild; 92 } 93 else{ 94 isleftchild = false; 95 current = current.rightchild; 96 } 97 if (current == null) 98 return false; 99 } 100 //如果要删除的节点没有孩子节点 101 if (current.leftchild == null && current.rightchild == null){ 102 if (current == root) 103 root = null; 104 else if (isleftchild) 105 parent.leftchild = null; 106 else 107 parent.rightchild = null; 108 } 109 //如果待删除的节点只有左孩子节点 110 else if (current.rightchild == null) 111 if (current == root) 112 root = current.leftchild; 113 else if (isleftchild) 114 parent.leftchild = current.leftchild; 115 else 116 parent.rightchild = current.leftchild; 117 //如果待删除节点只有右孩子节点 118 else if (current.leftchild == null) 119 if (current == root) 120 root = current.rightchild; 121 else if (isleftchild) 122 parent.leftchild = current.rightchild; 123 else 124 parent.rightchild = current.leftchild; 125 //如果左右孩子节点都存在 126 else{ 127 Node successor = getSuccessor(current); 128 if (current == root) 129 root = successor; 130 else if (isleftchild) 131 parent.leftchild = successor; 132 else 133 parent.rightchild = successor; 134 successor.leftchild = current.leftchild; 135 } 136 return true; 137 } 138 //获取要删除节点的后继节点 139 private Node getSuccessor(Node delnode){ 140 Node successorparent = delnode; 141 Node successor = delnode; 142 Node current = delnode.rightchild; 143 while (current != null){ 144 successorparent = successor; 145 successor = current; 146 current = current.leftchild; 147 } 148 if (successor != delnode.rightchild){ 149 successorparent.leftchild = successor.rightchild; 150 successor.rightchild = delnode.rightchild; 151 } 152 return successor; 153 } 154 }
6.3.TTest.java
1 package com.cn.tree; 2 3 public class TTest { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Tree t = new Tree(); 6 t.insert(4, 4.0); 7 t.insert(1, 1.0); 8 t.insert(3, 3.0); 9 t.insert(2, 2.0); 10 t.insert(6, 6.0); 11 t.insert(5, 5.0); 12 Node node = t.find(4); 13 node.displayNode(); 14 // node.displayNode(); 15 t.inorder(node); 16 // System.out.println(t.max().iData); 17 // System.out.println(t.min().iData); 18 t.delete(1); 19 t.inorder(node); 20 } 21 }
7.二叉树的效率:如果是满二叉树,常见操作的效率为O(logN),如果树不满,就不好确定了。
8.红黑树:他是二叉树的升级版,主要针对二叉搜索树在插入有序数据(正序或逆序)时,树其实就成为链表。二叉树就会失去平衡,成为非平衡树。对于非平衡树,它的查找(添加,删除)指定数据项的能力就丧失了。红黑树的平衡是在它的插入(删除也是)过程中取得的。对于一个要插入的数据项,插入例程要检查不会破坏树一定的特征。如果破坏了,程序就会进行修正,根据需要更改树的结构。通过维持树的特征,保持树的平衡。
9.红黑树的特征:①节点都有颜色 ②在插入和删除的过程中,要遵循保持这些颜色的不同排列的规则。
10.红黑规则:当插入(或删除)一个新节点时,必须要遵循一定的规则,我们称之为红黑规则,如果遵循这些规则,树就是平衡的。
①每一个节点不是红色就是黑色;
②跟总是黑色的;
③如果节点是红色的,则它的子节点必须是黑色的(反之不一定必须为真);
④从根到叶子节点或空子节点的每条路径,必须包含相同数目的黑色节点(从根到叶节点路径上的黑色高度必须相同)。
空子节点:非叶节点可以接子节点的位置。换句话说就是一个有右子节点的节点可能接左子节点的位置。或者是有左子节点的节点可能接右子节点的位置。
重复关键字值的处理:如果有多余一个数据项的关键字值相同,需要把有相同关键字的数据项分配到其他也有相同关键字的数据项两侧,也就是说如果有50,50,50,要把第 二个50放到第一个50的右边,并且把第三个50放到第一个50的左边,否则树将不平衡。目前只讨论不含有相同数据项的序列。
11.修正违规的情况:①改变节点颜色 ②执行旋转操作。
11.1.变色: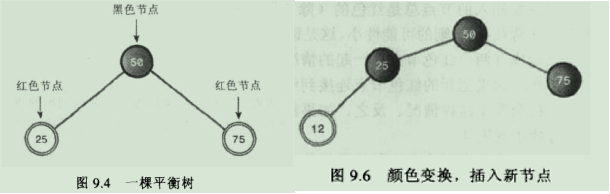
11.2.旋转: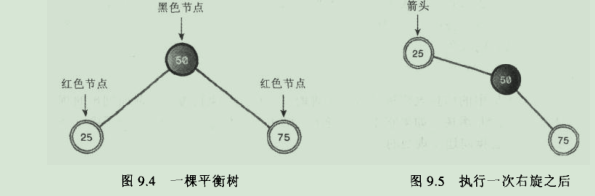
12.黑色高度: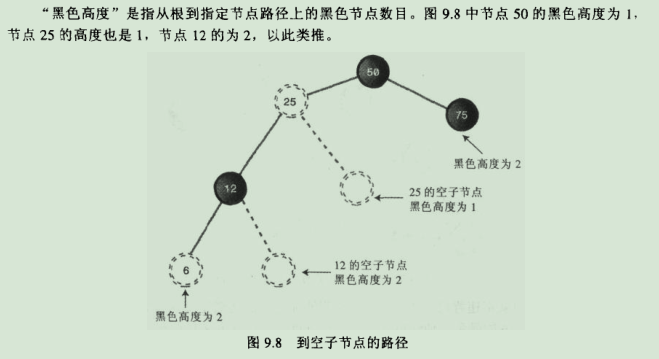
13.具体的删除插入详情请查看《java数据结构与算法》一书。