题目:二维数组中的查找
描述
在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。
请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
思路
根据二维数组递增的特性,查找的形式如下: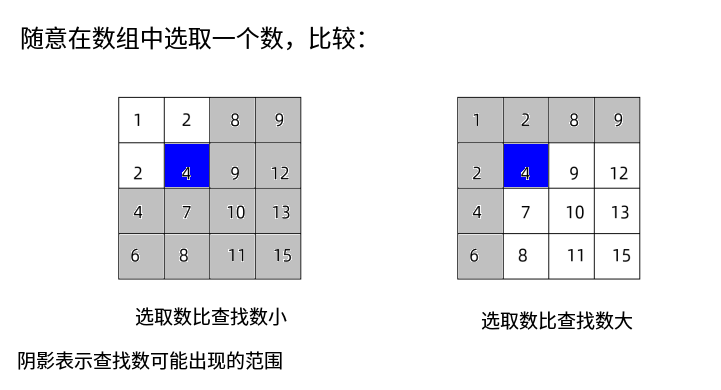
-
暴力破解可以解决问题
按行遍历,直到等于查找数/大于查找数/越界 -
可以从边界出发
利用特性,可以确定一整列或整行的是否在查找范围
比如:从右上角出发,第一个数字表示该列的最小值,该行最大值
如果查找数比该列最小值还小,则表示该列不在查找范围
如果查找数比该行最大值还大,则表示该行不在查找范围
类似递归方法,每次都在缩减数据规模,将问题转化为更小的同样性质的问题
/******************************************************************* Copyright(c) 2016, Harry He All rights reserved. Distributed under the BSD license. (See accompanying file LICENSE.txt at https://github.com/zhedahht/CodingInterviewChinese2/blob/master/LICENSE.txt) *******************************************************************/ //================================================================== // 《剑指Offer——名企面试官精讲典型编程题》代码 // 作者:何海涛 //================================================================== // 面试题4:二维数组中的查找 // 题目:在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按 // 照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个 // 整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。 #include <cstdio> #if 0 bool Find(int* matrix, int rows, int columns, int number) { bool found = false; if (matrix != nullptr && rows > 0 && columns > 0) { int row = 0; int column = columns - 1; while (row < rows && column >= 0) { if (matrix[row * columns + column] == number) { found = true; break; } else if (matrix[row * columns + column] > number) --column; else ++row; } } return found; } //从右上角开始 bool Find(int* matrix, int rows, int columns, int number) { bool result = false; int row = 0; int column = columns - 1 ; int tmp; // row>=rows ;column < 0 蕴含着自动终止条件,找不到正确的值,可以自动退出while,平时while写的太少了 while (matrix != nullptr && row < rows && column >= 0) { tmp = matrix[row*columns + column]; if (tmp > number) { column--; } else if (tmp < number) { row++; } else { result = true; // 为什么要有break,成立之后,row column不更新,跳不出while break; } } return result; } #endif //从左下角开始 bool Find(int* matrix, int rows, int columns, int number) { bool result = false; int row = rows-1; int column = 0; int tmp; // row>=rows ;column < 0 蕴含着自动终止条件,找不到正确的值,可以自动退出while,平时while写的太少了 //while (matrix != nullptr && row < rows && column >= 0) while (matrix != nullptr && row>=0 && column < columns ) { tmp = matrix[row*columns + column]; if (tmp > number) { row--; } else if (tmp < number) { column++; } else { result = true; // 为什么要有break,成立之后,row column不更新,跳不出while break; } } return result; } // ====================测试代码==================== void Test(char* testName, int* matrix, int rows, int columns, int number, bool expected) { if (testName != nullptr) printf("%s begins: ", testName); bool result = Find(matrix, rows, columns, number); if (result == expected) printf("Passed. "); else printf("Failed. "); } // 1 2 8 9 // 2 4 9 12 // 4 7 10 13 // 6 8 11 15 // 要查找的数在数组中 void Test1() { int matrix[][4] = { { 1, 2, 8, 9 },{ 2, 4, 9, 12 },{ 4, 7, 10, 13 },{ 6, 8, 11, 15 } }; Test("Test1", (int*)matrix, 4, 4, 7, true); } // 1 2 8 9 // 2 4 9 12 // 4 7 10 13 // 6 8 11 15 // 要查找的数不在数组中 void Test2() { int matrix[][4] = { { 1, 2, 8, 9 },{ 2, 4, 9, 12 },{ 4, 7, 10, 13 },{ 6, 8, 11, 15 } }; Test("Test2", (int*)matrix, 4, 4, 5, false); } // 1 2 8 9 // 2 4 9 12 // 4 7 10 13 // 6 8 11 15 // 要查找的数是数组中最小的数字 void Test3() { int matrix[][4] = { { 1, 2, 8, 9 },{ 2, 4, 9, 12 },{ 4, 7, 10, 13 },{ 6, 8, 11, 15 } }; Test("Test3", (int*)matrix, 4, 4, 1, true); } // 1 2 8 9 // 2 4 9 12 // 4 7 10 13 // 6 8 11 15 // 要查找的数是数组中最大的数字 void Test4() { int matrix[][4] = { { 1, 2, 8, 9 },{ 2, 4, 9, 12 },{ 4, 7, 10, 13 },{ 6, 8, 11, 15 } }; Test("Test4", (int*)matrix, 4, 4, 15, true); } // 1 2 8 9 // 2 4 9 12 // 4 7 10 13 // 6 8 11 15 // 要查找的数比数组中最小的数字还小 void Test5() { int matrix[][4] = { { 1, 2, 8, 9 },{ 2, 4, 9, 12 },{ 4, 7, 10, 13 },{ 6, 8, 11, 15 } }; Test("Test5", (int*)matrix, 4, 4, 0, false); } // 1 2 8 9 // 2 4 9 12 // 4 7 10 13 // 6 8 11 15 // 要查找的数比数组中最大的数字还大 void Test6() { int matrix[][4] = { { 1, 2, 8, 9 },{ 2, 4, 9, 12 },{ 4, 7, 10, 13 },{ 6, 8, 11, 15 } }; Test("Test6", (int*)matrix, 4, 4, 16, false); } // 鲁棒性测试,输入空指针 void Test7() { Test("Test7", nullptr, 2, 2, 16, false); } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { Test1(); Test2(); Test3(); Test4(); Test5(); Test6(); Test7(); return 0; }