视频地址
一、基础语法
1 安装
1.1 最简单的安装方式
直接在页面用script引入,此种方式引入尽量将js放在head里面,避免抖屏
2 简单使用
创建vue实例:new Vue()
el:元素,让vue接管界面哪个element(元素),el参数就是元素id,该元素也成称为挂载点,挂载点中的内容称为模板
data:挂载点下面有一些数据,放到data里面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>简单使用</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!--Vue实例挂载点,-->
<div id="root">
<!--模板-->
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
//创建一个vue实例
new Vue({
//让vue接管界面哪个element(元素),el参数就是元素id
el: '#root',
// 模板内容还可以用以下方式书写
// template: '<h1>{{msg}}</h1>',
data:{
msg:'Hello World!'
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
关系:
- id为root的标签叫做vue实例的挂载点,vue只会处理挂载点下面的内容,实例和挂载点唯一对应
- 挂载点中的内容称为模板,模板有两种书写方式:第一种直接写在挂载点内部;第二种写在vue实例的template属性里面,格式:template: <标签内容>
3 数据、事件、方法
3.1 数据绑定
<body>
<div id="root">
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
<h1 v-text="number"></h1>
<div v-html="content"></div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
msg: 'Hello World!',
number: 123,
content: '<h1>对标签进行转义</h1>',
}
});
</script>
</body>
- {{msg}}:插值表达式。
- v-text:意思是标签h1中的内容由number指定,直接填写数据原始内容。
- v-html:对内容进行html转义。
3.2 事件、方法
v-on:进行事件绑定,后面跟着事件类型和方法名。方法在methods中进行定义。v-on:可以简写为@
<body>
<div id="root">
<div v-on:click="handleClick">{{msg}}</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
msg: 'Hello',
number: 123,
content: '<h1>对标签进行转义</h1>',
},
methods: {
handleClick: function () {
this.msg = 'World';
},
}
});
</script>
</body>
4 属性绑定、数据双向绑定
4.1 属性单项绑定
绑定方法:v-bind:属性名,缩写::属性名
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:v-on="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:v-bind="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>属性绑定、数据双向绑定</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div v-bind:title="title">{{msg}}</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
msg: 'Hello World',
title: '这是个问候语'
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
- 使用[v-bind:title=“title”]属性绑定后,双引号里面的title就是一个表达式,所以里面可以写js的内容比如[v-bind:title="'dell li + 'title"]
- [v-bind:]可以缩写为[:]
4.2 数据双向绑定
<body>
<div id="root">
<input v-model="msg">
<div v-text="msg"></div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
msg: 'Hello World',
title: '这是个问候语'
}
});
</script>
</body>
4.3 计算属性和侦听器
该例将实现以下功能:全名fullName通过firstName、lastName计算得到,firstName、lastName发生改变fullName也随之改变,count就加1。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:v-on="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:v-bind="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:v-text="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>计算属性和侦听器</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
姓:<input v-model="firstName">
名:<input v-model="lastName"><br>
姓名:{{fullName}}<br>
名字改变次数:{{count}}
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
firstName: 'Chen',
lastName: 'Yuhua',
count: 0,
},
//属性计算,一个属性通过其他属性计算而来,firstName lastName中有人的值发生改变时fullName才会重新计算
computed:{
fullName:function () {
return this.firstName + '' + this.lastName;
}
},
//属性监听
watch:{
fullName:function () {
this.count++;
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
1.属性计算:使用vue的conputed属性,一个属性通过其他属性计算而来,firstName lastName中有人的值发生改变时fullName才会重新计算,否则使用缓存值
2. 属性监听:使用vue的watch属性,监听属性或者计算属性的变化
4.4 v-if、v-show、v-for
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:v-on="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:v-bind="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:v-text="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-if、v-show、v-for</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!--控制消息的隐藏显示-->
<button @click="handleShow">{{btnVal}}</button>
<h1 v-if="show">v-if:{{msg}}</h1>
<h1 v-show="show">v-show:{{msg}}</h1>
<ul>
<!--遍历数组 key可以提高效率-->
<li v-for="(item,index) of list" :key="index">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
show:true,
msg:'你好!中国',
btnVal: '隐藏',
list:[1,2,3,4]
},
methods:{
handleShow: function () {
this.show = !this.show;
if (this.show) {
this.btnVal = '隐藏';
}else{
this.btnVal = '显示';
}
},
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
4.4.1 v-if、v-show区别
v-if: 直接创建或者删除标签来控制元素的显示和隐藏,代价较大。
v-show:通过css样式控制元素的显示和隐藏。
若是需要元素频繁的显示和隐藏应该使用v-show。
4.4.2 v-for循环
:key可以提高渲染效率,每项数据的key值不能相同。
二、vue中的组件
2.1 todolist功能开发
功能:输入框中输入内容,提交后清空输入框,在列表中进行展示。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:v-on="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:v-bind="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:v-text="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>todolist功能实现</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div>
<input v-model="inputValue">
<button @click="handleSubmit">提交</button>
</div>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) of list" :key="index">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
inputValue:'',
list:[],
},
methods: {
handleSubmit: function () {
this.list.push(this.inputValue);
this.inputValue = '';
},
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.2 todolist组件拆分
组件:页面的某一部分,实际项目开发中,一个内容较多的网页内容可以拆分称多个部分,每个部分就是一个组件,便于维护。
2.2.1 将列表进行组件拆分
- 全局组件。
<ul> <!--组件使用--> <todo-item></todo-item> </ul> <script> <!--组件注册--> Vue.component('todo-item', { template:'<li>item</li>' }); </script>这种方式定义的组件叫做全局组件,定义好之后在项目中的任何地方都可以使用。
- 局部组件。
<!--组件使用--> <ul> <todo-item></todo-item> </ul> <script> <!--组件定义--> var todoItem = { template:'<li>item</li>' } new Vue({ el: '#root', // 组件注册 compoments:{ 'todo-item':todoItem } }); </script>通过此种方式定义的组件就是局部组件,想要使用就需要使用vue的compoments属性定义到挂载点之下。意思就是在该vue实例里面想要使用todoItem这个组件,就需要进行组件注册,使用todo-item这个标签使用。
- 功能实现
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:v-on="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:v-bind="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:v-text="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>todolist功能实现</title> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="root"> <div> <input v-model="inputValue"> <button @click="handleSubmit">提交</button> </div> <ul> <!--:content 向子组件把item值传递过去--> <todo-item v-for="(item,index) of list" :key="index" :content="item" ></todo-item> </ul> </div> <script> Vue.component('todo-item',{ //接收父组件传过来的content值 props:['content'], template:'<li>{{content}}</li>' }) new Vue({ el: '#root', data: { inputValue: '', list: [], }, methods: { handleSubmit: function () { this.list.push(this.inputValue); this.inputValue = ''; }, } }); </script> </body> </html>Vue中父组件向子组件是通过属性进行传值的,子组件需要使用props进行属性值的接收。
2.3 组件和实例的关系
每个Vue的组件都是一个Vue的实例,都拥有data、template、methods等属性。任何一个Vue项目都是由多个Vue实例组成。组件是否是实例可以用以下代码验证:
Vue.component('todo-item',{
//接收父组件传过来的content值
props:['content'],
template:'<li @click="handleClick">{{content}}</li>',
methods:{
handleClick:function(){
alert("clicked!")
}
}
})
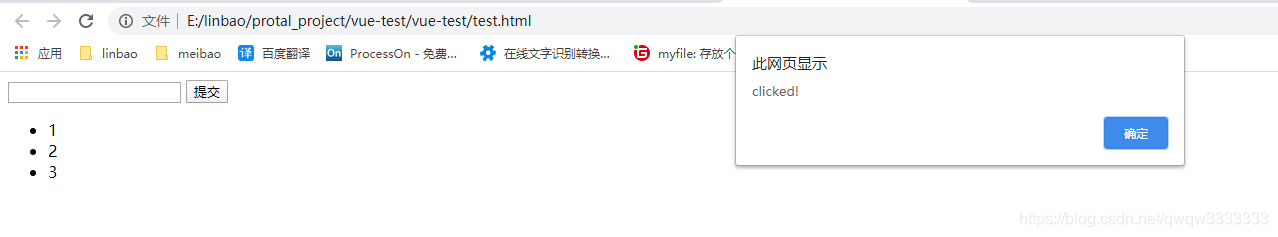
注意:如果一个Vue实例没有template属性,它会将挂载点下所有内容当做模板使用。
2.4 实现todolist删除功能
该实例实现以下功能:输入框提交内容后,清空输入框,列表对内容进行展示,点击列表某项,该项将被删除。

由于子组件的删除依赖父组件的list的值,所以点击子组件item时需要将信息传递给父组件,让父组件删除list中对应的值。子组件需要父组件将index下标传递过来,子组件向父组件通信需要一个发布订阅的模式,通过$emit发布delete事件同时将index传递出去,父组件创建子组件的时候需要监听delete事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:v-on="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:v-bind="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:v-text="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>todolist删除功能实现</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div>
<input v-model="inputValue">
<button @click="handleSubmit">提交</button>
</div>
<ul>
<!--:content 向子组件进行传值-->
<todo-item
v-for="(item,index) of list"
:key="index"
:content="item"
:index="index"
@delete="handleDelete"
></todo-item>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
Vue.component('todo-item',{
//接收父组件传过来的content值
props:['content',"index"],
template:'<li @click="handleClick">{{content}}</li>',
methods:{
handleClick:function () {
//通过$emit发布事件:定义“delete”事件,向父组件传值“index”
this.$emit('delete', this.index);
}
}
})
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
inputValue: '',
list: [],
},
methods: {
handleSubmit: function () {
this.list.push(this.inputValue);
this.inputValue = '';
},
handleDelete:function (index) {
this.list.splice(index, 1);
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
父组件向子组件通过“属性”传值,子组件向父组件通过“$emit()”进行通知传值。
三、Vue-cli的使用
3.1 简介和使用
3.1.1 简介
Vue 提供了一个官方的 CLI,为单页面应用 (SPA) 快速搭建繁杂的脚手架。它为现代前端工作流提供了 batteries-included 的构建设置。只需要几分钟的时间就可以运行起来并带有热重载、保存时 lint 校验,以及生产环境可用的构建版本。
3.1.2 使用
- 安装node。
- 安装npm。
- 创建项目。
npm install -g @vue/cli-init
# vue init now works exactly the same as vue-cli@2.x
vue init webpack my-project
- 运行项目。
npm run dev
3.2.3 项目目录介绍
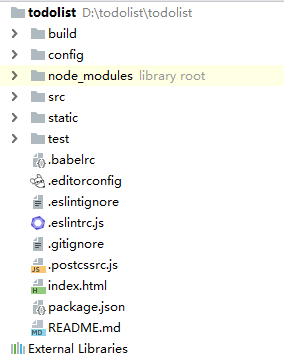
build:webpack配置文件,不需要关注。
config:针对开发环境,线上环境的配置,不需要关注。
node_modules:项目依赖。
src:源代码放置目录。
- main.js
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command
// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
// 挂载点在id为app的节点
el: '#app',
router,
// 注册一个局部组件, import App from './App' 从当前目录下App引入的组件。
// components: { App }等价于components: { App:App }引入一个名为App的组件,如果健和值相同,直接这么简写
components: { App },
// 模板显示的就是App组件下的内容,
template: '<App/>'
})
- App.vue包含一个组件所有内容。
<template>
<div id="app">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
static:静态文件目录。
test:测试目录。
index.html:整个网页最外层的html,有个id为app的挂载点,Vue的根实例挂在在该挂载点上。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<title>todolist</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- built files will be auto injected -->
</body>
</html>
3.2 使用Vue-cli开发todolist
目录文件
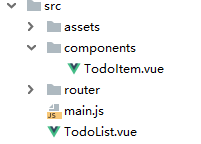
main.js
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command
// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.
import Vue from 'vue'
import router from './router'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
// 挂载点在id为app的节点
el: '#app',
router,
// 注册一个局部组件, import App from './App' 从当前目录下App引入的组件。
// components: { App }等价于components: { App:App }引入一个名为App的组件,如果健和值相同,直接这么简写
components: { TodoList },
// 模板显示的就是App组件下的内容,
template: '<TodoList/>'
})
TodoList.vue
<template>
<div>
<div>
<input v-model="inputValue"/>
<button @click="handleSubmit">提交</button>
</div>
<ul>
<todo-item
v-for="(item,index) of list"
:key="index"
:content="item"
:index="index"
@delete="handleDelete"
></todo-item>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 导入组件
import TodoItem from './components/TodoItem'
export default {
// 注册组件
components: {
'todo-item': TodoItem
},
// data之前是个对象,现在是个函数,书写各式如下
// data: function () {
// return {
// inputValue: ''
// }
// },
// 在ES6语法里可以对函数进行简化
data () {
return {
// 表示data函数有个返回值为inputValue
inputValue: '',
list: []
}
},
methods: {
handleSubmit () {
// Vue底层会做变更让this指该组件或者实例
// this.list应该指向实例的list,为何指向data的list呢?这也是Vue底层做的处理,this.list==this.$data.list,
// 给出this.list会自动去data里面找,如果没找到,会去computed计算属性里面面找。
this.list.push(this.inputValue)
this.inputValue = ''
},
handleDelete (index) {
this.list.splice(index, 1)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
TodeItem.vue
<template>
<div >
<li
@click="handleDelete"
>{{content}}</li>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['content', 'index'],
methods: {
handleDelete () {
this.$emit('delete', this.index)
}
}
}
</script>
<!-- Add "scoped" attribute to limit CSS to this component only -->
<!-- 添加"scoped"属性,该css样式只针对该组件,去掉后会影响所有组件 -->
<style scoped>
<style scoped>
</style>
一个vue只有一个最外层标签
整个教程整理自慕课网教学视频,视频地址