/** * Attempts to authenticate the given token by iterating over the internal collection of * {@link Realm}s. For each realm, first the {@link Realm#supports(org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken)} * method will be called to determine if the realm supports the {@code authenticationToken} method argument. * <p/> * If a realm does support * the token, its {@link Realm#getAuthenticationInfo(org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken)} * method will be called. If the realm returns a non-null account, the token will be * considered authenticated for that realm and the account data recorded. If the realm returns {@code null}, * the next realm will be consulted. If no realms support the token or all supporting realms return null, * an {@link AuthenticationException} will be thrown to indicate that the user could not be authenticated. * <p/> * After all realms have been consulted, the information from each realm is aggregated into a single * {@link AuthenticationInfo} object and returned. * * @param authenticationToken the token containing the authentication principal and credentials for the * user being authenticated. * @return account information attributed to the authenticated user. * @throws IllegalStateException if no realms have been configured at the time this method is invoked * @throws AuthenticationException if the user could not be authenticated or the user is denied authentication * for the given principal and credentials. */ protected AuthenticationInfo doAuthenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { assertRealmsConfigured(); Collection<Realm> realms = getRealms(); if (realms.size() == 1) { return doSingleRealmAuthentication(realms.iterator().next(), authenticationToken); } else { return doMultiRealmAuthentication(realms, authenticationToken); } }
多Realm存在的目的:
将数据保存在多个数据库情况,可以将通过多Realm方式获取两个部分数据。提高数据的安全性。
关于applicationContext.xml配置两个realm的详情:

第一种方式:
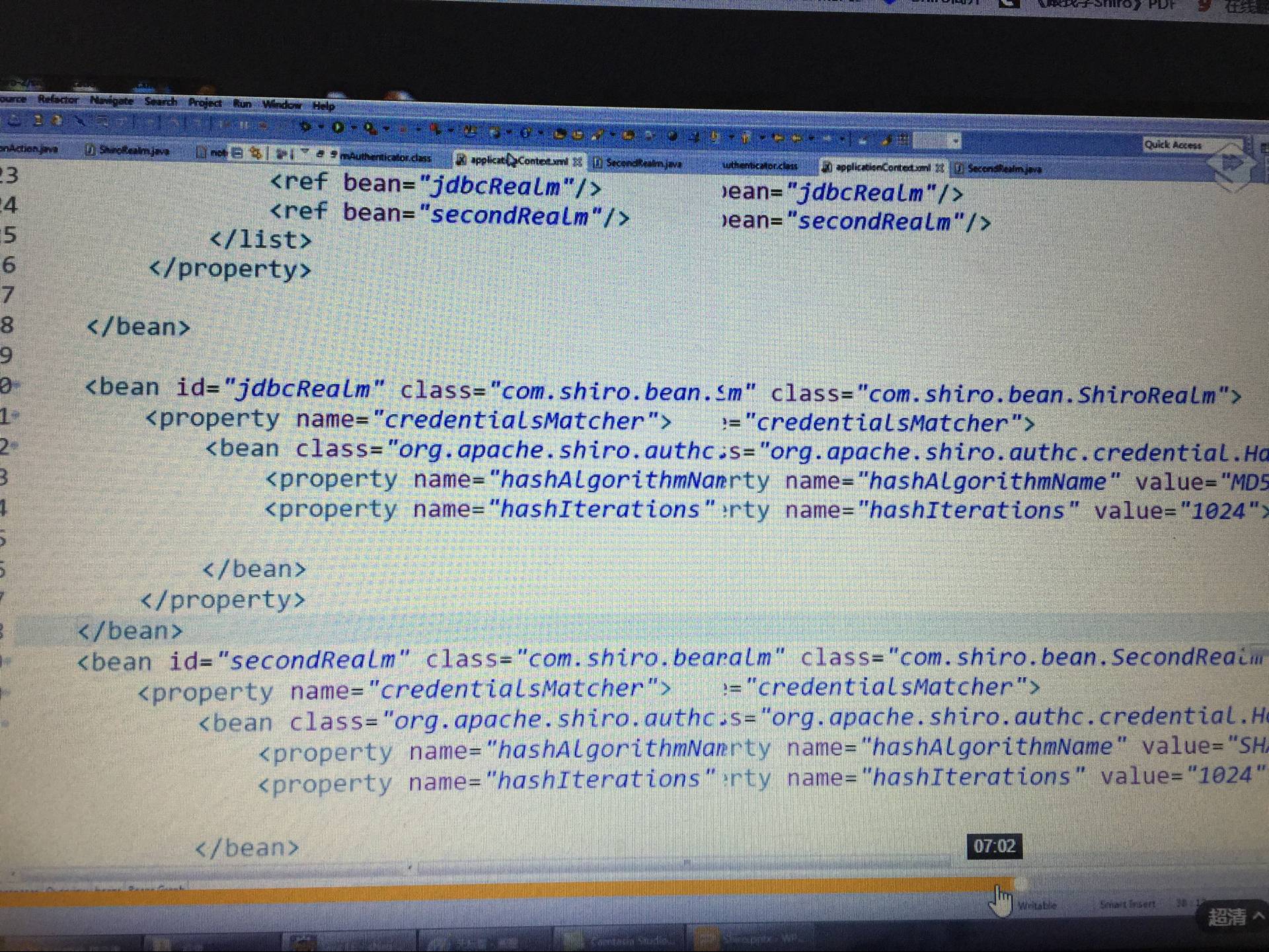
第二种方式:
realm的bean同第一种,只修改securityManage的配置

详解:
由于ModularRealmAuthenticator认证器中是有getRealms属性的,
public void setRealms(Collection<Realm> realms) { this.realms = realms; }
protected AuthenticationInfo doAuthenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { assertRealmsConfigured(); Collection<Realm> realms = getRealms(); if (realms.size() == 1) { return doSingleRealmAuthentication(realms.iterator().next(), authenticationToken); } else { return doMultiRealmAuthentication(realms, authenticationToken); } }
一个realm时配置realm:
<bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager"> <property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManager"/> <property name="realm" ref="jdbcRealm"/> </bean> 两个realm时配置realm:
<bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager"> <property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManager"/> <property name="realms"> <list> <ref bean=""/> <ref bean=" "/> </list> </property> </bean>