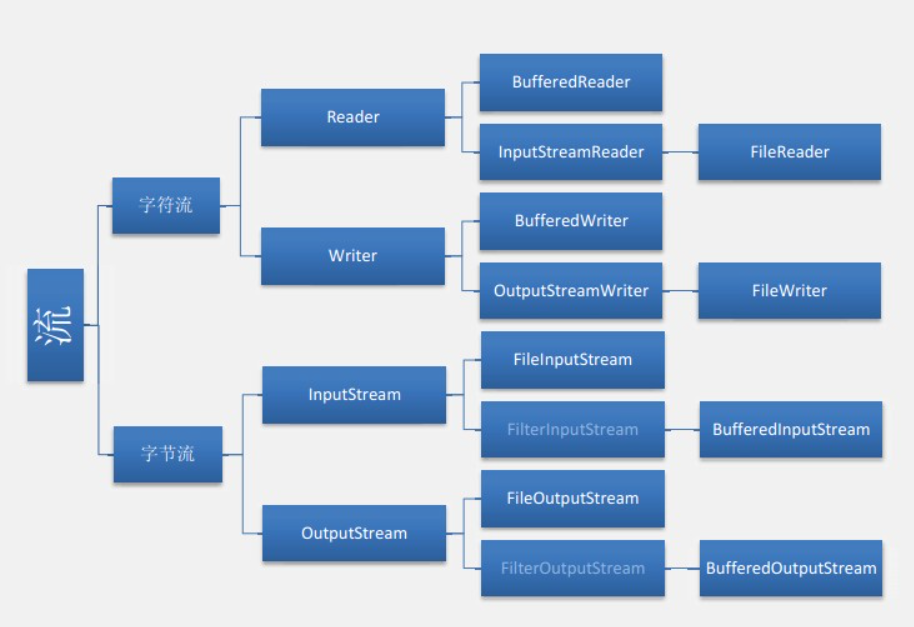
Java中的IO流
根据流的方向分为 输入流和输出流
根据读取文字的大小 字节流和字符流 字节流按字节读取 读取中文时容易乱码 字符流按字符读取 通常用于读取中文
根据读取的方式 节点流和缓存流
文件输入流和输出流(FileInputStream FileOutputStream)
FileInputStream fis=null; FileOutputStream fos=null; try { fis=new FileInputStream("D:\test.txt"); }catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
如果第二个参数省略,或传入false 则表示每次写入时将文件清空,从文件头部开始写入
如果第二个参数传入true,则表示不清空文件,在文章末尾处添加
fos=new FileOutputStream("D:\out.txt",true);
输出方式
一个字节一个字节的读取字节 int n=-1; while ((n=fis.read())!=-1) { sb.append((char)n); } 将byte数组直接声明为输入流的长度,一次性读出所有文字 byte[ ] bytes=new byte[fis.available()]; fis.read(bytes); sb.append(new String(bytes)); 一次读取1024个字节 byte[ ] bytes=new byte[1024]; int n=-1; while (( n=fis.read(bytes)) !=-1){ sb.append(new String(bytes)); } 将字符串转换为byte数组,并通过输出流输入文件 sb.reverse(); fos.write(sb.toString().getBytes()); System.out.println(sb);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally {
}
finally 无论上述代码是否会出现异常 都会执行的一段代码
通常用于关闭各种资源
传输图片
public static void main(String[] args) { try { FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("D:\test.txt"); FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("D:\test.txt"); int n=-1; while ((n=fis.read())!=-1) { fos.write(n); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
}
缓冲输入流和缓冲输出流(BufferedInputStream BufferedOutputStream)
作用
在基本流的基础上进行包装,读取或写入文件时,将通过缓存进行,即,先将内容写入到缓存区,缓存区满以后但进行读取或写入操作可以大大减小文件的操作次数,提高写入效率
FileInputStream fis=null; FileOutputStream fos=null; BufferedInputStream bis=null; BufferedOutputStream bos=null; long date1=new Date().getTime(); try {
bis =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\test.txt"));//这种写法,我们成为IO链,IO关闭时只需要关闭最外层流,内层流将自动关闭
bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\out.txt",true)); StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer(); //一个字节一个字节的读取字节 int n=-1; while ((n=fis.read())!=-1) { sb.append((char)n); } System.out.println(sb); long date2=new Date().getTime(); System.out.println("--------"+(date1-date2)); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { // fis.close(); bis.close(); // fos.close(); bos.flush();//在程序最后,刷新缓存流,将缓存流中未满的内容,写入到文件中 bos.close();//调用close方法,将自动刷新 } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
BufferedOutputStream 在关闭前通常调用bos.flush();表示关闭前刷新缓存流,将缓存流中未满的内容,写入到文件中 但是一般close()方法,将自动刷新缓存流
数据输入流与数据输出流(DataInputStream DataOutputStream)
采用二进制对文件进行读写操作与基本流相比,可以直接读写Java中的基本数据类型
另外 如果操作的文件是一个二进制文件,需要使用DataOutputStream替代FileOutputStream
注意使用DataOutputStream 写入文件为二进制文件 只能使用DataInputStream进行读取
String name="hhh"; int age=23; double height=134.6; String ads="yantai"; DataInputStream dis=null; DataOutputStream dos=null; try { dos=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("d:\test.txt")); dos.writeUTF(name); dos.writeInt(age); dos.writeDouble(height); dos.writeUTF(ads); dis=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("d:\tout.txt")); String uname = dis.readUTF(); int uage = dis.readInt(); double uheight = dis.readDouble(); String uads = dis.readUTF(); System.out.println(uname+"---"+uage+"---"+uheight+"---"+uads); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try { dis.close(); dos.flush(); dos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
对象输入流和对象输出流(ObjectInputStream ObjectOutputStream)
直接继承自import java.io.outputStream; 抽象类与基本流相同,可以直接使用readwrite方法进行读写
与DataInputStream相同,可以直接读写Java中的基本数据类型 readint() writedouble()
可以只用readObject() writeObject()直接对对象进行操作
需要对对象进行对象的序列化与反序列化
序列化 将程序中的对象 持久化的保存在文件中的过程
反序列化 将文件中的对象 重新读取到程序中的过程
如果,要对对象进行序列操作,实现可序化接口后,那么实体类必须实现可序化接口
class person implements Serializable{}
注意,当一个实体类 实现可序化接口后 可以添加一个序列化版本号ID 会自动生成一个静态属性 例如 private static final long serialVersionUID = 2545980081191079819L;
添加之后,可以用ID表示序列化与反序列化时操作的对象 是同一个对象
如果不添加id 当序列化添加一个新对象之后 反序列化会产生错误
public static void main(String[] args) { person zhangsan=new person("张三", 28, 178.5, "烟台"); ObjectInputStream ois =null; ObjectOutputStream oos =null; try { oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("d:\test.txt")); oos.writeObject(zhangsan); ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("d:\test.txt")); person p=(person)ois.readObject(); System.out.println(p); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { ois.close(); oos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
class person implements Serializable{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 2545980081191079819L; private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public person(String name) { super(); this.name = name; } }
输入字符流与输出字符流(FileWriter FileReader)
字符流
在处理数据单元是,以一个字符为单位,而字节流,以一个字符节为单位
字符的基类
reader writer 这两个是抽象类FileWriter_FileReader
filereader filewriter 是直接继承自抽象类的两个字符基本流
filereader filewriter 在读写文件时,只能使用系统默认编码格式
无法指定编码,如果文件格式与系统默认格式不一样,那使用这两个方法读写将造成中文乱码
public static void main(String[] args) { FileWriter fw=null; FileReader fr=null; try { fw=new FileWriter("D:/io.txt"); String s="1358kkkkk将"; for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { fw.write(s.charAt(i)); } fw.flush(); fr=new FileReader("D:/io.txt"); int n=0; StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer(); while ((n=fr.read())!=-1 ){ sb.append((char)n); } System.out.println(sb.toString()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
InputStreamReader OutputStreamWriter
1.将字节流转为字符流,同时支持自定义读写的编码格式
2.常见编码格式
ASCII 美国标准信息码
ISO8859-1 欧洲码
ANSI编码 分为多种
简体中文
GB2312
GBK
繁体中文
big-5
Unicode编码 国际标准码 兼容绝大部分国家的编码格式
可以分为 UTF-6 UTF-8 UTF-16
字符缓冲输入流与字符缓冲输出流(BufferedWriter BufferedReader)
bw=new BufferedWriter( new OutputStreamWriter( new FileOutputStream("D:/out.txt"),"UTF-8")) ;//表示用UTF-8对字符串进行解码为字节数组 bw.write(sb.toString()+"kkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk");
原来的字符串 s是UTF-8的编码格式
String s=sb.toString()+"kkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk"; s=new String(s.getBytes("UTF-8"),"GBK");//表示将解码后的字节数组 重新使用GBK的编码,组合成字符串 bw.write(s);
最终,一个UTF-8的字符串,经过解码编码转换为GBK格式的字符串