实验三 Java基本程序设计(2)
实验时间 2018-9-13
1、实验目的与要求
(1)进一步掌握Eclipse集成开发环境下java程序开发基本步骤;
(2)熟悉PTA平台线上测试环境;
(3)掌握Java语言构造基本程序语法知识(ch1-ch3);
(4)利用已掌握Java语言基本程序设计知识,学习设计开发含有一个主类、类内可有多个方法的应用程序。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:采用个人账号登录https://pintia.cn/,使用邀请码588329加入PTA平台NWNU-2017NISE教学班(西北师范大学 计算机科学与工程学院 2017级 网络与信息安全),完成《2018秋季西北师范大学面向对象程序设计(Java)(ch1-ch3)测试题1》,测试时间120分钟;
实验2-实验3在课后完成
实验2:公民身份证号码按照GB11643—1999《公民身份证号码》国家标准编制,由18位数字组成:前6位为行政区划分代码,第7位至14位为出生日期码,第15位至17位为顺序码,第18位为校验码。从键盘输入1个身份证号,将身份证号的年月日抽取出来,按年-月-日格式输出。注意:输入使用Scanner类的nextLine()方法,以免出错。
输入样例:
34080019810819327X
输出样例:
1981-08-19
1 package c; 2 import java.util.Scanner; 3 4 5 public class A { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 9 Scanner in= new Scanner(System.in); 10 System.out.println("请输入身份证号码"); 11 String num = in.nextLine(); 12 int len =num.length(); 13 if(len<18||len>18) 14 System.out.println("输入错误"); 15 else 16 { 17 int i = 6; 18 String year = num.substring(i, i+4); 19 String month = num.substring(i+4, i+6); 20 String day = num.substring(i+6, i+8); 21 22 System.out.println(year+"-"+month+"-"+day);} 23 } 24 25 }

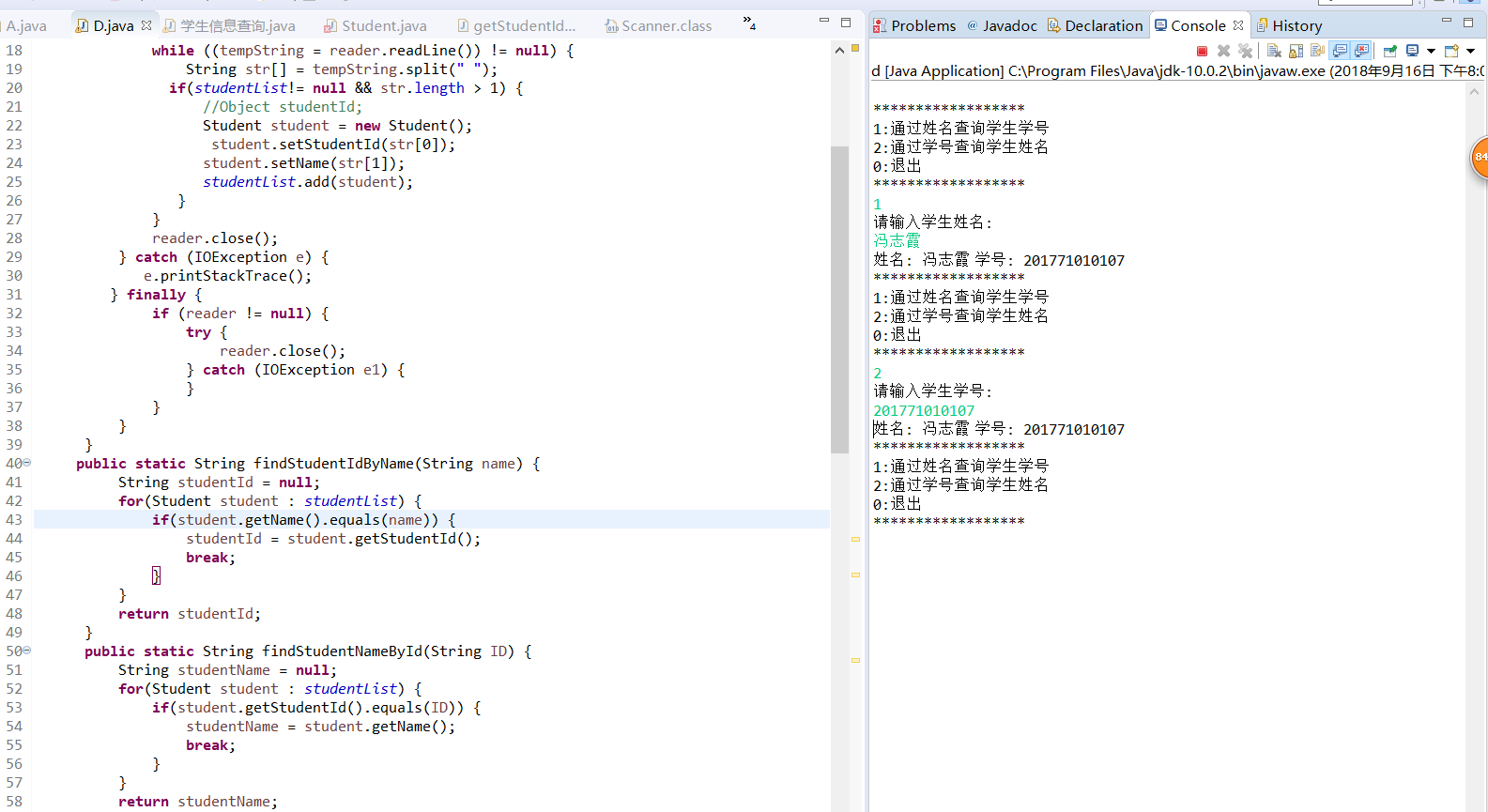
实验3:studentfile.txt文件内容是本班同学的学号与姓名,利用此文件编制一个程序,将studentfile.txt文件的信息读入到内存,并提供两类查询功能:(1)输入姓名查询学号;(2)输入学号查询姓名。要求程序具有友好人机交互界面。
编程建议:
(1)从文件中读入学生信息,可以编写如下函数:
public static void StudentsFromFile(String fileName))
(2)输入姓名查找学生学号,可以编写如下函数:
public static String findStudent(String name)
(3)输入学号查找学生姓名,可以编写如下函数:
public static String findStudent(String ID)
1 package d; 2 import java.io.BufferedReader; 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.FileReader; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.util.ArrayList; 7 import java.util.Scanner; 8 9 public class D { 10 private static ArrayList<Student>studentList = null; 11 public static void StudentsFromFile(String fileName){ 12 13 File file = new File(fileName); 14 BufferedReader reader = null; 15 try { 16 reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); 17 String tempString = null; 18 while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null) { 19 String str[] = tempString.split(" "); 20 if(studentList!= null && str.length > 1) { 21 //Object studentId; 22 Student student = new Student(); 23 student.setStudentId(str[0]); 24 student.setName(str[1]); 25 studentList.add(student); 26 } 27 } 28 reader.close(); 29 } catch (IOException e) { 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } finally { 32 if (reader != null) { 33 try { 34 reader.close(); 35 } catch (IOException e1) { 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 public static String findStudentIdByName(String name) { 41 String studentId = null; 42 for(Student student : studentList) { 43 if(student.getName().equals(name)) { 44 studentId = student.getStudentId(); 45 break; 46 } 47 } 48 return studentId; 49 } 50 public static String findStudentNameById(String ID) { 51 String studentName = null; 52 for(Student student : studentList) { 53 if(student.getStudentId().equals(ID)) { 54 studentName = student.getName(); 55 break; 56 } 57 } 58 return studentName; 59 } 60 public static void main(String args[]) { 61 String path = "C:\Users\Dell\Documents\Tencent Files\1689164469\FileRecv\实验三/studentfile.txt"; 62 studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(); 63 StudentsFromFile(path); 64 int statu = 1; 65 System.out.println(); 66 while(statu != 0) { 67 System.out.println("******************"); 68 System.out.println("1:通过姓名查询学生学号"); 69 System.out.println("2:通过学号查询学生姓名"); 70 System.out.println("0:退出"); 71 System.out.println("******************"); 72 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 73 statu = in.nextInt(); 74 75 switch(statu) { 76 case 1:{ System.out.println("请输入学生姓名:"); 77 Scanner scanner1 = new Scanner(System.in); 78 String name = scanner1.nextLine(); 79 String Id = findStudentIdByName(name); 80 if(Id != null) { 81 System.out.println("姓名: "+name+" 学号: "+Id); 82 }else { 83 System.out.println("不存在该学生!请重新查找"); 84 } 85 86 }break; 87 case 2:{ 88 System.out.println("请输入学生学号:"); 89 Scanner scanner2 = new Scanner(System.in); 90 String Id = scanner2.nextLine(); 91 String name = findStudentNameById(Id); 92 if(name != null) { 93 System.out.println("姓名: "+name+" 学号: "+Id); 94 }else { 95 System.out.println("不存在该学生!请重新查找"); 96 } 97 }break; 98 case 0: 99 statu = 0; break; 100 default: 101 System.out.println("输入错误"); 102 } 103 } 104 System.out.println("byebye!"); 105 } 106 107 } 108 109 110 111 112
总结:通过本次实验就觉得还是有很多困难的例如课堂上的编程题写出的代码能在eclipse上运行并出现正确结果可在指定的编译环境下就错误颇多,课后实验涉及到六的操作,动态数组的调用,循环结构的使用等等,为此查阅了资料并且做了摘抄如下是对流操作的总结:I/Ol流主要分为字节流与字符流
字符流:
Reader:用于读取字符流的抽象类。
|BufferedReader:从字符输入流中读取文本,缓冲各个字符,从而实现字符、数组和行的高效读取。 可以指定缓冲区的大小,或者可使用默认的大小。大 多数情况下,默认值就足够大了。
LineNumberReader:跟踪行号的缓冲字符输入流。此类定义了方法setLineNumber(int)和getLineNumbner(),它们可分别用于设置和获取当前行号。
|InputStreamReader:是字节流通向字符流的桥梁:它使用指定的 charset 读取字节并将其解码为字符。它使用的字符集可以由名称指定或显式给定,或者可以接受平台默认的字符集。
FileReader:用来读取字符文件的便捷类。此类的构造方法假定默认字符编码和默认字节缓冲区大小都是适当的。要自己指定这些值,可以先在 FileInputStream 上构造一个 InputStreamReader。
Writer:写入字符流的抽象类。
|BufferedWriter:将文本写入字符输出流,缓冲各个字符,从而提供单个字符、数组和字符串的高效写入。
|OutputStreamWriter:是字符流通向字节流的桥梁:可使用指定的 charset 将要写入流中的字符编码成字节。它使用的字符集可以由名称指定或显式给定,否则将接受平台默认的字符集。
FileWriter:用来写入字符文件的便捷类。此类的构造方法假定默认字符编码和默认字节缓冲区大小都是可接受的。要自己指定这些值,可以先在 FileOutputStream 上构造一个 OutputStreamWriter。
字节流:
InputStream:是表示字节输入流的所有类的超类。
|FileInputStream:从文件系统中的某个文件中获得输入字节。哪些文件可用取决于主机环境。FileInputStream 用于读取诸如图像数据之类的原始字节流。要读取字符流,请考虑使用 FileReader。
FilterInputStream:包含其他一些输入流,它将这些流用作其基本数据源,它可以直接传输数据或提供一些额外的功能。
BufferedInputStream:该类实现缓冲的输入流。
OutputStream:此抽象类是表示输出字节流的所有类的超类。
| FileOutputStream:文件输出流是用于将数据写入 File 或 FileDescriptor 的输出流。
|FilterOutputStream:此类是过滤输出流的所有类的超类。
BufferedOutputStream:该类实现缓冲的输出流。