一、简介
通过颜色定位和Sobel算子定位可以计算出一个个的矩形区域,这些区域都是潜在车牌区域,但是在进行SVM判别是否是车牌之前,还需要进行一定的处理。主要是考虑到以下几个问题:
1、定位区域存在一定程度的倾斜,需要旋转到正常视角;
2、定位区域存在偏斜,除了进行旋转之后,还需要进行仿射变换;
3、定位出区域的大小不一致,需要对车牌的尺寸进行统一。

仿射变换(Affine Transformation 或 Affine Map),又称仿射映射,是指在几何中,一个向量空间进行一次线性变换并接上一个平移,变换为另一个向量空间的过程。它保持了二维图形的“平直性”(即:直线经过变换之后依然是直线)和“平行性”(即:二维图形之间的相对位置关系保持不变,平行线依然是平行线,且直线上点的位置顺序不变)。
一个任意的仿射变换都能表示为乘以一个矩阵(线性变换)接着再加上一个向量(平移)的形式。
那么, 我们能够用仿射变换来表示如下三种常见的变换形式:
- 旋转,rotation (线性变换)
- 平移,translation(向量加)
- 缩放,scale(线性变换)
如果进行更深层次的理解,仿射变换代表的是两幅图之间的一种映射关系。这类变换可以用一个3*3的矩阵M来表示,其最后一行为(0,0,1)。该变换矩阵将原坐标为(x,y)变换为新坐标(x',y')。
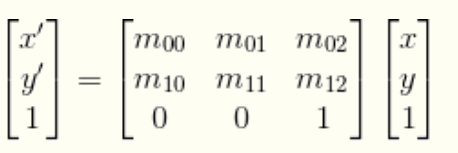
对应的opencv函数如下:
1、getRotationMatrix2D
Mat getRotationMatrix2D(Point2f center, angle, scale)
已知旋转中心坐标(坐标原点为图像左上端点)、旋转角度(单位为度°,顺时针为负,逆时针为正)、放缩比例,返回旋转/放缩矩阵。
2、warpAffine
void warpAffine(InputArray src,
OutputArray dst,
InputArray M,
Size dsize,
int flags=INTER_LINEAR,
int borderMode=BORDER_CONSTANT,
const Scalar& borderValue=Scalar())
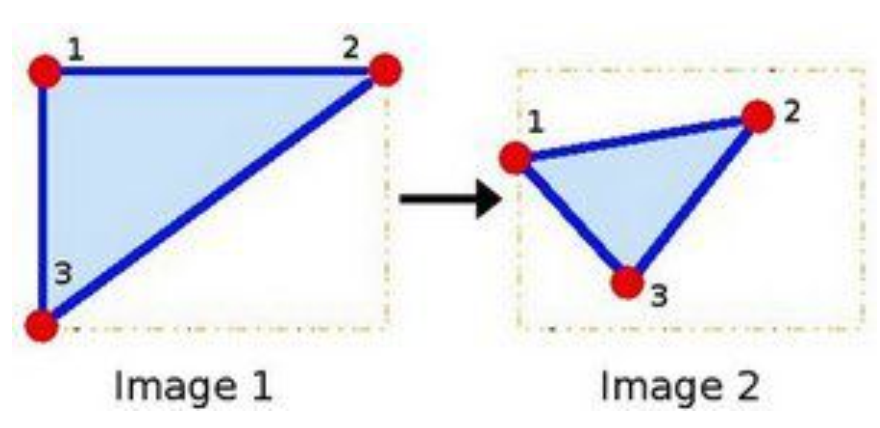
根据getRotationMatrix2D得到的变换矩阵,计算变换后的图像。warpAffine 方法要求输入的参数是原始图像的左上点,右上点,左下点,以及输出图像的左上点,右上点,左下点。注意,必须保证这些点的对应顺序,否则仿射的效果跟你预想的不一样。因此 opencv 需要的是三个点对(共六个点)的坐标,然后建立一个映射关系,通过这个映射关系将原始图像的所有点映射到目标图像上。
如下图所示:
二、偏斜扭转
具体偏斜扭转的代码如下所示:

1 int CPlateLocate::deskew(const Mat &src, const Mat &src_b, 2 vector<RotatedRect> &inRects, 3 vector<CPlate> &outPlates, bool useDeteleArea, Color color) { 4 Mat mat_debug; 5 src.copyTo(mat_debug); 6 7 for (size_t i = 0; i < inRects.size(); i++) { 8 RotatedRect roi_rect = inRects[i]; 9 10 float r = (float) roi_rect.size.width / (float) roi_rect.size.height; 11 float roi_angle = roi_rect.angle; 12 13 Size roi_rect_size = roi_rect.size; 14 if (r < 1) { 15 roi_angle = 90 + roi_angle; 16 swap(roi_rect_size.width, roi_rect_size.height); 17 } 18 19 if (m_debug) { 20 Point2f rect_points[4]; 21 roi_rect.points(rect_points); 22 for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) 23 line(mat_debug, rect_points[j], rect_points[(j + 1) % 4], 24 Scalar(0, 255, 255), 1, 8); 25 } 26 27 // changed 28 // rotation = 90 - abs(roi_angle); 29 // rotation < m_angel; 30 // m_angle=60 31 if (roi_angle - m_angle < 0 && roi_angle + m_angle > 0) { 32 Rect_<float> safeBoundRect; 33 bool isFormRect = calcSafeRect(roi_rect, src, safeBoundRect); 34 if (!isFormRect) continue; 35 36 Mat bound_mat = src(safeBoundRect); 37 Mat bound_mat_b = src_b(safeBoundRect); 38 39 if (0) { 40 imshow("bound_mat_b", bound_mat_b); 41 waitKey(0); 42 destroyWindow("bound_mat_b"); 43 } 44 45 Point2f roi_ref_center = roi_rect.center - safeBoundRect.tl(); 46 47 Mat deskew_mat; 48 if ((roi_angle - 5 < 0 && roi_angle + 5 > 0) || 90.0 == roi_angle || 49 -90.0 == roi_angle) { 50 deskew_mat = bound_mat; 51 } else { 52 53 54 Mat rotated_mat; 55 Mat rotated_mat_b; 56 57 if (!rotation(bound_mat, rotated_mat, roi_rect_size, roi_ref_center, 58 roi_angle)) 59 continue; 60 61 if (!rotation(bound_mat_b, rotated_mat_b, roi_rect_size, roi_ref_center, 62 roi_angle)) 63 continue; 64 65 // we need affine for rotatioed image 66 double roi_slope = 0; 67 68 if (isdeflection(rotated_mat_b, roi_angle, roi_slope)) { 69 affine(rotated_mat, deskew_mat, roi_slope); 70 } else 71 deskew_mat = rotated_mat; 72 } 73 74 75 Mat plate_mat; 76 plate_mat.create(HEIGHT, WIDTH, TYPE); 77 78 // haitungaga add,affect 25% to full recognition. 79 if (useDeteleArea) 80 deleteNotArea(deskew_mat, color); 81 82 83 if (deskew_mat.cols * 1.0 / deskew_mat.rows > 2.3 && 84 deskew_mat.cols * 1.0 / deskew_mat.rows < 6) { 85 86 if (deskew_mat.cols >= WIDTH || deskew_mat.rows >= HEIGHT) 87 resize(deskew_mat, plate_mat, plate_mat.size(), 0, 0, INTER_AREA); 88 else 89 resize(deskew_mat, plate_mat, plate_mat.size(), 0, 0, INTER_CUBIC); 90 91 CPlate plate; 92 plate.setPlatePos(roi_rect); 93 plate.setPlateMat(plate_mat); 94 if (color != UNKNOWN) plate.setPlateColor(color); 95 96 outPlates.push_back(plate); 97 } 98 } 99 } 100 101 return 0; 102 }
下面我们对代码的主要逻辑过程做一个简单的梳理,对于定位后的车牌,首先进行旋转角度的判定,在-5°~5°范围内车牌直接输出,在-60°~ -5°和 5°~60°范围内车牌,首先进行偏斜程度的判定,如果偏斜程度不严重,旋转后输出,否则旋转角度后还需要仿射变换。
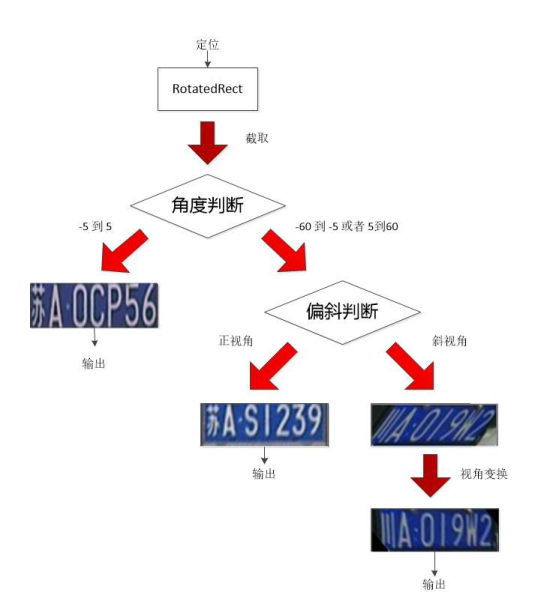
rotation()函数主要用于对倾斜的图片进行旋转, 具体的代码如下:

1 bool CPlateLocate::rotation(Mat &in, Mat &out, const Size rect_size, 2 const Point2f center, const double angle) { 3 Mat in_large; 4 in_large.create(int(in.rows * 1.5), int(in.cols * 1.5), in.type()); 5 6 float x = in_large.cols / 2 - center.x > 0 ? in_large.cols / 2 - center.x : 0; 7 float y = in_large.rows / 2 - center.y > 0 ? in_large.rows / 2 - center.y : 0; 8 9 float width = x + in.cols < in_large.cols ? in.cols : in_large.cols - x; 10 float height = y + in.rows < in_large.rows ? in.rows : in_large.rows - y; 11 12 /*assert(width == in.cols); 13 assert(height == in.rows);*/ 14 15 if (width != in.cols || height != in.rows) return false; 16 17 Mat imageRoi = in_large(Rect_<float>(x, y, width, height)); 18 addWeighted(imageRoi, 0, in, 1, 0, imageRoi); 19 20 Point2f center_diff(in.cols / 2.f, in.rows / 2.f); 21 Point2f new_center(in_large.cols / 2.f, in_large.rows / 2.f); 22 23 Mat rot_mat = getRotationMatrix2D(new_center, angle, 1); 24 25 /*imshow("in_copy", in_large); 26 waitKey(0);*/ 27 28 Mat mat_rotated; 29 warpAffine(in_large, mat_rotated, rot_mat, Size(in_large.cols, in_large.rows), 30 CV_INTER_CUBIC); 31 32 /*imshow("mat_rotated", mat_rotated); 33 waitKey(0);*/ 34 35 Mat img_crop; 36 getRectSubPix(mat_rotated, Size(rect_size.width, rect_size.height), 37 new_center, img_crop); 38 39 out = img_crop; 40 41 if (0) { 42 imshow("out", out); 43 waitKey(0); 44 destroyWindow("out"); 45 } 46 47 /*imshow("img_crop", img_crop); 48 waitKey(0);*/ 49 50 return true; 51 }
在旋转的过程当中,遇到一个问题,就是旋转后的图像被截断了,如下图所示:

仔细分析下代码可以发现,getRotationMatrix2D() 函数主要根据旋转中心和角度进行旋转,当旋转角度还小时,一切都还好,但当角度变大时,明显我们看到的外接矩形的大小也在扩增。在这里,外接矩形被称为视框,也就是我需要旋转的正方形所需要的最小区域。随着旋转角度的变大,视框明显增大。 如下图所示: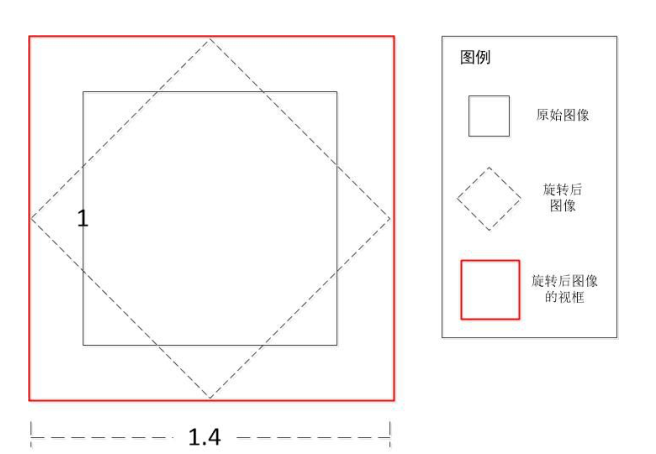
EasyPR使用了一个极为简单的策略,它将原始图像与目标图像都进行了扩大化。首先新建一个尺寸为原始图像 1.5 倍的新图像,接着把原始图像映射到新图像上,于是我们得到了一个显示区域(视框)扩大化后的原始图像。显示区域扩大以后,那些在原图像中没有值的像素被置了一个初值。接着调用 warpAffine 函数,使用新图像的大小作为目标图像的大小。warpAffine 函数会将新图像旋转,并用目标图像尺寸的视框去显示它。于是我们得到了一个所有感兴趣区域都被完整显示的旋转后图像,这样,我们再使用 getRectSubPix()函数就可以获得想要的车牌区域了。
接下来就是分析截取后的车牌区域。车牌区域里的车牌分为正角度和偏斜角度两种。对于正的角度而言,可以看出车牌区域就是车牌,因此直接输出即可。而对于偏斜角度而言,车牌是平行四边形,与矩形的车牌区域不重合。如何判断一个图像中的图形是否是平行四边形?
一种简单的思路就是对图像二值化,然后根据二值化图像进行判断。为了判断二值化图像中白色的部分是平行四边形。一种简单的做法就是从图像中选择一些特定的行。计算在这个行中,第一个全为0的串的长度。从几何意义上来看, 这就是平行四边形斜边上某个点距离外接矩形的长度。假设我们选择的这些行位于二值化图像高度的 1/4,2/4,3/4 处的话,如果是白色图形是矩形的话, 这些串的大小应该是相等或者相差很小的,相反如果是平行四边形的话,那么这些串的大小应该不等,并 且呈现一个递增或递减的关系。通过这种不同,我们就可以判断车牌区域里的图形,究竟是矩形还是平行 四边形。
偏斜判断的另一个重要作用就是,计算平行四边形倾斜的斜率,这个斜率值用来在下面的仿射变换中 发挥作用。我们使用一个简单的公式去计算这个斜率,那就是利用上面判断过程中使用的串大小,假设二值化图像高度的 1/4,2/4,3/4 处对应的串的大小分别为 len1,len2,len3,车牌区域的高度为 Height。 一个计算斜率 slope 的计算公式就是:(len3-len1)/Height*2。

函数 isdeflection() 的主要功能是判断车牌偏斜的程度,并且计算偏斜的值。具体代码如下:

1 bool CPlateLocate::isdeflection(const Mat &in, const double angle, 2 double &slope) { 3 int nRows = in.rows; 4 int nCols = in.cols; 5 6 assert(in.channels() == 1); 7 8 int comp_index[3]; 9 int len[3]; 10 11 comp_index[0] = nRows / 4; 12 comp_index[1] = nRows / 4 * 2; 13 comp_index[2] = nRows / 4 * 3; 14 15 const uchar* p; 16 17 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { 18 int index = comp_index[i]; 19 p = in.ptr<uchar>(index); 20 21 int j = 0; 22 int value = 0; 23 while (0 == value && j < nCols) value = int(p[j++]); 24 25 len[i] = j; 26 } 27 28 // len[0]/len[1]/len[2] are used to calc the slope 29 30 double maxlen = max(len[2], len[0]); 31 double minlen = min(len[2], len[0]); 32 double difflen = abs(len[2] - len[0]); 33 34 double PI = 3.14159265; 35 36 double g = tan(angle * PI / 180.0); 37 38 if (maxlen - len[1] > nCols / 32 || len[1] - minlen > nCols / 32) { 39 40 double slope_can_1 = 41 double(len[2] - len[0]) / double(comp_index[1]); 42 double slope_can_2 = double(len[1] - len[0]) / double(comp_index[0]); 43 double slope_can_3 = double(len[2] - len[1]) / double(comp_index[0]); 44 slope = abs(slope_can_1 - g) <= abs(slope_can_2 - g) ? slope_can_1 45 : slope_can_2; 46 return true; 47 } else { 48 slope = 0; 49 } 50 51 return false; 52 }
我们已经实现了旋转功能,并且在旋转后的区域中截取了车牌区域,然后判断车牌区域中的图形是一 个平行四边形。下面要做的工作就是把平行四边形扭正成一个矩形。

函数 affine() 的主要功能是对图像进行根据偏斜角度,进行仿射变换。具体代码如下:

1 void CPlateLocate::affine(const Mat &in, Mat &out, const double slope) { 2 3 Point2f dstTri[3]; 4 Point2f plTri[3]; 5 6 float height = (float) in.rows; 7 float width = (float) in.cols; 8 float xiff = (float) abs(slope) * height; 9 10 if (slope > 0) { 11 12 // right, new position is xiff/2 13 14 plTri[0] = Point2f(0, 0); 15 plTri[1] = Point2f(width - xiff - 1, 0); 16 plTri[2] = Point2f(0 + xiff, height - 1); 17 18 dstTri[0] = Point2f(xiff / 2, 0); 19 dstTri[1] = Point2f(width - 1 - xiff / 2, 0); 20 dstTri[2] = Point2f(xiff / 2, height - 1); 21 } else { 22 23 // left, new position is -xiff/2 24 25 plTri[0] = Point2f(0 + xiff, 0); 26 plTri[1] = Point2f(width - 1, 0); 27 plTri[2] = Point2f(0, height - 1); 28 29 dstTri[0] = Point2f(xiff / 2, 0); 30 dstTri[1] = Point2f(width - 1 - xiff + xiff / 2, 0); 31 dstTri[2] = Point2f(xiff / 2, height - 1); 32 } 33 34 Mat warp_mat = getAffineTransform(plTri, dstTri); 35 36 Mat affine_mat; 37 affine_mat.create((int) height, (int) width, TYPE); 38 39 if (in.rows > HEIGHT || in.cols > WIDTH) 40 41 warpAffine(in, affine_mat, warp_mat, affine_mat.size(), 42 CV_INTER_AREA); 43 else 44 warpAffine(in, affine_mat, warp_mat, affine_mat.size(), CV_INTER_CUBIC); 45 46 out = affine_mat; 47 }
最后使用 resize 函数将车牌区域统一化为 EasyPR 的车牌大小,大小为136*36。
