1.向服务器发送请求的途径
# 向服务器发送请求的途径 1. 浏览器地址栏,默认get请求 2. form表单: get请求 post请求 3. a标签,默认get请求 4. Ajax 特点: (1) 异步请求 (2) 局部刷新 # 比如注册用户名时提醒,用户名已存在 方式: get post
2、简介
AJAX(Asynchronous Javascript And XML)翻译成中文就是“异步Javascript和XML”。即使用Javascript语言与服务器进行异步交互,传输的数据为XML(当然,传输的数据不只是XML,现在更多使用json数据)。
- 同步交互:客户端发出一个请求后,需要等待服务器响应结束后,才能发出第二个请求;
- 异步交互:客户端发出一个请求后,无需等待服务器响应结束,就可以发出第二个请求。
AJAX除了异步的特点外,还有一个就是:浏览器页面局部刷新;(这一特点给用户的感受是在不知不觉中完成请求和响应过程)
先学习jQuery的Ajax
2、基于jquery的ajax请求
1.在线jquery cdn
http://www.jq22.com/jquery-info122
1一个简单的例子Django文件 -Ajax传递数据


urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('index/', views.index), path('test_ajax/',views.test_ajax), ]

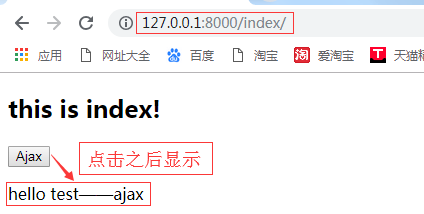
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse # Create your views here. def index(request): return render(request,'index.html') def test_ajax(request): return HttpResponse('hello test——ajax')
2,基于Ajax发送数据到服务器
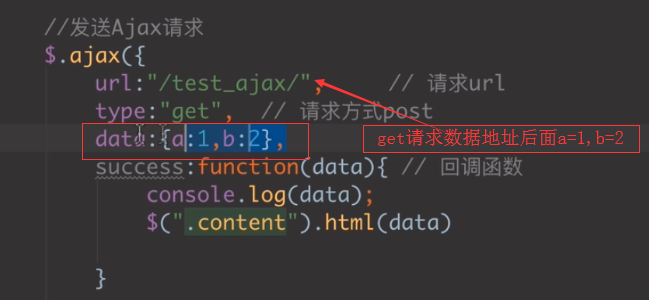
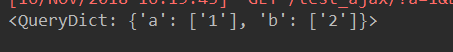
def test_ajax(request): print(request.GET) return HttpResponse('hello test——ajax')
print:
3 基于Ajax发送数据 实现一个计算功能----post请求

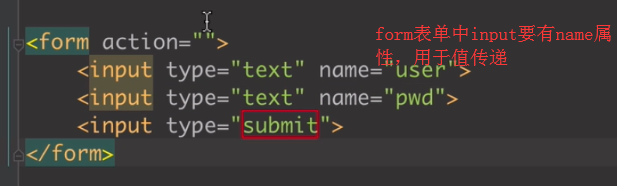
input不需要name值就可以取值;通过value
settings.py
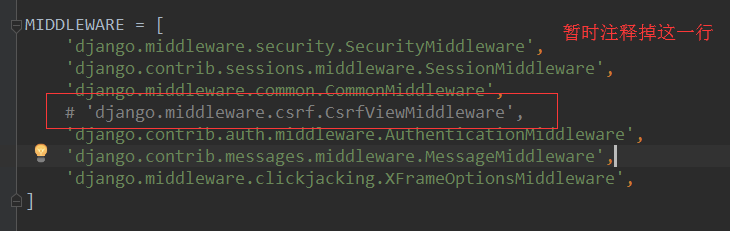

urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('index/', views.index), path('test_ajax/',views.test_ajax), path('calc/',views.calc), ]
def calc(request): print(request.POST)
post请求更安全,不会在浏览器中显示需要传递的数据 n1 = request.POST.get('n1') # n1,n2是ajax传递过来的参数 n2 = request.POST.get('n2') ret = int(n1) + int(n2) return HttpResponse(ret)

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script src="http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/jquery/jquery-2.1.4.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <h2>this is index!</h2> <button class="Ajax">Ajax</button> <p class="content"></p> <hr> <p>计算器</p> <input type="text" id="num1"> + <input type="text" id="num2"> = <input type="text" id="ret"> <button id="calc">计算</button> <script type="text/javascript"> $(function () { $('.Ajax').click(function () { {#alert(123)#} $.ajax({ url:'/test_ajax/', //请求url type:'get', //请求方式get data:{a:1,b:2}, success:function (data) { //回调函数 console.log(data); $('.content').html(data) } }) }); $('#calc').click(function () { $.ajax({ url:'/calc/', type:'post', data:{ "n1":$('#num1').val(), //n1,n2 是自定义的变量名 "n2":$('#num2').val() }, {# val()获取值-----val(data)设置值#} success:function (data) { $('#ret').val(data) } }) }) }) </script> {# 发送Ajax请求#} </body> </html>
get和post的区别
https://www.cnblogs.com/logsharing/p/8448446.html
用Ajax的实现form表单的提交-login验证--本质数据传输
ret_string = json.dumps(ret) # 序列化 某种格式--->string
var _data = JSON.parse(data) // 反序列化 string----> object {}
添加数据库表

from django.db import models # Create your models here. class User(models.Model): name=models.CharField(max_length=32) pwd=models.CharField(max_length=32)

from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path,re_path from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('index/', views.index), path('test_ajax/',views.test_ajax), path('calc/',views.calc), path('login/',views.login), ]

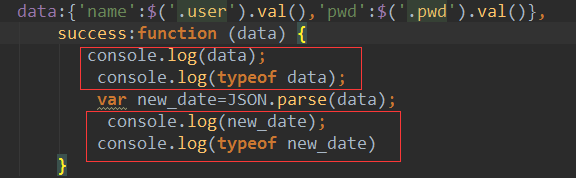
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script src="http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/jquery/jquery-2.1.4.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <h2>this is index!</h2> <button class="Ajax">Ajax</button> <p class="content"></p> <hr> <p>计算器</p> <input type="text" id="num1"> + <input type="text" id="num2"> = <input type="text" id="ret"> <button id="calc">计算</button> <hr> <p>form表单提交用ajax实现</p> <form action=""> 用户名<input type="text" class="user"> 密码<input type="password" class="pwd"> <input type="button" value="submit" class="logon_btn"> <span class="error" style="color: red; margin-left: 10px;"></span> </form> <script type="text/javascript"> $(function () { $('.Ajax').click(function () { {#alert(123)#} $.ajax({ url:'/test_ajax/', //请求url type:'get', //请求方式get data:{a:1,b:2}, success:function (data) { //回调函数 console.log(data); $('.content').html(data) } }) }); $('#calc').click(function () { $.ajax({ url:'/calc/', type:'post', data:{ "n1":$('#num1').val(), //n1,n2 是自定义的变量名 "n2":$('#num2').val() }, {# val()获取值-----val(data)设置值#} success:function (data) { $('#ret').val(data) } }) }); //登录验证 $('.logon_btn').click(function () { $.ajax( {url:'/login/', type:'post', data:{'name':$('.user').val(),'pwd':$('.pwd').val()}, success:function (data) { console.log(data); console.log(typeof data); var new_date=JSON.parse(data); console.log(new_date); console.log(typeof new_date) if (new_date.user){ alert('登录成功') } else {$('.error').html(new_date.msg) } } } ) }) }) </script> {# 发送Ajax请求#} </body> </html>

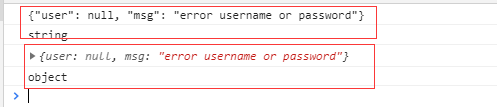
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse # Create your views here. def index(request): return render(request,'index.html') def test_ajax(request): print(request.GET) return HttpResponse('hello test——ajax') def calc(request): print(request.POST) n1 = request.POST.get('n1') # n1,n2是ajax传递过来的参数 n2 = request.POST.get('n2') ret = int(n1) + int(n2) return HttpResponse(ret) from app01.models import User def login(request): user=request.POST.get('name') pwd=request.POST.get('pwd') user_obj=User.objects.filter(name=user,pwd=pwd).first() ret = {"user": None, "msg": None} if user_obj: ret["user"] = user_obj.name else: ret["msg"] = "error username or password" import json ret_string = json.dumps(ret) # 序列化 某种格式--->string return HttpResponse(ret_string)
基于form表单的文件上传


<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h3>基于form表单的文件上传,之前上传的是key-value</h3> <form action="" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> 用户名<input type="text" name="user"> 头像<input type="file" name="avatar"> <input type="submit"> </form> </body> </html>

def file_put(request): if request.method=='POST': print(request.POST) print(request.FILES) file_obj=request.FILES.get('avatar') with open(file_obj.name,'wb') as f: for line in file_obj: f.write(line) return HttpResponse('ok') return render(request,'file_put.html')
2个重点
1、form表单enctype
<form action="" method="post"> <form action="" method="post" enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded"> # 默认是这个 <form action="" method="post" enctype="text/plain"> # 基本不用 <form action="" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> # 上传文件用
2、如何读取上传的图片
print(request.FILES) # 上传的文件保存在FILES # 保存文件 file_obj = request.FILES.get('userImg', '') # 取出文件对象 file_name = file_obj.name # 取出文件名称
<QueryDict: {'user': ['yuan'], 'pwd': ['111']}>
http请求头之contentType(请求头)
ContentType指的是请求体的编码类型,常见的类型共有3种:

1、application/x-www-form-urlencoded
这应该是最常见的 POST 提交数据的方式了。浏览器的原生 <form> 表单,如果不设置 enctype 属性,那么最终就会以 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 方式提交数据。
请求类似于下面这样(无关的请求头在本文中都省略掉了):
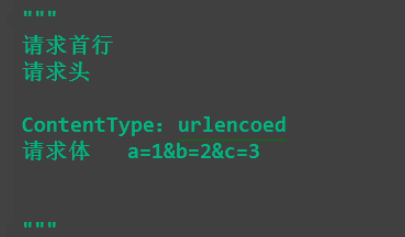
2 multipart/form-data-用于文件传输
3 application/json
application/json 这个 Content-Type 作为响应头大家肯定不陌生。实际上,现在越来越多的人把它作为请求头,用来告诉服务端消息主体是序列化后的 JSON 字符串。
由于 JSON 规范的流行,除了低版本 IE 之外的各大浏览器都原生支持 JSON.stringify,服务端语言也都有处理 JSON 的函数,使用 JSON 不会遇上什么麻烦。
JSON 格式支持比键值对复杂得多的结构化数据,这一点也很有用。记得我几年前做一个项目时,需要提交的数据层次非常深,我就是把数据 JSON 序列化之后来提交的。
不过当时我是把 JSON 字符串作为 val,仍然放在键值对里,以 x-www-form-urlencoded 方式提交。
ajax传递json数据
<h3>基于Ajax文件上传</h3> <form> 用户名<input type="text" name="user"> 密码<input type="password" name="pwd"> <input type="button" class="btn" value="Ajax"> </form> <script type="text/javascript"> $('.btn').click(function () { $.ajax({ url:'', type:'post', contentType:'application/json', data:JSON.stringify({a:1,b:2}), success:function (data) { console.log(data) } }) }) </script>
Ajax上传文件
file_put视图代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script src="http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/jquery/jquery-2.1.4.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <h3>ajax上传文件</h3> <form> username <input type="text" id="user"> userImg <input type="file" id="userImg"> <input type="button" value="提交" id="btn"> </form> <script> $('#btn').click(function () { var formdata = new FormData(); // FormData对象 formdata.append("user",$("#user").val()); formdata.append("userImg",$("#userImg")[0].files[0]); $.ajax({ url:"", type:"post", contentType:false, // 是否编码, // 告诉jQuery不要去处理发送的数据 processData:false, // 是否预处理 // 告诉jQuery不要去设置Content-Type请求头 data:formdata, success:function (data) { alert(data) } }) }) </script> </body> </html>
views.py
def file_put(request): if request.method=='POST': print('body',request.body)# 请求报文中的请求体 print('post',request.POST) print(request.FILES) file_obj=request.FILES.get('file') with open(file_obj.name,'wb') as f: for line in file_obj: f.write(line) return HttpResponse('ok') return render(request,'file_put.html')
FormData对象
详细解释
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/FormData/Using_FormData_Objects
https://blog.csdn.net/saharalili/article/details/79002568
FormData对象用以将数据编译成键值对,以便用XMLHttpRequest来发送数据。其主要用于发送表单数据,但亦可用于发送带键数据(keyed data),而独立于表单使用。
如果表单enctype属性设为multipart/form-data ,则会使用表单的submit()方法来发送数据,从而,发送数据具有同样形式。
调用append()方法来添加数据
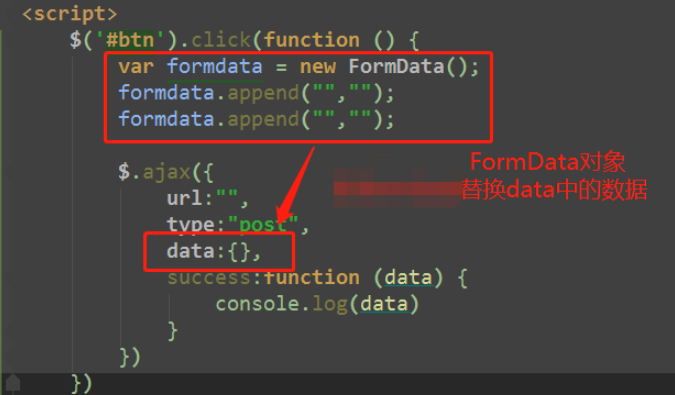

总结:
基于form表单的普通数据、文件传输:

<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/jquery/jquery-2.1.4.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h3>基于form表单的文件上传,之前上传的是key-value</h3>
<form action="" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> # 文件传输比加的内容
用户名<input type="text" name="user"> # form表单的普通数据传输
头像<input type="file" name="avatar">
<input class="submit" type="submit">
</form>
views.py
def file_put(request): if request.method=='POST': name=request.POST.get('user') # 接受普通的数据 print(name) file_obj=request.FILES.get('avatar') 接受文件数据 with open(file_obj.name,'wb') as f: for line in file_obj: f.write(line) return HttpResponse('ok') return render(request,'file_put.html')
----------------------------------------------------------------
基于Ajax的form表单数据传输

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script src="http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/jquery/jquery-2.1.4.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <h2>this is index!</h2> <button class="Ajax">Ajax</button> <p class="content"></p> <hr> <p>计算器</p> <input type="text" id="num1"> + <input type="text" id="num2"> = <input type="text" id="ret"> <button id="calc">计算</button> <hr> <p>form表单提交用ajax实现</p> <form action=""> 用户名<input type="text" class="user"> 密码<input type="password" class="pwd"> <input type="button" value="submit" class="logon_btn"> <span class="error" style="color: red; margin-left: 10px;"></span> </form> <script type="text/javascript"> $(function () { $('.Ajax').click(function () { {#alert(123)#} $.ajax({ url:'/test_ajax/', //请求url type:'get', //请求方式get data:{a:1,b:2}, success:function (data) { //回调函数 console.log(data); $('.content').html(data) } }) }); $('#calc').click(function () { $.ajax({ url:'/calc/', type:'post', data:{ "n1":$('#num1').val(), //n1,n2 是自定义的变量名 "n2":$('#num2').val() }, {# val()获取值-----val(data)设置值#} success:function (data) { $('#ret').val(data) } }) }); //登录验证 $('.logon_btn').click(function () { $.ajax( {url:'/login/', type:'post', data:{'name':$('.user').val(),'pwd':$('.pwd').val()}, success:function (data) { console.log(data); console.log(typeof data); var new_date=JSON.parse(data); console.log(new_date); console.log(typeof new_date); if (new_date.user){ alert('登录成功') } else {$('.error').html(new_date.msg) } } } ) }) }) </script> {# 发送Ajax请求#} </body> </html>

def test_ajax(request): print(request.GET) return HttpResponse('hello test——ajax') def calc(request): print(request.POST) n1 = request.POST.get('n1') # n1,n2是ajax传递过来的参数 n2 = request.POST.get('n2') ret = int(n1) + int(n2) return HttpResponse(ret) from app01.models import User def login(request): user=request.POST.get('name') pwd=request.POST.get('pwd') user_obj=User.objects.filter(name=user,pwd=pwd).first() ret = {"user": None, "msg": None} if user_obj: ret["user"] = user_obj.name else: ret["msg"] = "error username or password" import json ret_string = json.dumps(ret) # 序列化 某种格式--->string return HttpResponse(ret_string)
文件传输
file_put.html
<h3>基于Ajax文件上传</h3> <form > 用户名<input type="text" id="user"> 文件<input type="file" id="file"> <input type="button" id="btn" value="Ajax"> </form> <script type="text/javascript"> $('#btn').click(function () { var formdata=new FormData(); formdata.append('user',$('#user').val()); formdata.append('file',$('#file')[0].files[0]); $.ajax({ url:'', type:'post', {#contentType:'application/json',#} processData: false, // 不处理数据 contentType: false, // 不设置内容类型 data:formdata, success:function (data) { console.log(data) } }) }) </script>
views.py
def file_put(request): if request.method == 'POST': # 基于ajax数据传输 print('body',request.body)# 请求报文中的请求体 print('post',request.POST) print(request.FILES) file_obj = request.FILES.get('file') with open(file_obj.name, 'wb') as f: for line in file_obj: f.write(line) return HttpResponse('ok') return render(request, 'file_put.html')

