跨域基础
跨域:
1、是什么
你的目标和你自己现在的位置一样还是不一样
浏览器上的同源策略
特点:
1、跨域只存在于浏览器
2、不在浏览器发请求是不会存在跨域问题的
3、http请求分为两大类: 普通http请求(如百度请求)和ajax请求(跨域是出现在ajax请求)
2、在什么地方
浏览器会跨域 服务器不会
3、什么条件会跨域
同源(协议 ip 端口一致)不跨域
不同源就跨域(三个中间有一个不一样就跨域)
http://localhost:8080/ ------- 》 github (有得是后台解决了允许跨域,前端如何解决跨域)
4、解决跨域:前端可以解决、后端解决。一般后端解决比前端解决容易
1.如果端口9000的服务向端口8000的端口发送请求,这一定跨域了,此时我们需要在在webpack配置文件中devserer中配置Proxy代理
async searchAjax(q) {
try {
const result = await axios({
url: "http://localhost:9000/api/users/info",
method: "get"
});
console.log(result.data);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
在webpack配置文件中devserer中配置Proxy代理
//3. 增加 devServer 配置
devServer: {
open: true, // 自动打开浏览器
compress: true, // 启动gzip压缩
port: 9000, // 端口号
quiet:true,
// proxy:{
// // 请求路径 http://localhost:9000/api/users/info
// //api会把http://localhost:9000覆盖掉
// // 代理转发路径 http://localhost:8000/api/users/info
// // "/api":{
// // target :"http://localhost:8000", //目标路径
// // pathRewrite: {"^/api" : ""}, //代理会把身份标识去掉替换成空窜
// // changeOrigin:true
// // },
// }
},
配置代理服务器的原理图
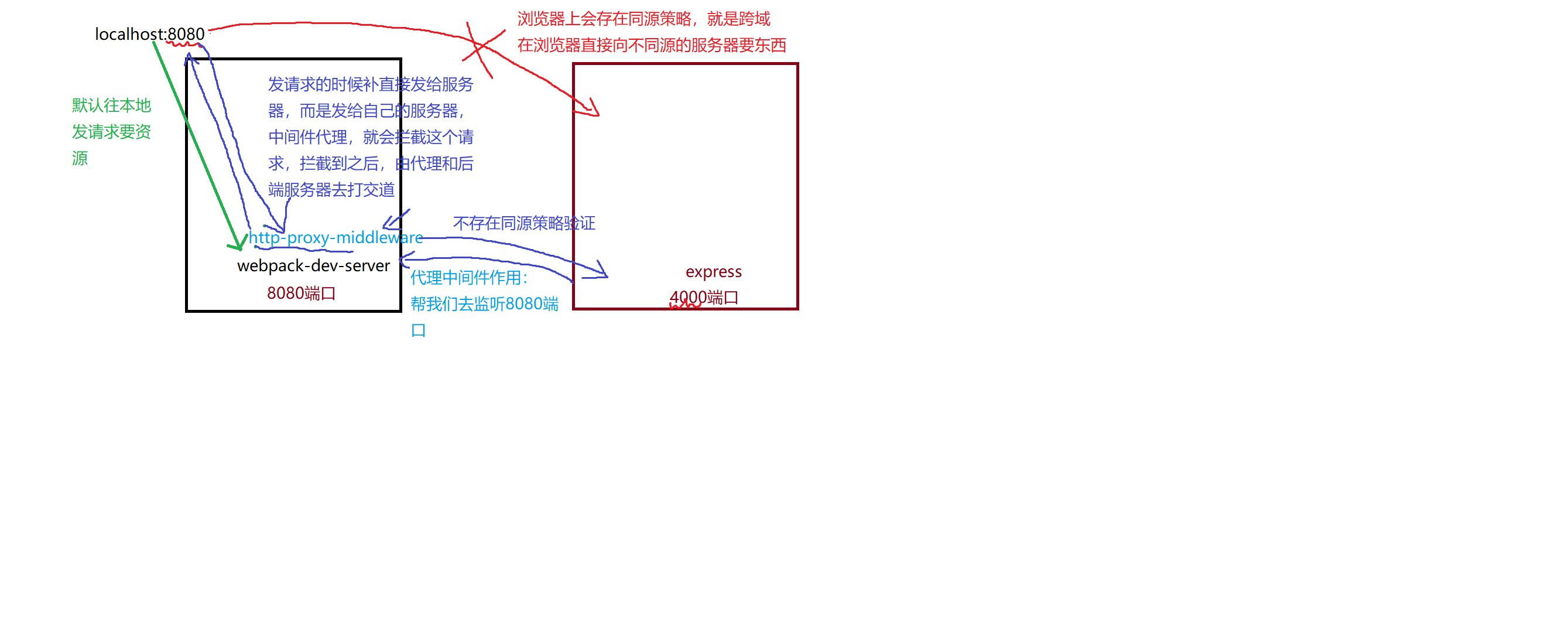
二, vuex的核心
1、状态管理是什么:
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式,是一个插件。
它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态(数据),并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
我们也可以认为它也是一种组件间通信的方式,并且适用于任意组件
2、理解:对vue应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(读/写)
3、为什么要有这个(问题):
1)多个视图依赖于同一状态
2)来自不同视图的行为需要变更同一状态
3)以前的解决办法
a.将数据以及操作数据的行为都定义在父组件
b.将数据以及操作数据的行为传递给需要的各个子组件(有可能需要多级传递)
4)vuex就是用来解决这个问题的
4、什么时候用:
Vuex 可以帮助我们管理共享状态,并附带了更多的概念和框架。这需要对短期和长期效益进行权衡。
也就是说应用简单(组件比较少)就不需要使用(但是可以),如果应用复杂,使用就会带来很大的便捷
5、Vuex核心:把所有的共享状态数据拿出来放在Vuex中进行集中式管理
1、安装vuex
2、创建单独的模块使用vuex 它是一个插件,按照插件使用方式
3、书写四个核心对象
4、暴露模块
5、在Vue配置项当中注册vuex对象,store
6、在核心对象写代码
优化:
1、如果用户再操作的时候就是很简单的数据更改,那么可以不用分发给actions,直接提交给mutations去更改
2、页面上如果数据不想写的太长,可以利用getters,去计算出来,然后在组件computed当中获取计算的这个数据
3、mapActions等
Vuex4个核心概念
state 代表初始状态数据 是一个包含n个属性(不是方法)的对象
getters 代表计算属性数据 是一个包含n个计算属性的方法的对象
actions 代表用户行为数据 是一个包含n个用户行为回调方法的对象,(用来映射组件用户的行为回调函数)
mutations 代表直接修改数据的数据 是一个包含n个直接修改状态数据方法的对象 (用来让action的行为调用)
注意:只能通过mutations的方法去直接修改,也就是说要想写state数据必须通过mutations
actions里面是用户操作的行为回调函数,它的内部可以写异步和判断
mutations里面是直接修改数据的函数数据,它的内部不可以写异步和判断
1.安装vuex, npm install vuex --save
2.新建文件夹vuex,文件store.js,
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 申明插件
Vue.use(Vuex)
3.在main.js引入import store from '@/vuex/store', 注册store
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
render: h => h(App),
store //如果我们声明使用(注册)store(vuex),那么每个组件对象都可以通过this.$store拿到我们的store对象
})
例子
1.入口文件main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from '@/App'
import store from '@/vuex/store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
render: h => h(App),
store //如果我们声明使用(注册)store(vuex),那么每个组件对象都可以通过this.$store拿到我们的store对象
})
2.app组件
<template> <div> <button @click="increment">+</button> <button @click="decrement">-</button> <button @click="incrementIfOdd">如果是奇数加{{count}}</button> <button @click="incrementAsync">异步加{{count}}</button> </div> </template> <script> // 从store中映射action和state,解构方式,供组件使用 import {mapActions,mapState} from 'vuex' export default { name: 'App' //数据定义到vuex(store)里面 // methods:mapActions(['increment','decrement','incrementIfOdd','incrementAsync']) methods:{ //最原始的写法 // increment(){ // //this.$store.dispatch分发触发 store对象内部actions内部对应的方法 // this.$store.dispatch('increment') // }, // decrement(){ // this.$store.dispatch('decrement') // }, // incrementIfOdd(){ // this.$store.dispatch('incrementIfOdd') // }, // incrementAsync(){ // this.$store.dispatch('incrementAsync') // } // 使用mapActions简化methods的写法 //1、如果methods方法名称和store对象actions内部的方法名称一致,可以使用下面这样的写法 // ...mapActions(['increment','decrement','incrementIfOdd','incrementAsync']) //2、如果methods方法的名称和store对象actions内部的方法名称不一致,那么就不能使用数组这样的写法 ...mapActions(['decrement','incrementIfOdd','incrementAsync']), ...mapActions({'increment':'iincrement'}) }, computed:{ // count(){ // return this.$store.state.count // } ...mapState(['count']) } //之前的,数据是定义在组件内的 // data(){ // return { // count:0 // } // }, // methods:{ // increment(){ // this.count++ // }, // decrement(){ // this.count-- // }, // incrementIfOdd(){ // if(this.count % 2 === 1){ // this.count++ // } // }, // incrementAsync(){ // setTimeout(() => { // this.count++ // }, 1000); // } // } } </script> <style scoped> </style>
store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 申明插件
Vue.use(Vuex)
const state = {
//是专门用来存(状态)数据的地方,它是一个包含多个属性和属性值的对象
count:0
}
const mutations = {
//专门用来更新数据的各种方法组成的对象
//这些个方法,必须是直接修改数据的方法, 不能在这些方法内部存在 判断 循环 异步
INCREMENT(state){
state.count++
},
DECREMENT(state){
state.count--
}
}
const actions = {
//专门用来和组件行为(用户行为)进行对接的各种方法组成的对象
//还有一个作用,用来对接成功后,告知相应的mutations中的对应方法去修改数据
// context有commit和state属性
// increment(context){
// //接到用户的操作请求(用户分发)之后,提交给相关的修改数据的函数去修改
// //在这里可以去写 if for 异步
// context.commit('INCREMENT')
// }
//解构方式
iincrement({commit}){
//接到用户的操作请求(用户分发)之后,提交给相关的修改数据的函数去修改
//在这里可以去写 if for 异步
commit('INCREMENT')
},
decrement({commit}){
//接到用户的操作请求(用户分发)之后,提交给相关的修改数据的函数去修改
//在这里可以去写 if for 异步
commit('DECREMENT')
},
incrementIfOdd({commit,state}){
//action内部的方法可以if for 异步 但是mutations里面的不行
if(state.count % 2 === 1){
commit('INCREMENT')
}
},
incrementAsync({commit}){
setTimeout(() => {
commit('INCREMENT')
}, 1000);
}
}
const getters = {
//一系列的方法,计算属性get方法,根据我们state内的数据计算出来用户要使用的数据
}
//暴露Store
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations,
getters,
actions
})
三,案例,在vuex中发送ajax请求,main组件获取vuex的数据
App组件
<template> <div class="container"> <Header></Header> <Main></Main> </div> </template> <script> import Header from '@/components/Header' import Main from '@/components/Main' export default { name: '', components:{ Header, Main } } </script> <style scoped> </style>
header组件
<template> <section class="jumbotron"> <h3 class="jumbotron-heading">Search Github Users</h3> <div> <input type="text" placeholder="enter the name you search" v-model="searchName" /> <button @click="search">Search</button> </div> </section> </template> <script> import {mapActions} from 'vuex' export default { name: "", data(){ return { searchName:'' } }, methods:{ // ...mapActions(['search']) search(){ //和store里面的某个actions方法去对应 //如果传递参数只有一个,可以直接传 //如果传递多个,必须使用对象 this.$store.dispatch('search',this.searchName) } } }; </script> <style scoped> </style>
main组件
<template> <div> <h2 v-if="isFirst">欢迎光临,请输入关键字进行搜索</h2> <h2 v-else-if="isLoading">正在搜索中,请稍后</h2> <h2 v-else-if="errMsg">请求出错:{{errMsg}}</h2> <div v-else class="row"> <div class="card" v-for="(user, index) in users" :key="user.userName"> <a :href="user.userUrl" target="_blank"> <img :src="user.userImg" style=" 100px" /> </a> <p class="card-text">{{user.userName}}</p> </div> </div> </div> </template> <script> import axios from 'axios' // 从store中映射出state,供组件使用数据 import {mapState} from 'vuex' export default { name: "", // 接收state里的数据,mapState()返回的是一个对象,解包对象 computed:{ ...mapState(['isFirst','isLoading','errMsg','users']) } // data(){ // return { // isFirst:true, // isLoading:false, // errMsg:'', // users:[] // } // }, // mounted(){ // this.$bus.$on('searchAjax',this.searchAjax) // }, // methods:{ // searchAjax(q){ // //在发送ajax请求之前,让页面显示正在请求中 // this.isFirst = false // this.isLoading = true // //就可以根据searchName去发送ajax请求 // this.$http({ // url:'https://api.github.com/search/us', // method:'get', // params:{ // q // } // }).then(response => { // let userList = response.data.items.map(item => { // return { // userName:item.login, // userUrl:item.url, // userImg:item.avatar_url // } // }) // this.users = userList // this.isLoading = false //请求成功拿到数据,显示用户信息 // }).catch(error => { // this.errMsg = error.statusText // this.isLoading = false //请求失败拿到错误信息,显示错误信息 // }) // } // } }; </script> <style scoped> .card { float: left; width: 33.333%; padding: 0.75rem; margin-bottom: 2rem; border: 1px solid #efefef; text-align: center; } .card > img { margin-bottom: 0.75rem; border-radius: 100px; } .card-text { font-size: 85%; } </style>
store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 引入axios
import axios from 'axios'
// 申明插件
Vue.use(Vuex)
const state = {
isFirst:true,
isLoading:false,
errMsg:'',
users:[]
}
const mutations = {
REQUESTING(state){
state.isFirst = false
state.isLoading = true
},
REQUEST_SUCCESS(state,userList){
state.users = userList
state.isLoading = false //请求成功拿到数据,显示用户信息
},
REQUEST_FAILD(state,error){
state.errMsg = error.message
state.isLoading = false //请求失败拿到错误信息,显示错误信息
}
}
const actions = {
//{commit}解构
search(context,q){
//在发送ajax请求之前,让页面显示正在请求中
context.commit('REQUESTING')
//就可以根据searchName去发送ajax请求
axios({
url:'https://api.github.com/search/users',
method:'get',
params:{
q
}
}).then(response => {
//返回一个新数组,数组中有个对象
let userList = response.data.items.map(item => {
return {
userName:item.login,
userUrl:item.url,
userImg:item.avatar_url
}
})
//请求成功后,提交给mutations,修改state的数据
context.commit('REQUEST_SUCCESS',userList)
}).catch(error => {
//发送请求失败后,提交给mutations,修改state的数据,改变状态
context.commit('REQUEST_FAILD',error)
})
}
}
const getters = {}
// 向外暴露store,给main.js
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
})