c++中给对象分配内存常见有三种方法:
- 使用c++ 库函数 std::allocator (c++ library);
- 使用new,new[] 表达式,::operator new() 操作符,(c++ primitives);
- c 函数 malloc/free (CRT);
测试代码如下:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include<complex> 4 #include <memory> //内含 std::allocator 5 #include <extpool_allocator.h> // __pool_alloc 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 void test() 10 { 11 void* p1 = malloc(512); //512bytes 12 free(p1); 13 14 complex<int>* p2 = new complex<int>; //one object 15 delete p2; 16 17 void* p3 = ::operator new(512);// 512bytes 18 ::operator delete(p3); 19 20 #ifdef __GNUC__ 21 //以下函数都是non-static,一定要通过object调用,分配7个int的内存 22 void* p4 = allocator<int>().allocate(7);//allocator<int>()创建临时对象 23 allocator<int>().deallocate((int*)p4,7); 24 25 //void* p5 = alloc::allocate(512); //2.9 26 //alloc::deallocate(p5,512); 27 28 void* p6 = __gnu_cxx::__pool_alloc<int>().allocate(9); // 对应上面的 gnc2.9; 29 __gnu_cxx::__pool_alloc<int>().deallocate((int*)p6,9); 30 #endif // __GNUC__ 31 32 #ifdef _MSC_VER_ 33 int* p6 = allocator<int>().allocate(3, (int*)0); 34 allocator<int>().deallocate(p6,3); 35 #endif // _MSC_VER_ 36 return; 37 }
一、new
使用new表达式,编译器将其转化为先调用 operator new 运算符,然后调用构造函数。 new过程是先分配内存,然后调用构造函数;delete时,先调用析构函数,然后释放内存。

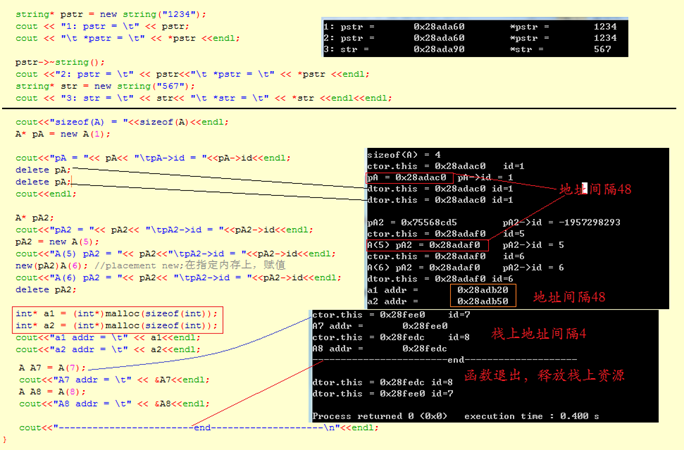
class A { public: int id; A() : id(0) { cout << "default ctor.this=" << this << " id=" << id << endl; } A(int i):id(i) { cout<< "ctor. this = " << this <<" id=" <<id <<endl; } ~A() { cout<<"dtor.this = "<<this <<endl; } }; void testCt() { string* pstr = new string; cout << "str = " << *pstr <<endl; // pstr->string::string("123"); //'class std::basic_string<char>' has no member named 'string'| pstr->~string(); cout<<"str = " <<endl; A* pA = new A(1); cout<< "pA->id = "<< pA->id<<endl; // pA->A::A(3);//error: cannot call constructor 'A::A' directly| // A::A(5); //error: cannot call constructor 'A::A' directly [-fpermissive]| cout<< "pA->id = "<<pA->id<<endl; delete pA; A* pA2; new(pA2)A(5); cout<< "pA2->id = "<<pA2->id<<endl; delete pA2; }
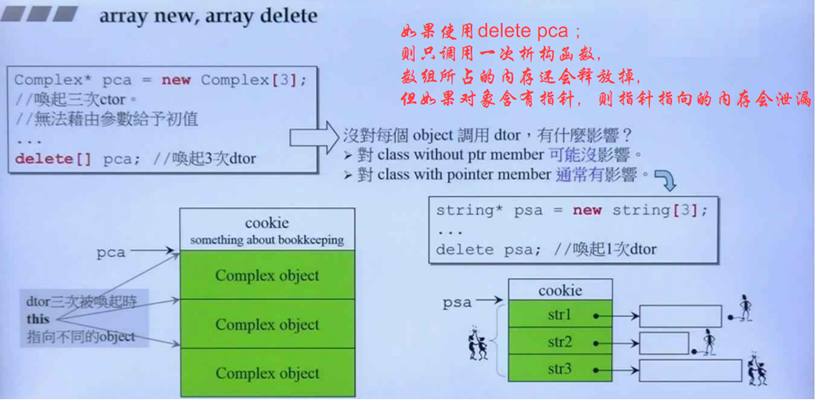
二、Array new, Replacement new

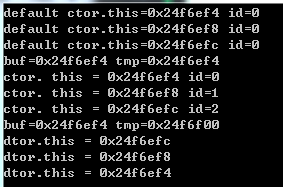
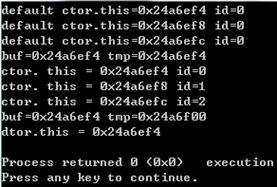
1 void testArrNew() 2 { 3 A* buf = new A[3]; //默认构造函数调用3次 调用顺序 0-1-2 4 //A必须有默认构造函数 new A[3]调用的是默认构造函数 5 6 A* tmp = buf;//记录A数组的起点位置 7 8 cout << "buf=" << buf << " tmp=" << tmp << endl; 9 10 for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) 11 { 12 new(tmp++)A(i); //placement new;在分配好的内存上,赋值 13 } 14 15 cout << "buf=" << buf << " tmp=" << tmp << endl; 16 17 //delete[] buf; 18 delete buf; 19 }
执行结果如下:
 |
 |
三、 placement new
先看一下placement new
char* buf = new char[sizeof(A) * 3];//申请内存 A* pc = new(buf)A();//在申请好的buf的内存,在buf上赋值
代码中 new(buf)A(); 就是placement new.
编译器会将上述代码转化为
A * pc; try { void* men = operator new(sizeof(A), buf); //申请内存 pc = static_cast<A*>(mem);//转换 pc->A::A();//构造函数 } catch (std::bad_alloc){ }
四、重载 operator new, operator new[], operator delete, operator delete[]
接管全局new,delete 函数,重载使用自己的操作符。
测试代码如下:
新建class Foo类

1 class Foo 2 { 3 private: 4 int _id; 5 long _data; 6 string _str; 7 8 public: 9 Foo():_id(0) 10 { 11 cout << "default ctor.this=" << this << " id=" << _id << endl; 12 } 13 Foo(int a):_id(a) 14 { 15 cout << "ctor.this=" << this << " id=" << _id << endl; 16 } 17 18 virtual 19 ~Foo() 20 { 21 cout << "dtor.this=" << this << " id=" << _id << endl; 22 } 23 24 //申请内存的函数必须是静态的 调用这个函数时一般都是正在创建这个对象 25 //所以当调用时,这个对象还不存在,需要声明成静态 26 static void* operator new(size_t size); 27 static void operator delete(void* pdead, size_t size); 28 static void* operator new[](size_t size); 29 static void operator delete[](void* pdead, size_t size); 30 }; 31 32 void* Foo::operator new(size_t size) 33 { 34 Foo* p = (Foo*)malloc(size); 35 cout <<"operator new().size="<< size << " return=" << p <<endl; 36 return p; //p 为内存起始点 37 } 38 39 void Foo::operator delete(void* pdead, size_t size)//pdead 删除点,和上面的p为同一个位置,size 为将要删除的内存大小 40 { 41 cout <<"operator delete.pdead=" << pdead << " size=" << size <<endl; 42 cout << endl; 43 free(pdead); 44 } 45 46 void* Foo::operator new[](size_t size) 47 { 48 Foo* p = (Foo*)malloc(size); 49 cout <<"operator new[].size="<< size <<" return=" << p << endl; 50 return p; 51 } 52 53 void Foo::operator delete[](void* pdead, size_t size) 54 { 55 cout<< "operator delete[].pdead=" << pdead << " size="<< size <<endl; 56 cout << endl; 57 free(pdead); 58 }
测试函数

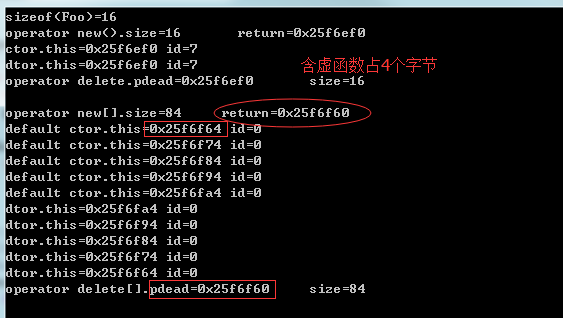
1 void testoperatornew() 2 { 3 cout << "sizeof(Foo)="<<sizeof(Foo) << endl; 4 Foo* p = new Foo(7); 5 delete p; 6 7 Foo* pArray = new Foo[5]; 8 delete [] pArray; 9 }
执行结果
重载new(),delete()
可以重载class member operator new(), 其中第一个参数必须是size_t,其余参数以new所指定的placement arguments 为初值,出现于new() 括号内的就是所谓的placems arguments.
也可以重载class member operator delete(),但他们不会被delete调用,只有当new所调用的ctor抛出异常,才会调用重载版的operator delete(),主要用来释放未完全创建成功的object所占有的内存。
示例代码

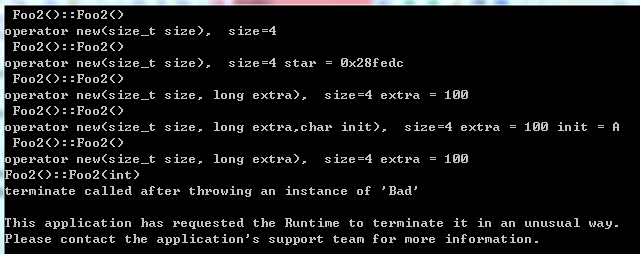
1 class Foo2 2 { 3 private: 4 int _id; 5 6 public: 7 Foo2() 8 { 9 cout << " Foo2()::Foo2() " << endl; 10 } 11 Foo2(int a) 12 { 13 cout << "Foo2()::Foo2(int) "<< endl; 14 throw Bad(); 15 } 16 17 18 void* operator new(size_t size) 19 { 20 cout << "operator new(size_t size), size="<< size <<endl; 21 return malloc(size); 22 } 23 24 // 标准库提供的placeent new()的重载形式 25 void* operator new(size_t size, void* star) 26 { 27 cout << "operator new(size_t size), size="<< size<< " star = " << star <<endl; 28 return malloc(size); 29 } 30 // 模拟标准库的形式,只传回pointer 31 void* operator new(size_t size, long extra) 32 { 33 cout << "operator new(size_t size, long extra), size="<< size <<" extra = " << extra<<endl; 34 return malloc(size+extra); 35 } 36 37 void* operator new(size_t size, long extra,char init) 38 { 39 cout << "operator new(size_t size, long extra,char init), size="<< size <<" extra = " << extra 40 <<" init = " << init<<endl; 41 return malloc(size+extra); 42 } 43 /* 又一个 ,但故意写错第一参数类型 44 void* operator new(long extra, char init) //error: 'operator new' takes type 'size_t' ('unsigned int') 45 { 46 return malloc(extra); //as first parameter [-fpermissive]| 47 } */ 48 49 void operator delete(void*,long) 50 { 51 cout<<" operator delete(void*,size_t) " <<endl; 52 } 53 void operator delete(void*,long,char) 54 { 55 cout<<" operator delete(void*,long,char) " <<endl; 56 } 57 }; 58 59 void testFoo2() 60 { 61 Foo2 start; 62 Foo2* p1= new Foo2; 63 Foo2* p2= new(&start) Foo2; 64 Foo2* p3= new(100) Foo2; 65 Foo2* p4= new(100,'A') Foo2; 66 Foo2* p5= new(100) Foo2(1); 67 Foo2* p6= new(100,'A') Foo2(1); 68 Foo2* p7= new(&start) Foo2(1); 69 Foo2* p8= new Foo2(1); 70 }
运行结果
 五、内存池
五、内存池
内存池的优点
1.减少malloc的使用,提高运行效率
2.减少内存碎片,减少cookie
构造简单的内存池,示例代码如下

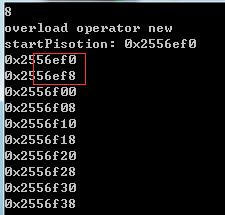
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include<complex> 4 #include <memory> //内含 std::allocator 5 #include <extpool_allocator.h> // __pool_alloc 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 class Screen 10 { 11 public: 12 Screen(int x): i(x) { } 13 int get() { return i; } 14 /************************重载 ××××*************/ 15 void* operator new(size_t); 16 void operator delete(void*, size_t); 17 /* **********************重载 ××××************ ***/ 18 private: 19 Screen* next;//4bit 20 static Screen* freeStore; 21 static const int screenChunk;//想要创建多少组 22 23 private: 24 int i; //4bit 25 }; 26 27 Screen* Screen::freeStore = 0; 28 const int Screen::screenChunk = 24; 29 30 /************************重载×××××××××××××××××××××××××*************/ 31 32 void* Screen::operator new(size_t size) 33 { 34 Screen* p; 35 if(!freeStore) 36 { 37 //linked list是空的,所以申请一大块内存 38 size_t chunk = screenChunk * size; //192 Screen的内存大小为8共24组 24 * 8 = 192 39 freeStore = p = 40 reinterpret_cast<Screen*>(new char[chunk]); 41 cout << "startPisotion: " << p << endl; 42 43 //将一大块内存分割成片段,当做linked list串接起来 44 for(; p != &freeStore[screenChunk-1]; ++p) 45 { 46 p->next = p+1; 47 } 48 p->next = 0; 49 } 50 p = freeStore; 51 freeStore = freeStore->next; 52 53 return p; 54 } 55 56 void Screen::operator delete(void* p, size_t) 57 { 58 //将delete object插回 free list前端 59 (static_cast<Screen*>(p)) -> next = freeStore; 60 freeStore = static_cast<Screen*>(p); 61 } 62 /************************重载×××××××××××××××××××××××××**************/ 63 void test_per() 64 { 65 cout << "sizeof(int)"<< sizeof(int*) << endl; 66 cout << "sizeof(Screen*)"<< sizeof(Screen*) << endl; 67 cout << "sizeof(Screen)"<< sizeof(Screen) << endl; 68 69 size_t const N = 10; 70 71 Screen* p[N]; 72 73 cout << "overload operator new" << endl; 74 for(int i=0; i<N; i++) 75 { 76 p[i] = new Screen(i); 77 } 78 79 for(int i = 0; i<10; i++) 80 { 81 cout << p[i] << endl;//输出每个Screen的内存起点 82 } 83 84 for(int i=0; i<N; i++) 85 { 86 delete p[i]; 87 } 88 89 cout << "glob operator new" << endl; 90 91 Screen* q[N]; 92 93 for(int i=0; i<N; i++) 94 { 95 q[i] = ::new Screen(i); 96 } 97 98 for(int i = 0; i<10; i++) 99 { 100 cout << q[i] << endl; 101 } 102 103 for(int i=0; i<N; i++) 104 { 105 ::delete q[i]; 106 } 107 } 108 109 int main() 110 { 111 test_per(); 112 return 0; 113 }
测试结果
 |
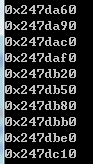 |
左边是重载了member operator new/delete 的结果,右边是没有使用重载而是使用global operator new/delete 的结果。class Screen 大小为8字节,使用重载的函数数组内相邻元素地址相隔8个字节,减少了使用malloc时的cookie;而不使用重载函数,相隔48个字节。
上述例子中,类中多出了一个指针Screen* next;//4bit ,增加了内存开销,可以采用union减少内存开销,代码如下:

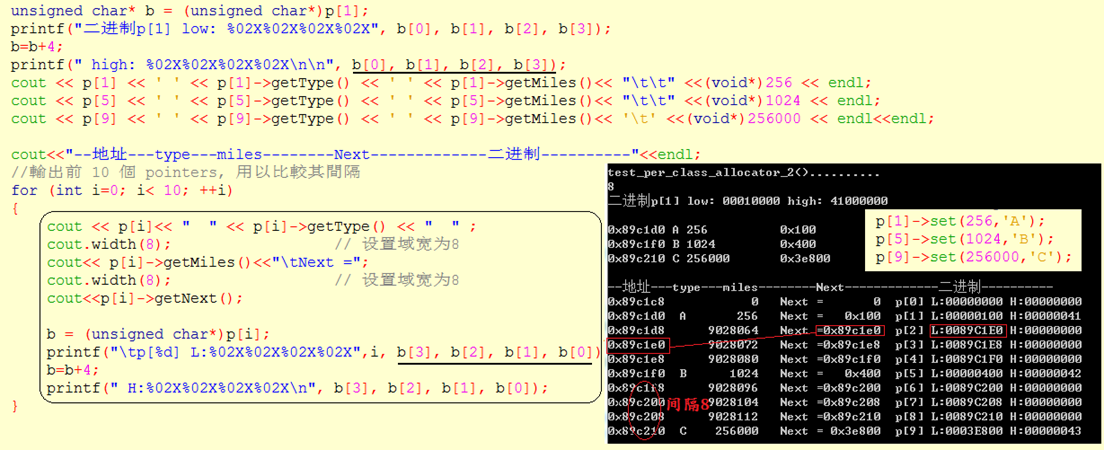
1 //ref. Effective C++ 2e, item10 2 //per-class allocator 3 4 class Airplane // customized memory management 5 { 6 private: 7 struct AirplaneRep 8 { 9 unsigned long miles; 10 char type; 11 }; 12 private: 13 union 14 { 15 AirplaneRep rep; //此针对 used object 16 Airplane* next; //此针对 free list 17 }; 18 public: 19 unsigned long getMiles() 20 { 21 return rep.miles; 22 } 23 char getType() 24 { 25 return rep.type; 26 } 27 void set(unsigned long m, char t) 28 { 29 rep.miles = m; 30 rep.type = t; 31 } 32 void* getNext() 33 { 34 return next; 35 } 36 public: 37 static void* operator new(size_t size); 38 static void operator delete(void* deadObject, size_t size); 39 private: 40 static const int BLOCK_SIZE; 41 static Airplane* headOfFreeList; 42 }; 43 44 Airplane* Airplane::headOfFreeList; 45 const int Airplane::BLOCK_SIZE = 128; 46 47 void* Airplane::operator new(size_t size) 48 { 49 //如果大小错误,转交给 ::operator new() 50 if (size != sizeof(Airplane)) 51 return ::operator new(size); 52 53 Airplane* p = headOfFreeList; 54 55 //如果 p 有效,就把list头部移往下一个元素 56 if (p) 57 headOfFreeList = p->next; 58 else 59 { 60 //free list 已空。配置一块够大内存, 61 //令足够容纳 BLOCK_SIZE 个 Airplanes 62 Airplane* newBlock = static_cast<Airplane*> 63 (::operator new(BLOCK_SIZE * sizeof(Airplane))); 64 //组成一个新的 free list:将小区块串在一起,但跳过 65 //#0 元素,因为要将它传回给呼叫者。 66 for (int i = 1; i < BLOCK_SIZE-1; ++i) 67 newBlock[i].next = &newBlock[i+1]; 68 newBlock[BLOCK_SIZE-1].next = 0; //以null结束 69 70 // 将 p 设至头部,将 headOfFreeList 设至 71 // 下一个可被运用的小区块。 72 p = newBlock; 73 headOfFreeList = &newBlock[1]; 74 } 75 return p; 76 } 77 78 // operator delete 接获一块内存。 79 // 如果它的大小正确,就把它加到 free list 的前端 80 void Airplane::operator delete(void* deadObject, 81 size_t size) 82 { 83 if (deadObject == 0) return; 84 if (size != sizeof(Airplane)) 85 { 86 ::operator delete(deadObject); 87 return; 88 } 89 90 Airplane *carcass = 91 static_cast<Airplane*>(deadObject); 92 93 carcass->next = headOfFreeList; 94 headOfFreeList = carcass; 95 } 96 97 //------------- 98 void test_per_class_allocator_2() 99 { 100 cout << " test_per_class_allocator_2().......... "; 101 102 cout << sizeof(Airplane) << endl; //8 103 104 size_t const N = 20; 105 Airplane* p[N]; 106 107 for (int i=0; i< N; ++i) 108 p[i] = new Airplane; 109 110 111 //随机测试 object 正常否 112 p[1]->set(256,'A'); 113 p[5]->set(1024,'B'); 114 p[9]->set(256000,'C'); 115 116 unsigned char* b = (unsigned char*)p[1]; 117 printf("二进制p[1] low: %02X%02X%02X%02X", b[0], b[1], b[2], b[3]); 118 b=b+4; 119 printf(" high: %02X%02X%02X%02X ", b[0], b[1], b[2], b[3]); 120 cout << p[1] << ' ' << p[1]->getType() << ' ' << p[1]->getMiles()<< " " <<(void*)256 << endl; 121 cout << p[5] << ' ' << p[5]->getType() << ' ' << p[5]->getMiles()<< " " <<(void*)1024 << endl; 122 cout << p[9] << ' ' << p[9]->getType() << ' ' << p[9]->getMiles()<< ' ' <<(void*)256000 << endl<<endl; 123 124 cout<<"--地址---type---miles--------Next-------------二进制----------"<<endl; 125 //输出前 10 个 pointers, 用以比较其间隔 126 for (int i=0; i< 10; ++i) 127 { 128 cout << p[i]<< " " << p[i]->getType() << " " ; 129 cout.width(8); // 设置域宽为8 130 cout<< p[i]->getMiles()<<" Next ="; 131 cout.width(8); // 设置域宽为8 132 cout<<p[i]->getNext(); 133 134 b = (unsigned char*)p[i]; 135 printf(" p[%d] L:%02X%02X%02X%02X",i, b[3], b[2], b[1], b[0]); 136 b=b+4; 137 printf(" H:%02X%02X%02X%02X ", b[3], b[2], b[1], b[0]); 138 } 139 140 141 for (int i=0; i< N; ++i) 142 delete p[i]; 143 144 cout << " global new test_per_class_allocator_2().......... "; 145 cout <<endl; 146 147 for (int i=0; i< N; ++i) 148 p[i] = ::new Airplane; 149 150 //随机测试 object 正常否 151 p[1]->set(256,'A'); 152 p[5]->set(1024,'B'); 153 p[9]->set(256000,'C'); 154 cout << p[1] << ' ' << p[1]->getType() << ' ' << p[1]->getMiles()<< ' ' <<(void*)256 << endl; 155 cout << p[5] << ' ' << p[5]->getType() << ' ' << p[5]->getMiles()<< ' ' <<(void*)1024 << endl; 156 cout << p[9] << ' ' << p[9]->getType() << ' ' << p[9]->getMiles()<< ' ' <<(void*)256000 << endl; 157 cout <<endl; 158 //输出前 10 个 pointers, 用以比较其间隔 159 for (int i=0; i< 10; ++i) 160 { 161 cout << p[i]<< ' ' << p[i]->getType() << ' ' ; 162 cout.width(8); // 设置域宽为8 163 cout<< p[i]->getMiles()<<" Next = "<<p[i]->getNext()<< endl; 164 } 165 for (int i=0; i< N; ++i) 166 ::delete p[i]; 167 }
测试结果如下
六、static allocate
上节分配内存的方法,每个类中都要重载new,delete; 因此将该部分提取出来,封装为一个类allocate; 将应用类的实现与内存分配细节分离开来
测试代码

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include<complex> 4 //#include <memory> //内含 std::allocator 5 //#include <extpool_allocator.h> // __pool_alloc 6 7 using namespace std ; 8 9 class myAllocator 10 { 11 private: 12 struct obj 13 { 14 struct obj* next; 15 }; 16 17 public: 18 void* allocate(size_t); 19 void deallocate(void*, size_t); 20 private: 21 obj* freeStore = nullptr; 22 const int CHUNK = 5; // 便于观察,设为5 23 }; 24 25 void myAllocator::deallocate(void* p, size_t size) 26 { 27 cout << "myAllocator::deallocate" << "size: " << size <<endl; 28 ((obj*)p)->next = freeStore; 29 freeStore = (obj*)p; 30 } 31 32 void* myAllocator::allocate(size_t size) 33 { 34 // cout << "myAllocator::allocate" << "size: " << size <<endl; 35 obj* p; 36 if(!freeStore) 37 { 38 size_t chunk = CHUNK * size; 39 freeStore = p = (obj*)malloc(chunk); 40 41 for(int i=0; i<(CHUNK-1); ++i) 42 { 43 p->next = (obj*)((char*)p + size); 44 p = p->next; 45 } 46 47 p->next = nullptr; 48 } 49 p= freeStore; 50 freeStore = freeStore -> next; 51 52 return p; 53 } 54 55 class Foo 56 { 57 public: 58 long L; 59 string str; 60 static myAllocator myAlloc; 61 public: 62 Foo(long l): L(l) 63 { 64 //todo 65 } 66 67 static void* operator new(size_t size) 68 { 69 return myAlloc.allocate(size); 70 } 71 72 static void operator delete(void* pdead, size_t size) 73 { 74 return myAlloc.deallocate(pdead, size); 75 } 76 }; 77 myAllocator Foo::myAlloc; 78 79 class Goo 80 { 81 public: 82 complex<double> L; 83 string str; 84 static myAllocator myAlloc; 85 public: 86 Goo(const complex<double>& l): L(l) 87 { 88 //todo 89 } 90 91 static void* operator new(size_t size) 92 { 93 return myAlloc.allocate(size); 94 } 95 96 static void operator delete(void* pdead, size_t size) 97 { 98 return myAlloc.deallocate(pdead, size); 99 } 100 }; 101 myAllocator Goo::myAlloc; 102 103 void test3() 104 { 105 size_t const N = 20; 106 Foo* p[N]; 107 108 cout << "overload operator new" << endl; 109 cout <<"sizeof(Foo) = "<< sizeof(Foo) << endl; 110 111 for(int i=0; i<N; i++) 112 { 113 p[i] = new Foo(i); 114 cout<<p[i] << ' '<<p[i]->L<<endl; 115 } 116 117 for(int i = 0; i<N; i++) 118 { 119 cout << p[i] << endl; 120 } 121 122 for(int i=0; i<N; i++) 123 { 124 delete p[i]; 125 } 126 127 cout << "glob operator new" << endl; 128 129 Foo* q[N]; 130 131 for(int i=0; i<N; i++) 132 { 133 q[i] = ::new Foo(i); 134 } 135 136 for(int i = 0; i<N; i++) 137 { 138 cout << q[i] << endl; 139 } 140 141 for(int i=0; i<N; i++) 142 { 143 ::delete q[i]; 144 } 145 146 Goo* pG[N]; 147 148 cout << "overload operator new" << endl; 149 cout <<"sizeof(Goo) = "<< sizeof(Goo) << endl; 150 151 for(int i=0; i<N; i++) 152 { 153 pG[i] = new Goo(complex<double>(i,i)); 154 cout<<pG[i] << ' '<<pG[i]->L<<endl; 155 } 156 157 for(int i=0; i<N; i++) 158 { 159 delete pG[i]; 160 } 161 } 162 163 int main() 164 { 165 test3(); 166 return 0; 167 }
执行结果
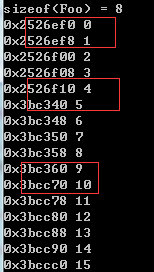 |
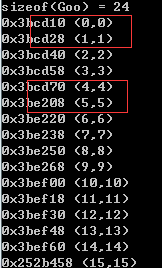 |
myAllocator 中const int CHUNK = 5; (便于观察,设为5),块内每5个元素地址相差一个元素大小,块与块之间地址相差较大。
优化升级
上述示例代码中,使用myAllocator的格式是固定的,因此可以将其提取出来定义为宏。
代码如下:

1 // DECLARE_POOL_ALLOC() --used in class definition 2 #define DECLARE_POOL_ALLOC() 3 public: 4 void* operator new(size_t size){ myAlloc.allocate(size); } 5 void operator delete(void* p){ myAlloc.deallocate(p, 0); } 6 protected: 7 static myAllocator myAlloc; 8 9 // IMPLEMENT_POOL_ALLOC() --used in class implemention file 10 #define IMPLEMENT_POOL_ALLOC(class_name) 11 myAllocator class_name::myAlloc; 12 13 class Foo 14 { 15 DECLARE_POOL_ALLOC() 16 public: 17 long L; 18 string str; 19 public: 20 Foo(long l): L(l) 21 { 22 //todo 23 } 24 }; 25 IMPLEMENT_POOL_ALLOC(Foo) 26 27 class Goo 28 { 29 DECLARE_POOL_ALLOC() 30 public: 31 complex<double> L; 32 string str; 33 public: 34 Goo(const complex<double>& l): L(l) 35 { 36 //todo 37 } 38 }; 39 IMPLEMENT_POOL_ALLOC(Goo)
七、何时重载operator new或operator delete
用来检测运用上的错误。如果delete new的内存失败,会导致内存泄漏。如果在new所得内存多次delete会导致不确定行为。使用编译器提供的operator new和operator delete不能检测上述行为。如果operator new持有一个链表,其存储动态分配所得内存,operator delete则将内存从链表删除,这样就能检测上述错误用法。如果编程错误,可能在分配内存的之前区域或之后区域写入数据;这时可以自己定义operator new分配超额内存,在多出部分写上特定byte patterns(即签名,signature),operator delete检测签名是否更改,是否发生了overrun 或 underrun。
为了强化效能。编译器所带的operator new和operator delete主要用于一般目的,它处理的内存请求有时很大,有时很小,它必须处理大数量短命对象的持续分配和归还。它们必须考虑碎片问题。定制版的operator new和operator delete通常在性能上胜过缺省版本,它们运行得比较快,需要的内存比较少。
为了收集使用上的统计数据。在重载之前,首先要了解软件如何使用动态内存。分配区块如何分布?寿命如何?它们是FIFO先进先出还是LIFO后进先出,或随机分配和归还?软件在不同执行阶段有不同的分配归还形态吗?任何时刻使用的最大动态分配量是多少?自己定义的operator new和operator delete可以轻松收集到这些信息。
为了增加分配和归还的速度。使用定制的针对特定类型对象的分配器,可以提高效率。例如,Boost提供的Pool程序库便是。如果在单线程程序中,你的编译器所带的内存管理具备线程安全,你可以写个不具备线程安全的分配器而大幅度改善速度。
为了降低缺省内存管理器带来的空间额外开销。泛用型分配器往往(虽然并非总是)不只比定制型慢,还使用更多空间,因为它们常常在每一个分配区块上招引某些额外开销。针对小型对象开放的分配器,例如Boost库的Pool,本质上消除了这样的额外开销。
为了弥补缺省分配器的非最佳对齐(suboptimal alignment)。X86体系结构上的double访问最快–如果它们是8-byte对齐。但是编译器自带的operator new并不保证分配double是8-byte对齐。
为了将相关对象成簇集中。如果特定的某个数据结构往往被一起使用,我们希望在处理这些数据时将“内存页错误”(page faults)的频率降至最低,那么为此数据结构创建另一个heap就有意义,这样就可以将它们成簇集中到尽可能少的内存也上。
为了获得非传统的行为。有时候我们需要做operator new和delete没做的事。例如,在归还内存时将其数据覆盖为0,以此增加应用程序的数据安全。
上述所有代码执行环境为GNU4.9.2
内容参考自:侯捷c++内存管理课程, Effective c++