简介
HttpClient是Apache Jakarta Common下的子项目,用来提供高效的、最新的、功能丰富的支持HTTP协议的客户端编程工具包,并且它支持HTTP协议最新的版本和建议。
HttpClient最新版本是HttpClient 4.5.3 (GA)。
官方下载:http://hc.apache.org/downloads.cgi
主要特性
- 基于标准、纯净的Java语言,实现了HTTP1.0和HTTP1.1。
- 以可扩展的面向对象的结构实现了HTTP全部的方法(GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, HEAD, OPTIONS, and TRACE)。
- 支持加密的HTTPS协议(HTTP通过SSL协议)。
- 通过HTTP代理方式建立透明的连接。
- 利用CONNECT方法通过HTTP代理建立隧道的HTTPS连接。
- Basic, Digest, NTLMv1, NTLMv2, NTLM2 Session, SNPNEGO/Kerberos认证方案。
- 插件式的自定义认证方案。
- 可插拔的安全套接字工厂,使得接入第三方解决方案变得更容易
- 连接管理支持使用多线程的的应用。支持设置最大连接数,同时支持设置每个主机的最大连接数,发现并关闭过期的连接。
- 自动化处理Set-Cookie:来自服务器的头,并在适当的时候将它们发送回cookie。
- 可以自定义Cookie策略的插件化机制。
- Request的输出流可以避免流中内容体直接从socket缓冲到服务器。
- Response的输入流可以有效的从socket服务器直接读取相应内容。
- 在HTTP1.0和HTTP1.1中使用用KeepAlive来保持持久连接。
- 可以直接获取服务器发送的响应码和响应头部。
- 具备设置连接超时的能力。
- 支持HTTP/1.1 响应缓存。
- 源代码基于Apache License 可免费获取。
一般使用步骤
使用HttpClient发送请求、接收响应,一般需要以下步骤。
HttpGet请求响应的一般步骤:
1). 创建HttpClient对象,可以使用HttpClients.createDefault();
2). 如果是无参数的GET请求,则直接使用构造方法HttpGet(String url)创建HttpGet对象即可;
如果是带参数GET请求,则可以先使用URIBuilder(String url)创建对象,再调用addParameter(String param, String value),或setParameter(String param, String value)来设置请求参数,并调用build()方法构建一个URI对象。只有构造方法HttpGet(URI uri)来创建HttpGet对象。
3). 创建HttpResponse,调用HttpClient对象的execute(HttpUriRequest request)发送请求,该方法返回一个HttpResponse。调用HttpResponse的getAllHeaders()、getHeaders(String name)等方法可获取服务器的响应头;调用HttpResponse的getEntity()方法可获取HttpEntity对象,该对象包装了服务器的响应内容。程序可通过该对象获取服务器的响应内容。通过调用getStatusLine().getStatusCode()可以获取响应状态码。
4). 释放连接。
HttpPost请求响应的一般步骤:
1). 创建HttpClient对象,可以使用HttpClients.createDefault();
2). 如果是无参数的GET请求,则直接使用构造方法HttpPost(String url)创建HttpPost对象即可;
如果是带参数POST请求,先构建HttpEntity对象并设置请求参数,然后调用setEntity(HttpEntity entity)创建HttpPost对象。
3). 创建HttpResponse,调用HttpClient对象的execute(HttpUriRequest request)发送请求,该方法返回一个HttpResponse。调用HttpResponse的getAllHeaders()、getHeaders(String name)等方法可获取服务器的响应头;调用HttpResponse的getEntity()方法可获取HttpEntity对象,该对象包装了服务器的响应内容。程序可通过该对象获取服务器的响应内容。通过调用getStatusLine().getStatusCode()可以获取响应状态码。
4). 释放连接。
官方文档中的示例
1 //1.获得一个httpclient对象 2 CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault(); 3 //2.生成一个get请求 4 HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet("http://localhost/"); 5 //3.执行get请求并返回结果 6 CloseableHttpResponse response = httpclient.execute(httpget); 7 try { 8 //4.处理结果 9 } finally { 10 response.close(); 11 }
实例代码实战
构建一个Maven项目,引入如下依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId> <artifactId>httpclient</artifactId> <version>4.3.5</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId> <version>1.7.7</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-io</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> </dependency>
实例1:普通的无参数GET请求
打开一个url,抓取响应结果输出成html文件
1 /** 2 *普通的GET请求 3 */ 4 public class DoGET { 5 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 6 // 创建Httpclient对象 7 CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault(); 8 // 创建http GET请求 9 HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("http://www.baidu.com"); 10 CloseableHttpResponse response = null; 11 try { 12 // 执行请求 13 response = httpclient.execute(httpGet); 14 // 判断返回状态是否为200 15 if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) { 16 //请求体内容 17 String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8"); 18 //内容写入文件 19 FileUtils.writeStringToFile(new File("E:\devtest\baidu.html"), content, "UTF-8"); 20 System.out.println("内容长度:"+content.length()); 21 } 22 } finally { 23 if (response != null) { 24 response.close(); 25 } 26 //相当于关闭浏览器 27 httpclient.close(); 28 } 29 } 30 }
实例2:执行带参数的GET请求
模拟使用百度搜索关键字"java",并保存搜索结果为html文件
1 import java.io.File; 2 import java.net.URI; 3 import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; 4 import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse; 5 import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet; 6 import org.apache.http.client.utils.URIBuilder; 7 import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient; 8 import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients; 9 import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils; 10 /** 11 * 带参数的GET请求 12 * 两种方式: 13 * 1.直接将参数拼接到url后面 如:?wd=java 14 * 2.使用URI的方法设置参数 setParameter("wd", "java") 15 */ 16 public class DoGETParam { 17 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 18 // 创建Httpclient对象 19 CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault(); 20 // 定义请求的参数 21 URI uri = new URIBuilder("http://www.baidu.com/s").setParameter("wd", "java").build(); 22 // 创建http GET请求 23 HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(uri); 24 //response 对象 25 CloseableHttpResponse response = null; 26 try { 27 // 执行http get请求 28 response = httpclient.execute(httpGet); 29 // 判断返回状态是否为200 30 if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) { 31 String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8"); 32 //内容写入文件 33 FileUtils.writeStringToFile(new File("E:\devtest\baidu-param.html"), content, "UTF-8"); 34 System.out.println("内容长度:"+content.length()); 35 } 36 } finally { 37 if (response != null) { 38 response.close(); 39 } 40 httpclient.close(); 41 } 42 } 43 }
实例3:执行普通的POST请求
无参数的POST请求,并设置Header来伪装浏览器请求
1 import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; 2 import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse; 3 import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost; 4 import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient; 5 import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients; 6 import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils; 7 8 import java.io.File; 9 10 /** 11 * 常规post请求 12 * 可以设置Header来伪装浏览器请求 13 */ 14 public class DoPOST { 15 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 16 // 创建Httpclient对象 17 CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault(); 18 // 创建http POST请求 19 HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://www.oschina.net/"); 20 //伪装浏览器请求 21 httpPost.setHeader("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/56.0.2924.87 Safari/537.36"); 22 CloseableHttpResponse response = null; 23 try { 24 // 执行请求 25 response = httpclient.execute(httpPost); 26 // 判断返回状态是否为200 27 if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) { 28 String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8"); 29 //内容写入文件 30 FileUtils.writeStringToFile(new File("E:\devtest\oschina.html"), content, "UTF-8"); 31 System.out.println("内容长度:"+content.length()); 32 } 33 } finally { 34 if (response != null) { 35 response.close(); 36 } 37 httpclient.close(); 38 } 39 } 40 }
实例4:执行带参数的POST请求
模拟开源中国检索java,并伪装浏览器请求,输出响应结果为html文件
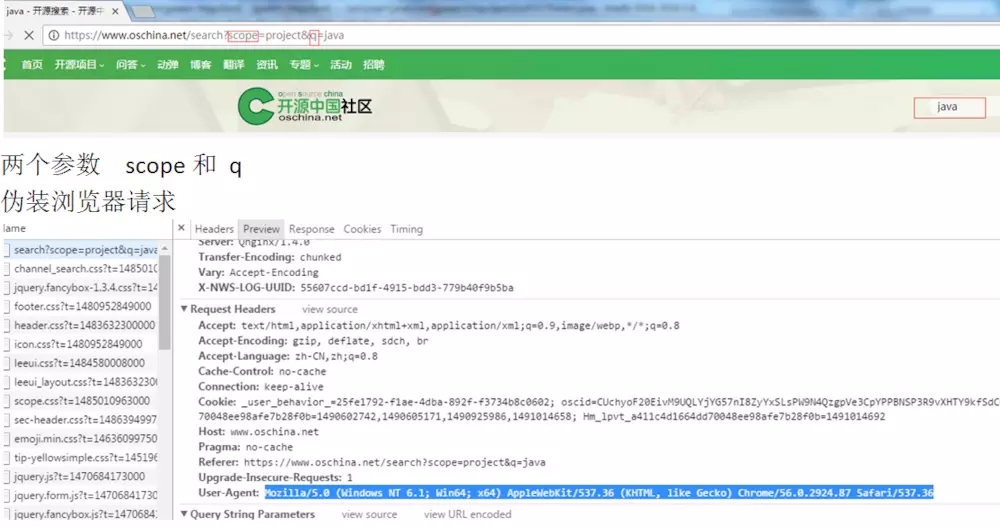
1 import java.io.File; 2 import java.util.ArrayList; 3 import java.util.List; 4 5 import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; 6 import org.apache.http.NameValuePair; 7 import org.apache.http.client.entity.UrlEncodedFormEntity; 8 import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse; 9 import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost; 10 import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient; 11 import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients; 12 import org.apache.http.message.BasicNameValuePair; 13 import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils; 14 15 /** 16 * 带有参数的Post请求 17 * NameValuePair 18 */ 19 public class DoPOSTParam { 20 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 21 // 创建Httpclient对象 22 CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault(); 23 // 创建http POST请求 24 HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://www.oschina.net/search"); 25 // 设置2个post参数,一个是scope、一个是q 26 List<NameValuePair> parameters = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>(0); 27 parameters.add(new BasicNameValuePair("scope", "project")); 28 parameters.add(new BasicNameValuePair("q", "java")); 29 // 构造一个form表单式的实体 30 UrlEncodedFormEntity formEntity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(parameters); 31 // 将请求实体设置到httpPost对象中 32 httpPost.setEntity(formEntity); 33 //伪装浏览器 34 httpPost.setHeader("User-Agent", 35 "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/56.0.2924.87 Safari/537.36"); 36 CloseableHttpResponse response = null; 37 try { 38 // 执行请求 39 response = httpclient.execute(httpPost); 40 // 判断返回状态是否为200 41 if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) { 42 String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8"); 43 //内容写入文件 44 FileUtils.writeStringToFile(new File("E:\devtest\oschina-param.html"), content, "UTF-8"); 45 System.out.println("内容长度:"+content.length()); 46 } 47 } finally { 48 if (response != null) { 49 response.close(); 50 } 51 httpclient.close(); 52 } 53 } 54 }
总结
本文介绍了HttpClient的特性,是按照官方英文文档翻译而来,然后分别介绍了HttpGet和HttpPost的一般使用步骤,最后给出了4个简单的实例的Java代码。下一章节我们会介绍HttpClient连接池管理以及Spring整合HttpClient的具体过程。