有人穷,就是因为懒,今天看到这句话,我觉得貌似这是在说我,废话少说,今天把那个BeanDefinition的最小化接口看下里面有什么
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition
public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement { /** * Scope identifier for the standard singleton scope: {@value}. * <p>Note that extended bean factories might support further scopes. * @see #setScope * @see ConfigurableBeanFactory#SCOPE_SINGLETON * scope:单例 singleton */ String SCOPE_SINGLETON = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON; /** * Scope identifier for the standard prototype scope: {@value}. * <p>Note that extended bean factories might support further scopes. * @see #setScope * @see ConfigurableBeanFactory#SCOPE_PROTOTYPE * scope:proptotype,多例 */ String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE; /** * Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a major part * of the application. Typically corresponds to a user-defined bean. * 角色:属于应用程序的bean,用户自定义的bean类型 */ int ROLE_APPLICATION = 0; /** * Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a supporting * part of some larger configuration, typically an outer * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}. * {@code SUPPORT} beans are considered important enough to be aware * of when looking more closely at a particular * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}, * but not when looking at the overall configuration of an application. * 角色:支持?不甚了解,先跳过 */ int ROLE_SUPPORT = 1; /** * Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is providing an * entirely background role and has no relevance to the end-user. This hint is * used when registering beans that are completely part of the internal workings * of a {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}. * 角色:属于框架自身的bean */ int ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE = 2; // Modifiable attributes /** * Set the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any. * 设置beanDefinition的parent BeanDefinition */ void setParentName(@Nullable String parentName); /** * Return the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any. * parent bean的名字 */ @Nullable String getParentName(); /** * Specify the bean class name of this bean definition. * <p>The class name can be modified during bean factory post-processing, * typically replacing the original class name with a parsed variant of it. * @see #setParentName * @see #setFactoryBeanName * @see #setFactoryMethodName * 设置bean class的名称 */ void setBeanClassName(@Nullable String beanClassName); /** * Return the current bean class name of this bean definition. * <p>Note that this does not have to be the actual class name used at runtime, in * case of a child definition overriding/inheriting the class name from its parent. * Also, this may just be the class that a factory method is called on, or it may * even be empty in case of a factory bean reference that a method is called on. * Hence, do <i>not</i> consider this to be the definitive bean type at runtime but * rather only use it for parsing purposes at the individual bean definition level. * @see #getParentName() * @see #getFactoryBeanName() * @see #getFactoryMethodName() * 核心属性,此为bean的class名称 */ @Nullable String getBeanClassName(); /** * Override the target scope of this bean, specifying a new scope name. * @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON * @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE * 设置bean的scope作用域 */ void setScope(@Nullable String scope); /** * Return the name of the current target scope for this bean, * or {@code null} if not known yet. * scope,bean是单例的,还是每次new一个(prototype),就靠它了 */ @Nullable String getScope(); /** * Set whether this bean should be lazily initialized. * <p>If {@code false}, the bean will get instantiated on startup by bean * factories that perform eager initialization of singletons. * 设置它是不是延迟初始化的 */ void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit); /** * Return whether this bean should be lazily initialized, i.e. not * eagerly instantiated on startup. Only applicable to a singleton bean. * 懒加载bean?默认情况下,都是容器启动时,初始化;这也是官方推荐的,及早发现问题 * 如果设置了这个值,容器启动时不会初始化对象,首次getBean才初始化对象 */ boolean isLazyInit(); /** * Set the names of the beans that this bean depends on being initialized. * The bean factory will guarantee that these beans get initialized first. * 设置依赖的bean,bean工厂将保证首先初始化这些bean。 */ void setDependsOn(@Nullable String... dependsOn); /** * Return the bean names that this bean depends on. * 在本bean初始化之前,需要先初始化的bean:注意,这里不是说本bean依赖的其他需要注入的bean */ @Nullable String[] getDependsOn(); /** * Set whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean. * 基于类型的自动装配 * 那基于名称和基于类型有什么区别? * 假如自动注入一个TestService的接口,那么就会在spring里面找到TestService类型的bean注入进去 * 当你注入的时候,发现AutowireCandidate属性是false,那么是注入不进去的 * * 当你Autowired的时候,发现TestService接口实现类有多个,不知道注入哪一个 * 解决1:在某个实现类上打上@Primary注解,就是BeanDefinition的primary属性,那么就会注入这个bean * 解决2:在加了@Autowired的注解之上,再加一个@Qualifier注解指定bean name * 解决3:使用@Resource注解 * * * <p>Note that this flag is designed to only affect type-based autowiring. * It does not affect explicit references by name, which will get resolved even * if the specified bean is not marked as an autowire candidate. As a consequence, * autowiring by name will nevertheless inject a bean if the name matches. */ void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate); /** * Return whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean. * 是否够资格作为自动注入的候选bean,,,如果这里返回false,那就连自动注入的资格都没得 */ boolean isAutowireCandidate(); /** * Set whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate. * <p>If this value is {@code true} for exactly one bean among multiple * matching candidates, it will serve as a tie-breaker. * */ void setPrimary(boolean primary); /** * Return whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate. * 当作为依赖,要注入给某个bean时,当有多个候选bean时,本bean是否为头号种子选手, * 就像神奇宝贝里面,皮卡丘是小智在战斗时候的头号小精灵 */ boolean isPrimary(); /** * Specify the factory bean to use, if any. * This the name of the bean to call the specified factory method on. * @see #setFactoryMethodName */ void setFactoryBeanName(@Nullable String factoryBeanName); /** * Return the factory bean name, if any. * 核心属性,本属性获取工厂bean的名称,getFactoryMethodName获取工厂方法的名称,配合使用,生成 */ @Nullable String getFactoryBeanName(); /** * Specify a factory method, if any. This method will be invoked with * constructor arguments, or with no arguments if none are specified. * The method will be invoked on the specified factory bean, if any, * or otherwise as a static method on the local bean class. * @see #setFactoryBeanName * @see #setBeanClassName */ void setFactoryMethodName(@Nullable String factoryMethodName); /** * Return a factory method, if any. */ @Nullable String getFactoryMethodName(); /** * Return the constructor argument values for this bean. * <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing. * @return the ConstructorArgumentValues object (never {@code null}) * * 通过xml<bean>方法定义bean时,通过<constructor-arg>来定义构造器的参数,这里即:获取构造器参数 */ ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues(); /** * Return if there are constructor argument values defined for this bean. * @since 5.0.2 */ default boolean hasConstructorArgumentValues() { return !getConstructorArgumentValues().isEmpty(); } /** * Return the property values to be applied to a new instance of the bean. * <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing. * @return the MutablePropertyValues object (never {@code null}) * * 通过xml <bean>方式定义bean时, * 通过 <property name="testService" ref="testService"/> * 这种方式来注入依赖,这里即:获取property注入的参数值 */ MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues(); /** * Return if there are property values defined for this bean. * @since 5.0.2 */ default boolean hasPropertyValues() { return !getPropertyValues().isEmpty(); } /** * Set the name of the initializer method. * @since 5.1 */ void setInitMethodName(@Nullable String initMethodName); /** * Return the name of the initializer method. * @since 5.1 */ @Nullable String getInitMethodName(); /** * Set the name of the destroy method. * @since 5.1 */ void setDestroyMethodName(@Nullable String destroyMethodName); /** * Return the name of the destroy method. * @since 5.1 */ @Nullable String getDestroyMethodName(); /** * Set the role hint for this {@code BeanDefinition}. The role hint * provides the frameworks as well as tools an indication of * the role and importance of a particular {@code BeanDefinition}. * @since 5.1 * @see #ROLE_APPLICATION * @see #ROLE_SUPPORT * @see #ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE */ void setRole(int role); /** * Get the role hint for this {@code BeanDefinition}. The role hint * provides the frameworks as well as tools an indication of * the role and importance of a particular {@code BeanDefinition}. * @see #ROLE_APPLICATION * @see #ROLE_SUPPORT * @see #ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE * 获取角色 */ int getRole(); /** * Set a human-readable description of this bean definition. * @since 5.1 */ void setDescription(@Nullable String description); /** * Return a human-readable description of this bean definition. * 获取描述 */ @Nullable String getDescription(); // Read-only attributes /** * Return a resolvable type for this bean definition, * based on the bean class or other specific metadata. * <p>This is typically fully resolved on a runtime-merged bean definition * but not necessarily on a configuration-time definition instance. * @return the resolvable type (potentially {@link ResolvableType#NONE}) * @since 5.2 * @see ConfigurableBeanFactory#getMergedBeanDefinition */ ResolvableType getResolvableType(); /** * Return whether this a <b>Singleton</b>, with a single, shared instance * returned on all calls. * @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON * 是否单例 */ boolean isSingleton(); /** * Return whether this a <b>Prototype</b>, with an independent instance * returned for each call. * @since 3.0 * @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE * 是否prototype */ boolean isPrototype(); /** * Return whether this bean is "abstract", that is, not meant to be instantiated. * 是否为抽象的,还记得<bean>方式定义的时候,可以这样指定吗? * <bean id="testByPropertyController" class="org.springframework.simple.TestByPropertyController" abstract="true"> */ boolean isAbstract(); /** * Return a description of the resource that this bean definition * came from (for the purpose of showing context in case of errors). */ @Nullable String getResourceDescription(); /** * Return the originating BeanDefinition, or {@code null} if none. * <p>Allows for retrieving the decorated bean definition, if any. * <p>Note that this method returns the immediate originator. Iterate through the * originator chain to find the original BeanDefinition as defined by the user. * * 未知。。。。 */ @Nullable BeanDefinition getOriginatingBeanDefinition(); }
beanName
这个接口里面没有这东西,但是呢,在使用注解的规则是按照beanClassName的值按照驼峰格式转换来的。
默认是类的路径名+#+0
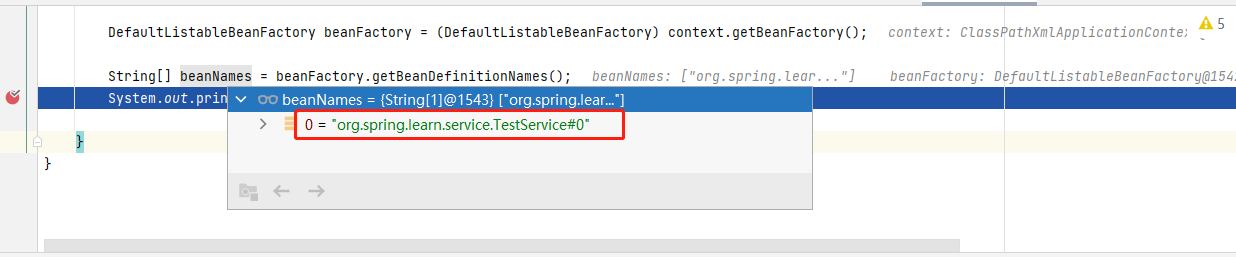
在spring的默认实现工厂里面,采用下面的字段存取bean和beanDefinition
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
/** Map of bean definition objects, keyed by bean name. */ /** * 存放注册BeanDefinition的map * key是beanName * 默认规则是:beanClassName按驼峰转换后的名字。 * 初始化容量是256 */ private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
这里的key是beanName,如果是同一个上下文里有两个相同的beanName的beanDefinition呢?
public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"application-context.xml"}); //默认就是true context.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(true); context.refresh(); //注入 GenericBeanDefinition beanDefinition = (GenericBeanDefinition) BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(TestServiceSameKey.class) .getBeanDefinition(); DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = (DefaultListableBeanFactory) context.getBeanFactory(); beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("testService",beanDefinition); //获取 TestServiceSameKey testServiceSameKey = context.getBean(TestServiceSameKey.class); testServiceSameKey.doSerivce(); }
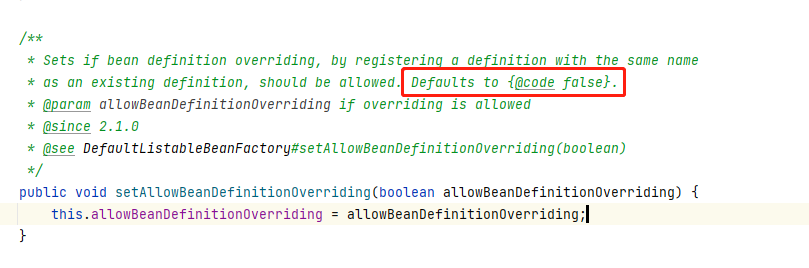
在spring里面默认是可以覆盖beanName相同的BeanDefinition,springboot结果又改成false了
有人就会说,你怎么知道的呢,不会是以讹传讹把,没有啊,下面是Springboot的注释。
当context.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(false);的时候,结果如下
Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionOverrideException: Invalid bean definition with name 'testService' defined in null: Cannot register bean definition [Generic bean: class [org.spring.learn.service.TestServiceSameKey]; scope=; abstract=false; lazyInit=null; autowireMode=0; dependencyCheck=0; autowireCandidate=true; primary=false; factoryBeanName=null; factoryMethodName=null; initMethodName=null; destroyMethodName=null] for bean 'testService': There is already [Generic bean: class [org.spring.learn.service.TestService]; scope=; abstract=false; lazyInit=false; autowireMode=0; dependencyCheck=0; autowireCandidate=true; primary=false; factoryBeanName=null; factoryMethodName=null; initMethodName=null; destroyMethodName=null; defined in class path resource [application-context.xml]] bound.
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:995)
at org.spring.learn.service.Run.main(Run.java:25)Process finished with exit code 1
提示说,这里已经存在相同beanName,testService
Scope
默认为singleton,在一个容器里面会有一个bean。prototype,每次去getBean的时候,都会new一个对象出来,这个一般不会在启动的时候初始化,如果写的有问题的话,
在初始化的时候不会报错,在Runtime时候报运行异常。
parentName
指定parentBean的名称,以前基于xml的时候可能会用,现在基于直接注解很少使用了
beanClassName
核心属性,bean的class类型,这里说的实际类型,而一般不是接口的名称,例如,我们的注解是写在具体class上的,及时加接口上,一般也是动态代理技术。
毕竟,创建bean要根据class的元数据来创建(一般是反射)
factoryBeanName、factoryMethodName
如果本bean是通过工厂来创造的,这两个对应的就是工厂bean的名称和工厂方法名称
lazyInit
是否延迟初始化,取值:true,false,default,默认是false。
简单说:true,设置true,启动时不初始化,false,启动时就初始化,官方也是推荐这种方式,有问题及早暴露出来
dependsOn
设置这个bean所依赖的被初始化的bean的名称,bean工厂将保证这些bean首先被初始化
autowireCandidate
设置为false的话,当其他的bean要注入这个bean,是注入不了,没有资格被别人注入。
primary
设置为true的话,举例说就是TestController里面@Autowired注入了TestService,接口实现类有几个,其中打了primary的bean,是优先注入到TestController,不然会报
二义性错误,程序期待注入一个结果有很多个。
ConstructorArgumentValues
构造函数属性值,通过xml<bean>方法定义bean时,通过<constructor-arg>来定义构造器的参数,这里即:获取构造器参数
MutablePropertyValues
property方式set注入属性值,通过xml <bean>方式定义bean时,通过 <property name="testService" ref="testService"/>
原博文链接https://www.cnblogs.com/grey-wolf/p/12051957.html,今天的作业就是都用下上面的属性呢?