tensorflow笔记(二)之构造一个简单的神经网络
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请指明转载地址
http://www.cnblogs.com/fydeblog/p/7425200.html
前言
这篇博客将一步步构建一个tensorflow的神经网络去拟合曲线,并将误差和结果可视化。博客的末尾会放本篇博客的jupyter notebook,可以下载自己调试调试。
实践——构造神经网络
本次构造的神经网络是要拟合一个二次曲线,神经网络的输入层是一个特征,即只有一个神经元,隐藏层有10个特征,即有10个神经元,输出为一个神经元,总结起来就是1—10—1的结构,如果没有神经网络结构的朋友,还请去补一补
首先我们先导入要用到的模块
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
然后我们先构造出原始数据,并画出它的图形(为了更加符合实际,我们会加一些噪声)
x_data = np.linspace(-1,1,300) [:, np.newaxis] # [:,np.newaxis] make row vector transform column vector noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape) y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise
x_data是一个范围-1到1,以300分之2等份的列向量,noise的shape与x_data一样,值属于正态分布,0到0.05之间,y_data则是x_data的平方,减0.5,加噪声
fig=plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) ax.scatter(x_data,y_data) plt.xlabel('x_data') plt.ylabel('y_data') plt.show()
现在我们先写一个添加神经网络层的函数,函数名为add_nn_layer
def add_nn_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None): Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size])) biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1) Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases if activation_function is None: outputs = Wx_plus_b else: outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b) return outputs
神经网络的基本构造是要有输入,还要有输入映射到下一层的权重和偏差,最后神经元还有一个激活函数(这个有没有看需求),控制输出
我们上面讲到这个神经网络的结构是1—10—1,所以要添加两个层,一层是从输入层到隐藏层,另一层是隐藏层到输出层。
从输入层到隐藏层,1—10,输入是300x1的向量,到第二层则是300x10,权重则是1x10,偏差的shape与输出相同
从隐藏层到输出层,10—1,输入是300x10的向量,输出是300x1,可见权重是10x1,偏差的shape与输出相同
由此可以知道上面函数中各种变量的构造原因,简单说神经网络的构造就是输入乘以权重加上偏差,进入神经元的激活函数,然后输出
接下来我们开始写其他代码
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
tf.placeholder函数是一个非常重要的函数,以后用到它的次数会非常多,它表示占位符,相应的值会在sess.run里面feed进去,这样处理会非常灵活,大部分的学习都是分批的,不是一次传入,占位符满足这种需求
这里的xs和ys都是列向量,列数为1,行数不确定,feed的输入行数是多少就是多少
# add hidden layer l1 = add_nn_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu) # add output layer prediction = add_nn_layer(l1, 10, 1, activation_function=None)
这里隐藏层的激活函数用的是tf.nn.relu,relu全名是修正线性单元,详细请参考wiki(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rectifier_(neural_networks) ),它的性质简单的说就是输入神经元的数据大于0则等于自身,小于0则等于0,使用它更符合神经网络的性质,即有抑制区域和激活区域,我试了没加激活函数和sigmoid激活函数,效果要比用relu差许多,你们可以试试。
#compute loss loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction),reduction_indices=[1])) # creat train op,then we can sess.run(train) to minimize loss train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
# creat init init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# creat a Session sess = tf.Session()
# system initialize sess.run(init)
# training for i in range(1000): sess.run(train, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}) prediction_value = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs: x_data}) if i % 50 == 0: # to see the step improvement print('loss:',sess.run(loss, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}))

最后我们来看一下拟合的效果
fig=plt.figure() bx = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) bx.scatter(x_data,y_data) bx.plot(x_data,prediction_value,'g-',lw=6) plt.xlabel('x_data') plt.ylabel('y_data') plt.show()
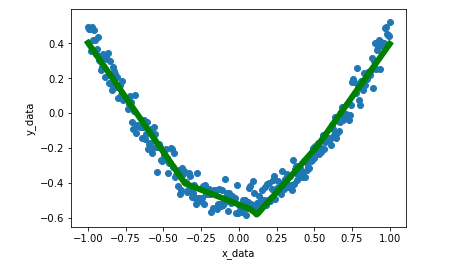
可见拟合的不错
结尾
下一个笔记将讲讲tensorboard的一些用法,敬请期待!
百度云链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1skAfUGH 密码: qw1g