新旧API使用 Flume和Kafka集成:
Kafka有两套API: 过时的API 和新API
准备工作
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId>
<version>0.11.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka_2.12</artifactId>
<version>0.11.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka-streams</artifactId>
<version>0.11.0.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Kafka生产者API
旧
import java.util.Properties;
import kafka.javaapi.producer.Producer;
import kafka.producer.KeyedMessage;
import kafka.producer.ProducerConfig;
public class OldProducer {
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static void main(String[] args) {
//配置信息
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("metadata.broker.list", "datanode1:9092");
properties.put("request.required.acks", "1");
properties.put("serializer.class", "kafka.serializer.StringEncoder");
Producer<Integer, String> producer = new Producer<Integer,String>(new ProducerConfig(properties));
KeyedMessage<Integer, String> message = new KeyedMessage<Integer, String>("first", "hello kafka");
producer.send(message );
}
}
高级
import java.util.Properties;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.Producer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerRecord;
public class NewProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties props = new Properties();
// Kafka服务端的主机名和端口号
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "datanode1:9092");
// 等待所有副本节点的应答
props.put("acks", "all");
// 消息发送最大尝试次数
props.put("retries", 0);
// 一批消息处理大小
props.put("batch.size", 16384);
// 请求延时
props.put("linger.ms", 1);
// 发送缓存区内存大小
props.put("buffer.memory", 33554432);
// key序列化
props.put("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
// value序列化
props.put("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
Producer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props);
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
producer.send(new ProducerRecord<String, String>("first", Integer.toString(i), "hello kafka-" + i));
}
producer.close();
}
}
生产者带回调函数
import java.util.Properties;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.Callback;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.RecordMetadata;
public class CallBackProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties props = new Properties();
// Kafka服务端的主机名和端口号
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "datanode2:9092");
// 等待所有副本节点的应答
props.put("acks", "all");
// 消息发送最大尝试次数
props.put("retries", 0);
// 一批消息处理大小
props.put("batch.size", 16384);
// 增加服务端请求延时
props.put("linger.ms", 1);
// 发送缓存区内存大小
props.put("buffer.memory", 33554432);
// key序列化
props.put("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
// value序列化
props.put("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
KafkaProducer<String, String> kafkaProducer = new KafkaProducer<>(props);
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
kafkaProducer.send(new ProducerRecord<String, String>("first", "hello --" + i), new Callback() {
@Override
public void onCompletion(RecordMetadata metadata, Exception exception) {
if (metadata != null) {
System.err.println(metadata.partition() + "---" + metadata.offset());
}
}
});
}
kafkaProducer.close();
}
}
自定义分区
需求:将所有数据存储到topic的第0号分区上
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.Partitioner;
import org.apache.kafka.common.Cluster;
public class CustomPartitioner implements Partitioner {
@Override
public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs) {
}
@Override
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
// 控制分区
return 0;
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
}
import java.util.Properties;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.Producer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerRecord;
public class PartitionerProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties props = new Properties();
// Kafka服务端的主机名和端口号
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "datanode1:9092");
// 等待所有副本节点的应答
props.put("acks", "all");
// 消息发送最大尝试次数
props.put("retries", 0);
// 一批消息处理大小
props.put("batch.size", 16384);
// 增加服务端请求延时
props.put("linger.ms", 1);
// 发送缓存区内存大小
props.put("buffer.memory", 33554432);
// key序列化
props.put("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
// value序列化
props.put("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
// 自定义分区
props.put("partitioner.class", "producer.CustomPartitioner");
Producer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props);
producer.send(new ProducerRecord<String, String>("first", "1", "hello kafka"));
producer.close();
}
}
Kafka消费者
旧
使用低级API读取指定topic,指定partition,指定offset的数据。
1消费者使用低级API 的主要步骤:
| 步骤 | 主要工作 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 根据指定的分区从主题元数据中找到主副本 |
| 2 | 获取分区最新的消费进度 |
| 3 | 从主副本拉取分区的消息 |
| 4 | 识别主副本的变化,重试 |
2方法描述:
| findLeader() | 客户端向种子节点发送主题元数据,将副本集加入备用节点 |
|---|---|
| getLastOffset() | 消费者客户端发送偏移量请求,获取分区最近的偏移量 |
| run() | 消费者低级AP I拉取消息的主要方法 |
| findNewLeader() | 当分区的主副本节点发生故障,客户将要找出新的主副本 |
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import kafka.api.FetchRequest;
import kafka.api.FetchRequestBuilder;
import kafka.api.PartitionOffsetRequestInfo;
import kafka.cluster.BrokerEndPoint;
import kafka.common.ErrorMapping;
import kafka.common.TopicAndPartition;
import kafka.javaapi.FetchResponse;
import kafka.javaapi.OffsetResponse;
import kafka.javaapi.PartitionMetadata;
import kafka.javaapi.TopicMetadata;
import kafka.javaapi.TopicMetadataRequest;
import kafka.javaapi.consumer.SimpleConsumer;
import kafka.message.MessageAndOffset;
public class OldConsumer {
private List<String> m_replicaBrokers = new ArrayList<>();
public OldConsumer() {
m_replicaBrokers = new ArrayList<>();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
OldConsumer example = new OldConsumer();
// 最大读取消息数量
long maxReads = Long.parseLong("3");
// 要订阅的topic
String topic = "first";
// 要查找的分区
int partition = Integer.parseInt("0");
// broker节点的ip
List<String> seeds = new ArrayList<>();
seeds.add("192.168.1.101");
seeds.add("192.168.1.102");
seeds.add("192.168.1.103");
// 端口
int port = Integer.parseInt("9092");
try {
example.run(maxReads, topic, partition, seeds, port);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Oops:" + e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void run(long a_maxReads, String a_topic, int a_partition, List<String> a_seedBrokers, int a_port) throws Exception {
// 获取指定Topic partition的元数据
PartitionMetadata metadata = findLeader(a_seedBrokers, a_port, a_topic, a_partition);
if (metadata == null) {
System.out.println("Can't find metadata for Topic and Partition. Exiting");
return;
}
if (metadata.leader() == null) {
System.out.println("Can't find Leader for Topic and Partition. Exiting");
return;
}
String leadBroker = metadata.leader().host();
String clientName = "Client_" + a_topic + "_" + a_partition;
SimpleConsumer consumer = new SimpleConsumer(leadBroker, a_port, 100000, 64 * 1024, clientName);
long readOffset = getLastOffset(consumer, a_topic, a_partition, kafka.api.OffsetRequest.EarliestTime(), clientName);
int numErrors = 0;
while (a_maxReads > 0) {
if (consumer == null) {
consumer = new SimpleConsumer(leadBroker, a_port, 100000, 64 * 1024, clientName);
}
FetchRequest req = new FetchRequestBuilder().clientId(clientName).addFetch(a_topic, a_partition, readOffset, 100000).build();
FetchResponse fetchResponse = consumer.fetch(req);
if (fetchResponse.hasError()) {
numErrors++;
// Something went wrong!
short code = fetchResponse.errorCode(a_topic, a_partition);
System.out.println("Error fetching data from the Broker:" + leadBroker + " Reason: " + code);
if (numErrors > 5)
break;
if (code == ErrorMapping.OffsetOutOfRangeCode()) {
// We asked for an invalid offset. For simple case ask for
// the last element to reset
readOffset = getLastOffset(consumer, a_topic, a_partition, kafka.api.OffsetRequest.LatestTime(), clientName);
continue;
}
consumer.close();
consumer = null;
leadBroker = findNewLeader(leadBroker, a_topic, a_partition, a_port);
continue;
}
numErrors = 0;
long numRead = 0;
for (MessageAndOffset messageAndOffset : fetchResponse.messageSet(a_topic, a_partition)) {
long currentOffset = messageAndOffset.offset();
if (currentOffset < readOffset) {
System.out.println("Found an old offset: " + currentOffset + " Expecting: " + readOffset);
continue;
}
readOffset = messageAndOffset.nextOffset();
ByteBuffer payload = messageAndOffset.message().payload();
byte[] bytes = new byte[payload.limit()];
payload.get(bytes);
System.out.println(String.valueOf(messageAndOffset.offset()) + ": " + new String(bytes, "UTF-8"));
numRead++;
a_maxReads--;
}
if (numRead == 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
}
}
}
if (consumer != null)
consumer.close();
}
public static long getLastOffset(SimpleConsumer consumer, String topic, int partition, long whichTime, String clientName) {
TopicAndPartition topicAndPartition = new TopicAndPartition(topic, partition);
Map<TopicAndPartition, PartitionOffsetRequestInfo> requestInfo = new HashMap<TopicAndPartition, PartitionOffsetRequestInfo>();
requestInfo.put(topicAndPartition, new PartitionOffsetRequestInfo(whichTime, 1));
kafka.javaapi.OffsetRequest request = new kafka.javaapi.OffsetRequest(requestInfo, kafka.api.OffsetRequest.CurrentVersion(), clientName);
OffsetResponse response = consumer.getOffsetsBefore(request);
if (response.hasError()) {
System.out.println("Error fetching data Offset Data the Broker. Reason: " + response.errorCode(topic, partition));
return 0;
}
long[] offsets = response.offsets(topic, partition);
return offsets[0];
}
private String findNewLeader(String a_oldLeader, String a_topic, int a_partition, int a_port) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
boolean goToSleep = false;
PartitionMetadata metadata = findLeader(m_replicaBrokers, a_port, a_topic, a_partition);
if (metadata == null) {
goToSleep = true;
} else if (metadata.leader() == null) {
goToSleep = true;
} else if (a_oldLeader.equalsIgnoreCase(metadata.leader().host()) && i == 0) {
// first time through if the leader hasn't changed give
// ZooKeeper a second to recover
// second time, assume the broker did recover before failover,
// or it was a non-Broker issue
//
goToSleep = true;
} else {
return metadata.leader().host();
}
if (goToSleep) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
System.out.println("Unable to find new leader after Broker failure. Exiting");
throw new Exception("Unable to find new leader after Broker failure. Exiting");
}
private PartitionMetadata findLeader(List<String> a_seedBrokers, int a_port, String a_topic, int a_partition) {
PartitionMetadata returnMetaData = null;
loop:
for (String seed : a_seedBrokers) {
SimpleConsumer consumer = null;
try {
consumer = new SimpleConsumer(seed, a_port, 100000, 64 * 1024, "leaderLookup");
List<String> topics = Collections.singletonList(a_topic);
TopicMetadataRequest req = new TopicMetadataRequest(topics);
kafka.javaapi.TopicMetadataResponse resp = consumer.send(req);
List<TopicMetadata> metaData = resp.topicsMetadata();
for (TopicMetadata item : metaData) {
for (PartitionMetadata part : item.partitionsMetadata()) {
if (part.partitionId() == a_partition) {
returnMetaData = part;
break loop;
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error communicating with Broker [" + seed + "] to find Leader for [" + a_topic + ", " + a_partition + "] Reason: " + e);
} finally {
if (consumer != null)
consumer.close();
}
}
if (returnMetaData != null) {
m_replicaBrokers.clear();
for (BrokerEndPoint replica : returnMetaData.replicas()) {
m_replicaBrokers.add(replica.host());
}
}
return returnMetaData;
}
}

新
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import kafka.consumer.Consumer;
import kafka.consumer.ConsumerConfig;
import kafka.consumer.ConsumerIterator;
import kafka.consumer.KafkaStream;
import kafka.javaapi.consumer.ConsumerConnector;
public class CustomConsumer {
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("zookeeper.connect", "datanode1:2181");
properties.put("group.id", "g1");
properties.put("zookeeper.session.timeout.ms", "500");
properties.put("zookeeper.sync.time.ms", "250");
properties.put("auto.commit.interval.ms", "1000");
// 创建消费者连接器
ConsumerConnector consumer = Consumer.createJavaConsumerConnector(new ConsumerConfig(properties));
HashMap<String, Integer> topicCount = new HashMap<>();
topicCount.put("first", 1);
Map<String, List<KafkaStream<byte[], byte[]>>> consumerMap = consumer.createMessageStreams(topicCount);
KafkaStream<byte[], byte[]> stream = consumerMap.get("first").get(0);
ConsumerIterator<byte[], byte[]> it = stream.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(new String(it.next().message()));
}
}
}
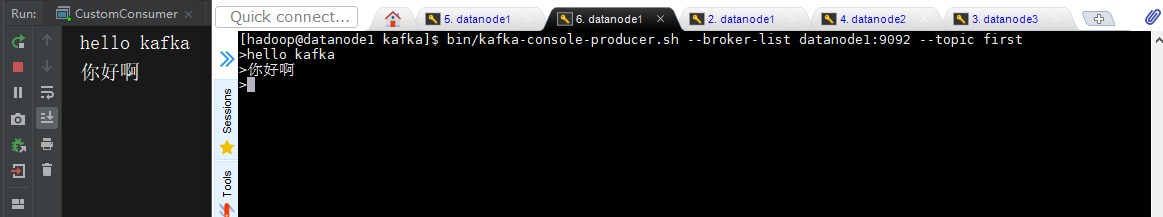
Kafka拦截器
拦截器原理
Producer拦截器(interceptor)在Kafka 0.10版本被引入,主要用于实现clients端的定制化控制逻辑。
对于producer而言,interceptor使得用户在消息发送前以及producer回调逻辑前有机会对消息做一些定制化需求,比如修改消息等。同时,producer允许用户指定多个interceptor按序作用于同一条消息从而形成一个拦截链(interceptor chain)。Intercetpor的实现接口是org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerInterceptor,其定义的方法包括:
(1)configure(configs)
获取配置信息和初始化数据时调用。
(2)onSend(ProducerRecord):
该方法封装进KafkaProducer.send方法中,即它运行在用户主线程中。Producer确保在消息被序列化以及计算分区前调用该方法。用户可以在该方法中对消息做任何操作,但最好保证不要修改消息所属的topic和分区,否则会影响目标分区的计算
(3)onAcknowledgement(RecordMetadata, Exception):
该方法会在消息被应答或消息发送失败时调用,并且通常都是在producer回调逻辑触发之前。onAcknowledgement运行在producer的IO线程中,因此不要在该方法中放入很重的逻辑,否则会拖慢producer的消息发送效率
(4)close:
关闭interceptor,主要用于执行一些资源清理工作
如前所述,interceptor可能被运行在多个线程中,因此在具体实现时用户需要自行确保线程安全。另外倘若指定了多个interceptor,则producer将按照指定顺序调用它们,并仅仅是捕获每个interceptor可能抛出的异常记录到错误日志中而非在向上传递。这在使用过程中要特别留意。
案例
TimeInterceptor
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerInterceptor;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.RecordMetadata;
import java.util.Map;
public class TimeInterceptor implements ProducerInterceptor<String, String> {
@Override
public ProducerRecord<String, String> onSend(ProducerRecord<String, String> record) {
//给value添加时间戳
return new ProducerRecord<String, String>(record.topic(), record.partition(), record.timestamp(),
record.key(), "时间戳" +"-----"+ record.value());
}
@Override
public void onAcknowledgement(RecordMetadata metadata, Exception exception) {
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
@Override
public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs) {
}
}
CounterInterceptor
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerInterceptor;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.RecordMetadata;
import java.util.Map;
public class CounterInterceptor implements ProducerInterceptor<String, String> {
private int sucessCount = 0;
private int errorCount = 0;
@Override
public ProducerRecord<String, String> onSend(ProducerRecord<String, String> record) {
return new ProducerRecord<String, String>(record.topic(), record.partition(), record.timestamp(),
record.key(), "计数的" +"-----"+ record.value());
}
@Override
public void onAcknowledgement(RecordMetadata metadata, Exception exception) {
if (exception == null) {
sucessCount++;
} else {
errorCount++;
}
}
@Override
public void close() {
System.out.println("成功条数" + sucessCount);
System.out.println("失败条数" + errorCount);
}
@Override
public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs) {
}
}
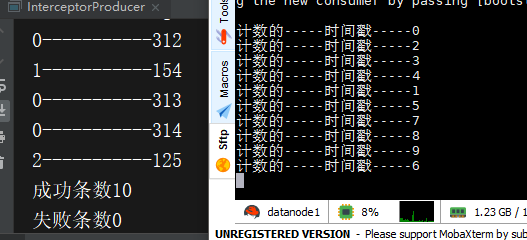
InterceptorProducer
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Properties;
public class InterceptorProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//配置信息
Properties props = new Properties();
//Kafka集群
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "datanode1:9092");
ArrayList<String> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
//这个调用是有逻辑顺序的 按照顺序调用的
interceptors.add("intercepter.TimeInterceptor");
interceptors.add("intercepter.CounterInterceptor");
props.put(ProducerConfig.INTERCEPTOR_CLASSES_CONFIG, interceptors);
//KV 序列化类
props.put("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
props.put("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
Producer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
producer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("second", String.valueOf(i), String.valueOf(i)),
(metadata, exception) -> System.out.println(metadata.partition() + "-----------" + metadata.offset()));
producer.close();
}
}
Kafka Streams
Apache Kafka开源项目的一个组成部分。是一个功能强大,易于使用的库。用于在Kafka上构建高可分布式、拓展性,容错的应用程序。但是用的不多.目前用Spark和Flink做流式实时计算的比较多。
特点
功能强大 :高扩展性,弹性,容错
轻量级 :无需专门的集群 一个库,而不是框架
完全集成:100%的Kafka 0.10.0版本兼容 易于集成到现有的应用程序
实时性: 毫秒级延迟 并非微批处理 窗口允许乱序数据 允许迟到数据
由来
当前已经有非常多的流式处理系统,最知名且应用最多的开源流式处理系统有Spark Streaming和Apache Storm。Apache Storm发展多年,应用广泛,提供记录级别的处理能力,当前也支持SQL on Stream。而Spark Streaming基于Apache Spark,可以非常方便与图计算,SQL处理等集成,功能强大,对于熟悉其它Spark应用开发的用户而言使用门槛低。另外,目前主流的Hadoop发行版,如Cloudera和Hortonworks,都集成了Apache Storm和Apache Spark,使得部署更容易。
既然Apache Spark与Apache Storm拥用如此多的优势,那为何还需要Kafka Stream呢?主要有如下原因。
第一,Spark和Storm都是流式处理框架,而Kafka Stream提供的是一个基于Kafka的流式处理类库。框架要求开发者按照特定的方式去开发逻辑部分,供框架调用。开发者很难了解框架的具体运行方式,从而使得调试成本高,并且使用受限。而Kafka Stream作为流式处理类库,直接提供具体的类给开发者调用,整个应用的运行方式主要由开发者控制,方便使用和调试。
第二,虽然Cloudera与Hortonworks方便了Storm和Spark的部署,但是这些框架的部署仍然相对复杂。而Kafka Stream作为类库,可以非常方便的嵌入应用程序中,它对应用的打包和部署基本没有任何要求。
第三,就流式处理系统而言,基本都支持Kafka作为数据源。例如Storm具有专门的kafka-spout,而Spark也提供专门的spark-streaming-kafka模块。事实上,Kafka基本上是主流的流式处理系统的标准数据源。换言之,大部分流式系统中都已部署了Kafka,此时使用Kafka Stream的成本非常低。
第四,使用Storm或Spark Streaming时,需要为框架本身的进程预留资源,如Storm的supervisor和Spark on YARN的node manager。即使对于应用实例而言,框架本身也会占用部分资源,如Spark Streaming需要为shuffle和storage预留内存。但是Kafka作为类库不占用系统资源。
第五,由于Kafka本身提供数据持久化,因此Kafka Stream提供滚动部署和滚动升级以及重新计算的能力。
第六,由于Kafka Consumer Rebalance机制,Kafka Stream可以在线动态调整并行度。
数据清洗

LogProcessor
import org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.Processor;
import org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.ProcessorContext;
public class LogProcessor implements Processor<byte[], byte[]> {
private ProcessorContext context = null;
@Override
public void init(ProcessorContext context) {
this.context = context;
}
@Override
public void process(byte[] key, byte[] value) {
String line = new String(value);
if (line.contains(">>>")) {
String[] split = line.split(">>>");
line = split[1];
}
context.forward(key, line.getBytes());
}
@Override
public void punctuate(long l) {
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
}
MyStream
import org.apache.kafka.streams.KafkaStreams;
import org.apache.kafka.streams.StreamsConfig;
import org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.ProcessorSupplier;
import org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.TopologyBuilder;
import java.util.Properties;
public class MyStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//配置信息
Properties props = new Properties();
//Kafka集群
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "datanode1:9092");
props.put(StreamsConfig.APPLICATION_ID_CONFIG, "LogStream");
//创建拓扑对象
TopologyBuilder builder = new TopologyBuilder();
builder.addSource("SOURCE", "first").addProcessor("PROCESSOR", (ProcessorSupplier<byte[], byte[]>)
LogProcessor::new, "SOURCE")
.addSink("SINK", "second", "PROCESSOR");
//创建kafkastream
KafkaStreams streams = new KafkaStreams(builder, props);
streams.start();
}
}
Kafka与Flume比较
| flume | Kafka |
|---|---|
| cloudera公司研发: | linkedin公司研发: |
| 适合多个生产者; | 适合数据下游消费众多的情况; |
| 适合下游数据消费者不多的情况; | 适合数据安全性要求较高的操作,支持replication。 |
| 适合数据安全性要求不高的操作; | |
| 适合与Hadoop生态圈对接的操作。 |
常用模型
线上数据 —> flume—> kafka —> flume(根据情景增删该流程) —> HDFS
Flume和Kafka集成
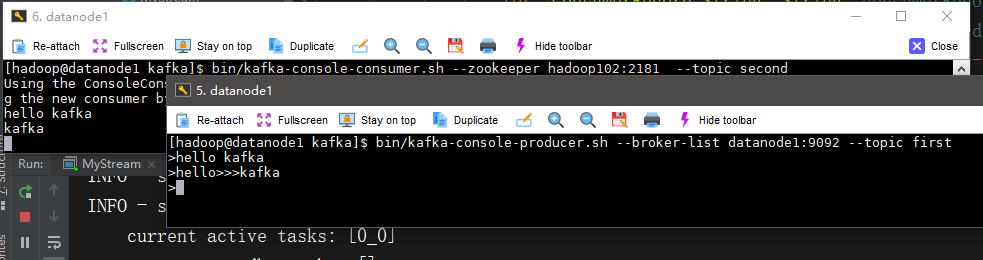
# define a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # source a1.sources.r1.type = exec a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F -c +0 /opt/module/datas/flume.log a1.sources.r1.shell = /bin/bash -c # sink a1.sinks.k1.type = org.apache.flume.sink.kafka.KafkaSink a1.sinks.k1.kafka.bootstrap.servers = datanode1:9092,datanode2:9092,datanode3:9092 a1.sinks.k1.kafka.topic = three a1.sinks.k1.kafka.flumeBatchSize = 20 a1.sinks.k1.kafka.producer.acks = 1 a1.sinks.k1.kafka.producer.linger.ms = 1 # channel a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # bind a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
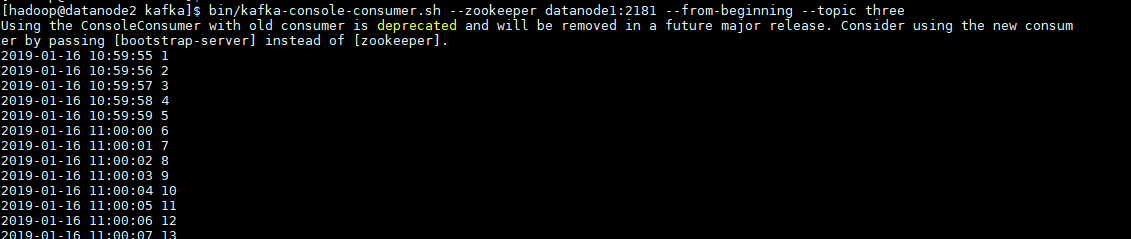
启动消费者
[hadoop@datanode2 kafka]$ bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --zookeeper datanode1:2181 --from-beginning --topic three
启动flume
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent -c conf/ -n a1 -f job/flume-kafka.conf
测试脚本
#!bin/bash i=1 while [ true ] let i+=1 d=$( date +%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S ) do echo "$d $i">>/opt/module/datas/flume.log sleep 1 done
Kafka配置信息
Broker配置信息
| 属性 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| broker.id | 必填参数,broker的唯一标识 | |
| log.dirs | /tmp/kafka-logs | Kafka数据存放的目录。可以指定多个目录,中间用逗号分隔,当新partition被创建的时会被存放到当前存放partition最少的目录。 |
| port | 9092 | BrokerServer接受客户端连接的端口号 |
| zookeeper.connect | null | Zookeeper的连接串,格式为:hostname1:port1,hostname2:port2,hostname3:port3。可以填一个或多个,为了提高可靠性,建议都填上。注意,此配置允许我们指定一个zookeeper路径来存放此kafka集群的所有数据,为了与其他应用集群区分开,建议在此配置中指定本集群存放目录,格式为:hostname1:port1,hostname2:port2,hostname3:port3/chroot/path 。需要注意的是,消费者的参数要和此参数一致。 |
| message.max.bytes | 1000000 | 服务器可以接收到的最大的消息大小。注意此参数要和consumer的maximum.message.size大小一致,否则会因为生产者生产的消息太大导致消费者无法消费。 |
| num.io.threads | 8 | 服务器用来执行读写请求的IO线程数,此参数的数量至少要等于服务器上磁盘的数量。 |
| queued.max.requests | 500 | I/O线程可以处理请求的队列大小,若实际请求数超过此大小,网络线程将停止接收新的请求。 |
| socket.send.buffer.bytes | 100 * 1024 | The SO_SNDBUFF buffer the server prefers for socket connections. |
| socket.receive.buffer.bytes | 100 * 1024 | The SO_RCVBUFF buffer the server prefers for socket connections. |
| socket.request.max.bytes | 100 1024 1024 | 服务器允许请求的最大值, 用来防止内存溢出,其值应该小于 Java heap size. |
| num.partitions | 1 | 默认partition数量,如果topic在创建时没有指定partition数量,默认使用此值,建议改为5 |
| log.segment.bytes | 1024 1024 1024 | Segment文件的大小,超过此值将会自动新建一个segment,此值可以被topic级别的参数覆盖。 |
| log.roll.{ms,hours} | 24 * 7 hours | 新建segment文件的时间,此值可以被topic级别的参数覆盖。 |
| log.retention.{ms,minutes,hours} | 7 days | Kafka segment log的保存周期,保存周期超过此时间日志就会被删除。此参数可以被topic级别参数覆盖。数据量大时,建议减小此值。 |
| log.retention.bytes | -1 | 每个partition的最大容量,若数据量超过此值,partition数据将会被删除。注意这个参数控制的是每个partition而不是topic。此参数可以被log级别参数覆盖。 |
| log.retention.check.interval.ms | 5 minutes | 删除策略的检查周期 |
| auto.create.topics.enable | true | 自动创建topic参数,建议此值设置为false,严格控制topic管理,防止生产者错写topic。 |
| default.replication.factor | 1 | 默认副本数量,建议改为2。 |
| replica.lag.time.max.ms | 10000 | 在此窗口时间内没有收到follower的fetch请求,leader会将其从ISR(in-sync replicas)中移除。 |
| replica.lag.max.messages | 4000 | 如果replica节点落后leader节点此值大小的消息数量,leader节点就会将其从ISR中移除。 |
| replica.socket.timeout.ms | 30 * 1000 | replica向leader发送请求的超时时间。 |
| replica.socket.receive.buffer.bytes | 64 * 1024 | The socket receive buffer for network requests to the leader for replicating data. |
| replica.fetch.max.bytes | 1024 * 1024 | The number of byes of messages to attempt to fetch for each partition in the fetch requests the replicas send to the leader. |
| replica.fetch.wait.max.ms | 500 | The maximum amount of time to wait time for data to arrive on the leader in the fetch requests sent by the replicas to the leader. |
| num.replica.fetchers | 1 | Number of threads used to replicate messages from leaders. Increasing this value can increase the degree of I/O parallelism in the follower broker. |
| fetch.purgatory.purge.interval.requests | 1000 | The purge interval (in number of requests) of the fetch request purgatory. |
| zookeeper.session.timeout.ms | 6000 | ZooKeeper session 超时时间。如果在此时间内server没有向zookeeper发送心跳,zookeeper就会认为此节点已挂掉。 此值太低导致节点容易被标记死亡;若太高,.会导致太迟发现节点死亡。 |
| zookeeper.connection.timeout.ms | 6000 | 客户端连接zookeeper的超时时间。 |
| zookeeper.sync.time.ms | 2000 | H ZK follower落后 ZK leader的时间。 |
| controlled.shutdown.enable | true | 允许broker shutdown。如果启用,broker在关闭自己之前会把它上面的所有leaders转移到其它brokers上,建议启用,增加集群稳定性。 |
| auto.leader.rebalance.enable | true | If this is enabled the controller will automatically try to balance leadership for partitions among the brokers by periodically returning leadership to the “preferred” replica for each partition if it is available. |
| leader.imbalance.per.broker.percentage | 10 | The percentage of leader imbalance allowed per broker. The controller will rebalance leadership if this ratio goes above the configured value per broker. |
| leader.imbalance.check.interval.seconds | 300 | The frequency with which to check for leader imbalance. |
| offset.metadata.max.bytes | 4096 | The maximum amount of metadata to allow clients to save with their offsets. |
| connections.max.idle.ms | 600000 | Idle connections timeout: the server socket processor threads close the connections that idle more than this. |
| num.recovery.threads.per.data.dir | 1 | The number of threads per data directory to be used for log recovery at startup and flushing at shutdown. |
| unclean.leader.election.enable | true | Indicates whether to enable replicas not in the ISR set to be elected as leader as a last resort, even though doing so may result in data loss. |
| delete.topic.enable | false | 启用deletetopic参数,建议设置为true。 |
| offsets.topic.num.partitions | 50 | The number of partitions for the offset commit topic. Since changing this after deployment is currently unsupported, we recommend using a higher setting for production (e.g., 100-200). |
| offsets.topic.retention.minutes | 1440 | Offsets that are older than this age will be marked for deletion. The actual purge will occur when the log cleaner compacts the offsets topic. |
| offsets.retention.check.interval.ms | 600000 | The frequency at which the offset manager checks for stale offsets. |
| offsets.topic.replication.factor | 3 | The replication factor for the offset commit topic. A higher setting (e.g., three or four) is recommended in order to ensure higher availability. If the offsets topic is created when fewer brokers than the replication factor then the offsets topic will be created with fewer replicas. |
| offsets.topic.segment.bytes | 104857600 | Segment size for the offsets topic. Since it uses a compacted topic, this should be kept relatively low in order to facilitate faster log compaction and loads. |
| offsets.load.buffer.size | 5242880 | An offset load occurs when a broker becomes the offset manager for a set of consumer groups (i.e., when it becomes a leader for an offsets topic partition). This setting corresponds to the batch size (in bytes) to use when reading from the offsets segments when loading offsets into the offset manager’s cache. |
| offsets.commit.required.acks | -1 | The number of acknowledgements that are required before the offset commit can be accepted. This is similar to the producer’s acknowledgement setting. In general, the default should not be overridden. |
| offsets.commit.timeout.ms | 5000 | The offset commit will be delayed until this timeout or the required number of replicas have received the offset commit. This is similar to the producer request timeout. |
Producer配置信息
| 属性 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| metadata.broker.list | 启动时producer查询brokers的列表,可以是集群中所有brokers的一个子集。注意,这个参数只是用来获取topic的元信息用,producer会从元信息中挑选合适的broker并与之建立socket连接。格式是:host1:port1,host2:port2。 | |
| request.required.acks | 0 | 参见3.2节介绍 |
| request.timeout.ms | 10000 | Broker等待ack的超时时间,若等待时间超过此值,会返回客户端错误信息。 |
| producer.type | sync | 同步异步模式。async表示异步,sync表示同步。如果设置成异步模式,可以允许生产者以batch的形式push数据,这样会极大的提高broker性能,推荐设置为异步。 |
| serializer.class | kafka.serializer.DefaultEncoder | 序列号类,.默认序列化成 byte[] 。 |
| key.serializer.class | Key的序列化类,默认同上。 | |
| partitioner.class | kafka.producer.DefaultPartitioner | Partition类,默认对key进行hash。 |
| compression.codec | none | 指定producer消息的压缩格式,可选参数为: “none”, “gzip” and “snappy”。关于压缩参见4.1节 |
| compressed.topics | null | 启用压缩的topic名称。若上面参数选择了一个压缩格式,那么压缩仅对本参数指定的topic有效,若本参数为空,则对所有topic有效。 |
| message.send.max.retries | 3 | Producer发送失败时重试次数。若网络出现问题,可能会导致不断重试。 |
| retry.backoff.ms | 100 | Before each retry, the producer refreshes the metadata of relevant topics to see if a new leader has been elected. Since leader election takes a bit of time, this property specifies the amount of time that the producer waits before refreshing the metadata. |
| topic.metadata.refresh.interval.ms | 600 * 1000 | The producer generally refreshes the topic metadata from brokers when there is a failure (partition missing, leader not available…). It will also poll regularly (default: every 10min so 600000ms). If you set this to a negative value, metadata will only get refreshed on failure. If you set this to zero, the metadata will get refreshed after each message sent (not recommended). Important note: the refresh happen only AFTER the message is sent, so if the producer never sends a message the metadata is never refreshed |
| queue.buffering.max.ms | 5000 | 启用异步模式时,producer缓存消息的时间。比如我们设置成1000时,它会缓存1秒的数据再一次发送出去,这样可以极大的增加broker吞吐量,但也会造成时效性的降低。 |
| queue.buffering.max.messages | 10000 | 采用异步模式时producer buffer 队列里最大缓存的消息数量,如果超过这个数值,producer就会阻塞或者丢掉消息。 |
| queue.enqueue.timeout.ms | -1 | 当达到上面参数值时producer阻塞等待的时间。如果值设置为0,buffer队列满时producer不会阻塞,消息直接被丢掉。若值设置为-1,producer会被阻塞,不会丢消息。 |
| batch.num.messages | 200 | 采用异步模式时,一个batch缓存的消息数量。达到这个数量值时producer才会发送消息。 |
| send.buffer.bytes | 100 * 1024 | Socket write buffer size |
| client.id | “” | The client id is a user-specified string sent in each request to help trace calls. It should logically identify the application making the request. |
Consumer配置信息
| 属性 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| group.id | Consumer的组ID,相同goup.id的consumer属于同一个组。 | |
| zookeeper.connect | Consumer的zookeeper连接串,要和broker的配置一致。 | |
| consumer.id | null | 如果不设置会自动生成。 |
| socket.timeout.ms | 30 * 1000 | 网络请求的socket超时时间。实际超时时间由max.fetch.wait + socket.timeout.ms 确定。 |
| socket.receive.buffer.bytes | 64 * 1024 | The socket receive buffer for network requests. |
| fetch.message.max.bytes | 1024 * 1024 | 查询topic-partition时允许的最大消息大小。consumer会为每个partition缓存此大小的消息到内存,因此,这个参数可以控制consumer的内存使用量。这个值应该至少比server允许的最大消息大小大,以免producer发送的消息大于consumer允许的消息。 |
| num.consumer.fetchers | 1 | The number fetcher threads used to fetch data. |
| auto.commit.enable | true | 如果此值设置为true,consumer会周期性的把当前消费的offset值保存到zookeeper。当consumer失败重启之后将会使用此值作为新开始消费的值。 |
| auto.commit.interval.ms | 60 * 1000 | Consumer提交offset值到zookeeper的周期。 |
| queued.max.message.chunks | 2 | 用来被consumer消费的message chunks 数量, 每个chunk可以缓存fetch.message.max.bytes大小的数据量。 |
| auto.commit.interval.ms | 60 * 1000 | Consumer提交offset值到zookeeper的周期。 |
| queued.max.message.chunks | 2 | 用来被consumer消费的message chunks 数量, 每个chunk可以缓存fetch.message.max.bytes大小的数据量。 |
| fetch.min.bytes | 1 | The minimum amount of data the server should return for a fetch request. If insufficient data is available the request will wait for that much data to accumulate before answering the request. |
| fetch.wait.max.ms | 100 | The maximum amount of time the server will block before answering the fetch request if there isn’t sufficient data to immediately satisfy fetch.min.bytes. |
| rebalance.backoff.ms | 2000 | Backoff time between retries during rebalance. |
| refresh.leader.backoff.ms | 200 | Backoff time to wait before trying to determine the leader of a partition that has just lost its leader. |
| auto.offset.reset | largest | What to do when there is no initial offset in ZooKeeper or if an offset is out of range ;smallest : automatically reset the offset to the smallest offset; largest : automatically reset the offset to the largest offset;anything else: throw exception to the consumer |
| consumer.timeout.ms | -1 | 若在指定时间内没有消息消费,consumer将会抛出异常。 |
| exclude.internal.topics | true | Whether messages from internal topics (such as offsets) should be exposed to the consumer. |
| zookeeper.session.timeout.ms | 6000 | ZooKeeper session timeout. If the consumer fails to heartbeat to ZooKeeper for this period of time it is considered dead and a rebalance will occur. |
| zookeeper.connection.timeout.ms | 6000 | The max time that the client waits while establishing a connection to zookeeper. |
| zookeeper.sync.time.ms | 2000 | How far a ZK follower can be behind a ZK leader |