一、运算符
计算机可以进行的运算有很多种,可不只加减乘除这么简单,运算按种类可分为算数运算、比较运算、逻辑运算、赋值运算、成员运算、身份运算、位运算,今天我们暂只学习算数运算、比较运算、逻辑运算、赋值运算
算数运算
以下假设变量:a=10,b=20

比较运算
以下假设变量:a=10,b=20

赋值运算
以下假设变量:a=10,b=20

逻辑运算

#三者的优先级从高到低分别是:not,or,and >>> 3>4 and 4>3 or 1==3 and 'x' == 'x' or 3 >3 False #最好使用括号来区别优先级,其实意义与上面的一样 >>> (3>4 and 4>3) or ((1==3 and 'x' == 'x') or 3 >3) False
身份运算
#is比较的是id #而==比较的是值
1、运算符分类
- 结果是值
算数运算:
a = 10 * 10
赋值运算:
a = a + 1 a+=1
- 结果是布尔值
比较运算:
a = 1 > 5
逻辑运算:
a = 1>6 or 1==1
成员运算:
a = "蚊" in "郑建文"
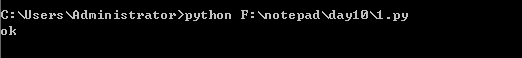
代码:
name = "郑建文" if "文" in name: ##判断该字符是否在该字符串中 print("ok") else: print("no")
执行结果:
二、基本数据类型
1.数字 int (所有的功能,都放在int里)
a1 = 123
a1 = 456
- int
- 将字符串转换为数字
a = "123"
print(type(a),a)
b = int(a)
print(type(b),b)
执行结果:

ps:字符串与整型混合不能转换
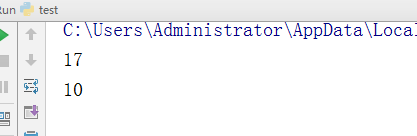
- -将这个字符串以十六进制的方式进行转换,转换为十进制
num = "0011" v = int(num, base=16) ##十六进制中的0011转换为10进制中的17,int是将所有的数字转换为十进制 print(v)
num = "a" #这个字符串以十六进制的方式进行转换
s= int(num, base=16)
print(s)
执行结果:
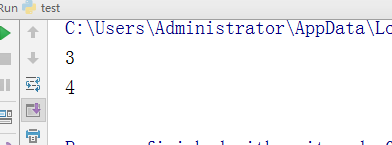
- bit_lenght
- # 当前数字的二进制,至少用n位表示
age = 5 r = age.bit_length() print(r) age = 9 c = age.bit_length() print(c)
执行结果:
2.字符串 str
s1 = "asdf"
s2 = "asdffas"
- -首字母大写,其他字母全部小写
test = "aLEX" v = test.capitalize() # 首字母大写,其他字母全部小写 print(v)
执行结果:

- -所有变小写,casefold更强大,很多未知的对相应变小写
test='XUPT'
v1 = test.casefold()
print(v1)
v2 = test.lower()
print(v2)
执行结果:

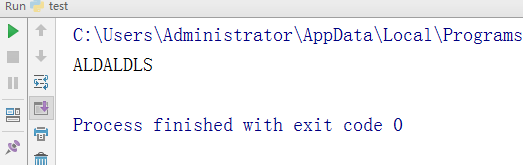
- -所有字母变大写
le='aldaldls' w=le.upper() print(w)
执行结果:
- -设置宽度,并将内容居中
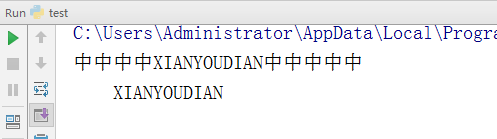
test='XIANYOUDIAN' v = test.center(20,'中') print(v) # 20 代指总长度
# ‘中’表示空白未知填充,一个字符,可有可无
test='XIANYOUDIAN' v = test.center(20) #总长度20位,不够左右两边空格填充
print(v)
执行结果:
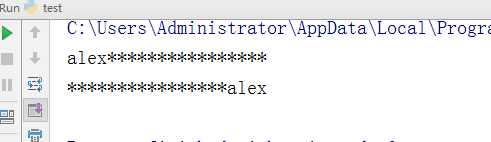
- -左边和右边以*填充(总共20位)
test = "alex" v = test.ljust(20,"*") print(v) test = "alex" v = test.rjust(20,"*") print(v)
执行结果:
- -左边以0填充(总共20位)
test = "alex" v = test.zfill(20) ##后边不能加其他参数 print(v)
执行结果:

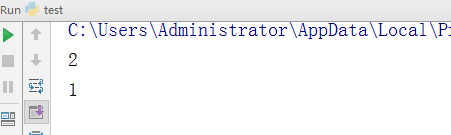
- -去字符串中寻找,寻找子序列的出现次数
test = "aLexalexr" v = test.count('ex') print(v) test = "aLexalexr" v = test.count('ex',6,8) ##大于等于6,小于8 print(v)
执行结果:
- -编码指定转化
encode
decode
- -以什么什么结尾,以什么什么开始
test = "alex" v = test.endswith('ex') ##也可以指定位置参数,从哪里开始统计 w = test.startswith('ex') print(v) print(w)
执行结果:

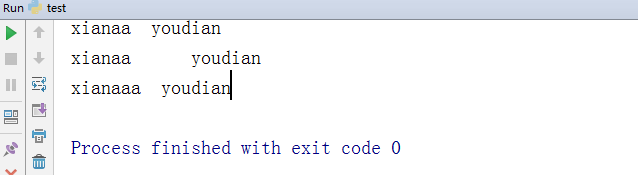
- -expandtabs
le='xianaa youdian' ## 为横向制表符,默认为4个空格,相当于一个tab print(le) ##输出结果y之前总共为4个字符的整数倍 a = le.expandtabs(6) ##设置6个6个分,到 时差几个就是几个空格 print(a) test = "xianaaa youdian" v = test.expandtabs(3) print(v)
执行结果:
- -利用expandtabs制表,左对齐
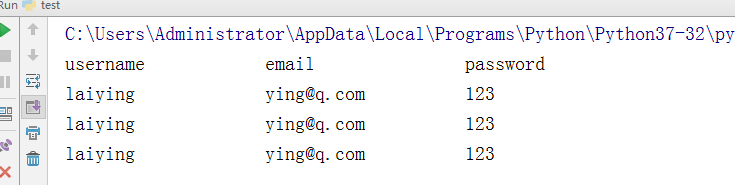
test = "username email password laiying ying@q.com 123 laiying ying@q.com 123 laiying ying@q.com 123" v = test.expandtabs(20) print(v)
执行结果:
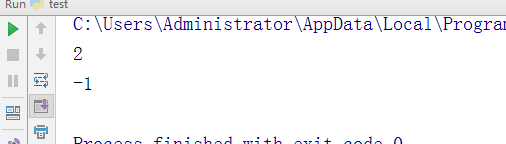
- -从开始往后找,找到第一个之后,获取其位置,位置格式为> 或 >=,未找到返回-1
test = "alexalex" v = test.find('ex') w = test.find('eax') print(v) print(w)
执行结果:
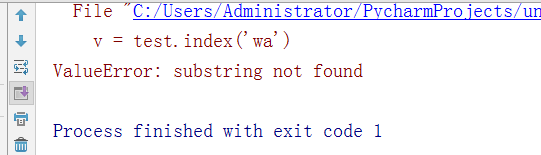
- -index和find功能相同,but当index找不到时,会报错不会返回-1
test = "alexalex"
v = test.index('wa')
print(v)
执行结果:
- -格式化,将一个字符串中的占位符替换为指定的值
test = 'i am {name}, age {a}' print(test) v = test.format(name='alex',a=19) print(v)
执行结果:

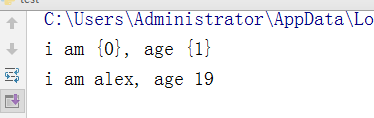
第二种方式:
test = 'i am {0}, age {1}' print(test) v = test.format('alex',19) print(v)
执行结果:
第三种方式,使用.format_map魔法:
test = 'i am {name}, age {a}' v1 = test.format(name='df',a=10) v2 = test.format_map({"name": 'alex', "a": 19}) ##变量名:所赋的值
print(v1)
print(v2)
执行结果:

- -判断字符串中只包含字母和数字
- test = "ad123" v = test.isalnum() print(v) test = "1232!!!" w = test.isalnum() print(w)
执行结果:

- -判断字符串中是否只有字母(含汉字)
test = "asdf李" v = test.isalpha() print(v) test = "asdf李111" q = test.isalpha() print(q)
执行结果:
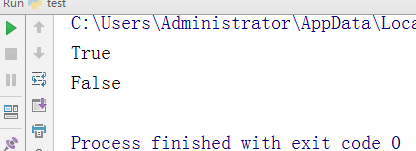
- -iddecimal ,isdigit,isnumeric 判断当前输入的值,是否是数字
test = "②" #这种特殊的数字 v1 = test.isdecimal() #判断是否是数字 v2 = test.isdigit() #判断是否是数字,还可以判断特殊的数字! 4 print(v1,v2) v3 = test.isnumeric() print(v1) print(v2) print(v3) test = "123" #这种特殊的数字 a1 = test.isdecimal() #判断是否是数字 a2 = test.isdigit() #判断是否是数字,还可以判断特殊的数字! 4 print(v1,v2) print(a1) print(a2)
执行结果:

代码2:
test = "三" #这种特殊的数字 v1 = test.isdecimal() v2 = test.isdigit() v3 = test.isnumeric() print(v1) print(v2) print(v3)
执行结果:
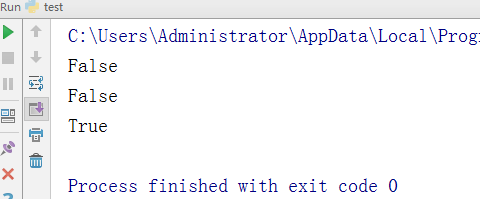
- -判断变量名是否合法(内置函数名如def、class也合法)
name = '_123swhthaitun' lee = '1csda' v1=name.isidentifier() v2=lee.isidentifier() print(v1) print(v2)
执行结果:

- -是否都可以打印出来
test = "oiuas dfkj" lee = 'adladd131@' v1 = test.isprintable() v2 = lee.isprintable() print(v1) print(v2)
执行结果:
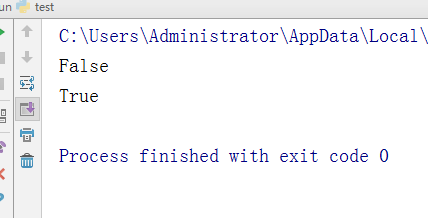
- -判断是否全是空格
test = " " lee = '123' v1 = lee.isspace() v2 = test.isspace() print(v1) print(v2)
执行结果:

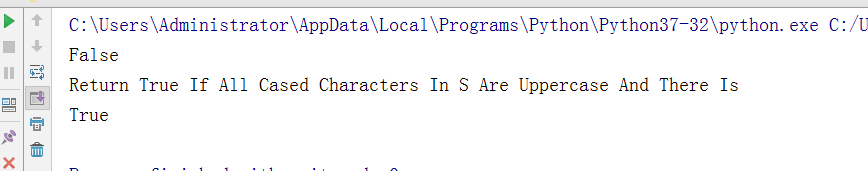
- -判断是否是标题,将不是标题的转换为标题
test = "Return True if all cased characters in S are uppercase and there is" v1 = test.istitle() #判断标题,首字母是否大写 print(v1) v2 = test.title() #把普通的字符串转换为首字母大写 print(v2) v3 = v2.istitle() #再判断v2,就是大写啦。所以是True print(v3)
执行结果:
- -重点:将字符串中的每一个元素按照指定分隔符进行拼接
test = "你是风儿我是沙" v = "_".join(test) print(v)
执行结果:

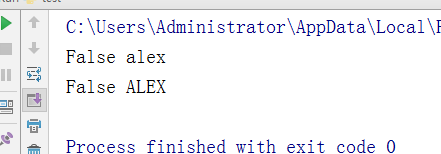
- -判断是否全部是大小写 和 转换为大小写
test = "ALeX" v1 = test.islower() #判断所有是否是小写; 用于验证码:不管用户输入的是大写或小写,统一转换为小写 v2 = test.lower() #所有转换为小写 print(v1, v2)
v3 = test.isupper() #判断是否是大写
v4 = test.upper() #转换为大写
print(v3,v4)
执行结果:
- -去除左右空白
test = " alex " v1 = test.lstrip() #处理左边的空格 v2 = test.rstrip() #处理右边的空格 v3 = test.strip() #两边都处理空格 print(v1) print(v2) print(v3)
执行结果:

此方法也可以取掉 和 产生的空白
test = " lex " v1 = test.lstrip() #处理左边的 or print(test) print(v1)
执行结果:

取掉最左边的执行字符
test = "xalex " v1 = test.lstrip('x') #处理左边的x print(v1)
执行结果:

取掉指定字符串
test = "xalex" v1 = test.rstrip('91lexex') #从右边开始往左边找,先进行最长字符串匹配 print(v1)
执行结果:
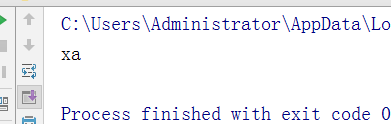
-对应字符替换
v = "asidufkasd;fiuadkf;adfkjalsdjf" m = str.maketrans("aeiou", "12345") #定义所有a替换为1,e替换为2,其他依此类推 new_v = v.translate(m) print(new_v)
执行结果:
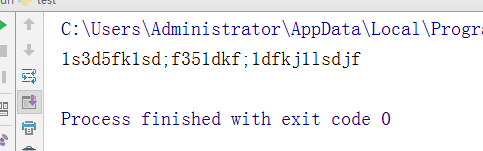
利用replace方法替换
test = "alexalexalex"
v = test.replace("ex",'bbb',2) ##将ex替换为bbb
print(v)
执行结果:

-以指定字符来分割字符串(显示执行的字符)返回三元元组,不够分为三部分就分为两部分
test = "testasdsddfg" v = test.partition('s') #找到第1个s进行分割,只能分成三部分 print(v) test = "testasdsddfg" v = test.rpartition('s') ##从末尾往前找,找到第一个s进行分割 print(v)
执行结果:

-split, rsplit 由执行字符分割(不显示指定的这个字符)返回三元元组
test = "testasdsddfg" v1 = test.split('s',2) print(v1) test = "testasdsddfg" v2 = test.rsplit('s',2) print(v2)
执行结果:
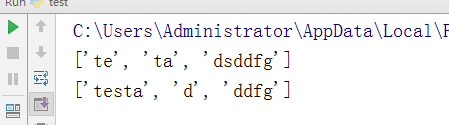
-根据换行分割
test = "asdfadfasdf asdfasdf adfasdf" v1 = test.splitlines() ##默认为False(不保留 ) print(v1) test = "asdfadfasdf asdfasdf adfasdf" v2 = test.splitlines(True) print(v2) test = "asdfadfasdf asdfasdf adfasdf" v3 = test.splitlines(False) #参数只能加True or False print(v3)
执行结果:

总结:上边的魔法中,最重要的有7个,分别是
- join
- split
- find
- strip
- upper
- lower
- replace
三、4个灰魔法
1.for循环
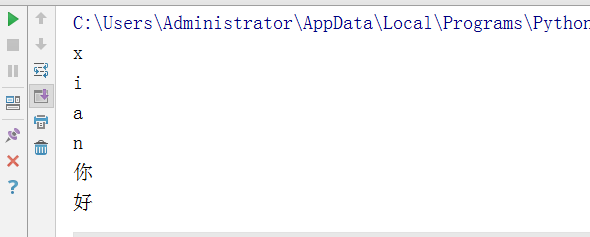
test='xian你好' for i in test: print(i)
输出结果:
range的用法:
v1 = range(100) ##(100)和(0,100)效果相同,也可以指定步长(0,100,5),输出0 5 10......95,还可以写入(100,0,-1),输出100 99 ......1
for i in v1: print(i)
输出0 1 2 3 4 5 6......99
2.索引----获取字符串中的指定字符(在字符串、列表中均可使用)
test = 'xianyoudian'
v = test[3]
print(v)
lee = ['we','age',12,[1,'1w'] ]
w = lee[2]
print(w)
执行结果:
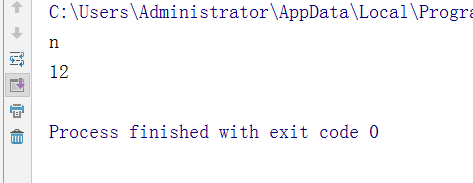
3.切片--获取字符串中的其中一段
test = 'xianyoudian' v1 = test[2:] ##大于等于2 v2 = test[:3] ##大于等于0小于3 v3 = test[1:5] ##大于等于1小于5 print(v1) print(v2) print(v3)
执行结果:

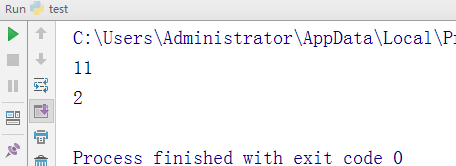
4.获取字符串的长度
test = 'xianyoudian' lee = '西安' v1 = len(test) v2 = len(lee) print(v1) print(v2)
执行结果:
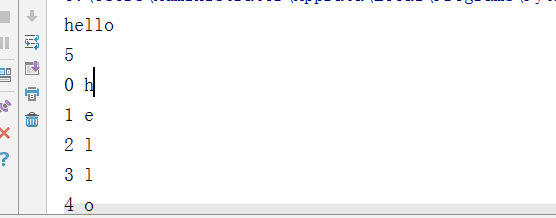
实例.将文字和对应的索引输出
代码1:
test = 'hello' print(test) l = len(test) print(l) r = range(0,l) ##0到字符串的长度 for item in r: print(item, test[item])
执行结果:
代码2:
test = 'hello' for item in range(0, len(test)): print(item, test[item])
执行结果:
补充:
# 字符串一旦创建,不可修改
# 一旦修改或者拼接,都会造成重新生成字符串# name = "zhengjianwen"
# age = "18"
#
# info = name + age
# print(info)