- 创建1个节点
- 连接3个节点
- 前序遍历、中序遍历、后续遍历二叉树(包括递归法与非递归法(辅助栈))
- 清除二叉树
- 在二叉搜索树中插入1个节点(和链表一样,注意使用二级指针,因为可能插入的是根节点)
- 在二叉搜索树中查找1个节点
- 在二叉搜索树中删除一个节点(和链表一样,注意使用二级指针,因为可能删除的是根节点)
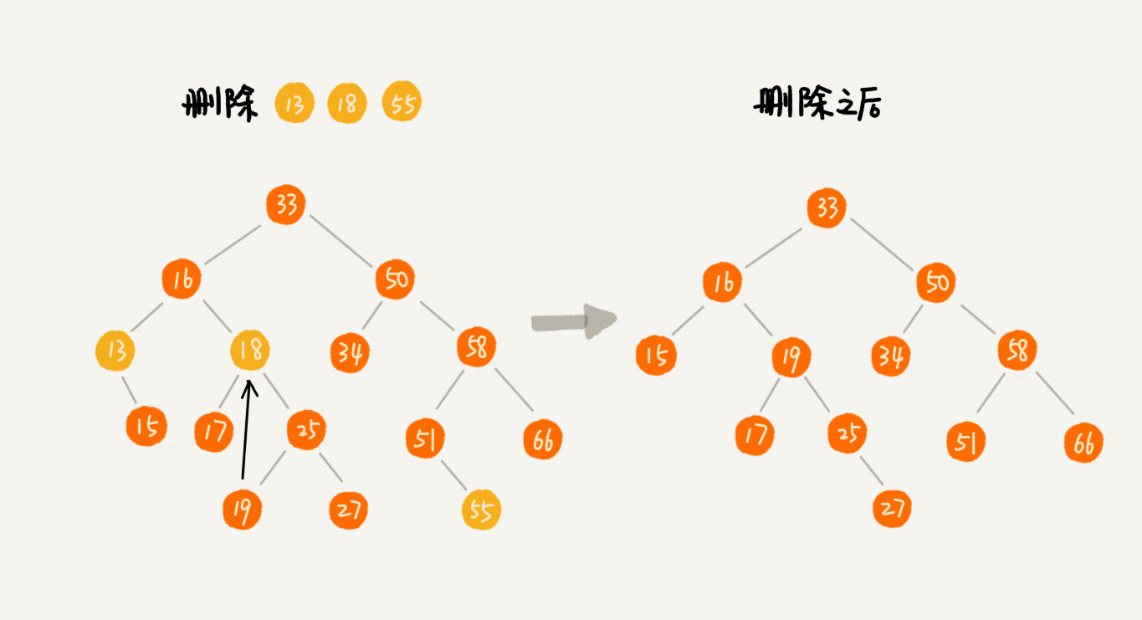
特别注意在二叉树中删除一个节点,有3中可能情况:
- 要删除的节点没有子节点(只需要直接将父节点中,指向要删除的节点指针置为null,比如下图中的删除节点55)
- 如果要删除的节点只有一个子节点(只有左子节点或者右子节点),我们只需要更新父节点中,指向要删除节点的指针,让它指向要删除节点的子节点就可以了。比如图中的删除节点 13
- 如果要删除的节点有两个子节点,这就比较复杂了。我们需要找到这个节点的右子树中的最小节点,把它替换到要删除的节点上。然后再删除掉这个最小节点,因为最小节点肯定没有左子节点(如果有左子结点,那就不是最小节点了),所以,我们可以应用上面两条规则来删除这个最小节点。比如图中的删除节点 18。
TreeNode.h如下
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int val):val(val),left(nullptr),right(nullptr){}
};
// 创建一个节点
TreeNode* CreateBinaryTreeNode(int value){
TreeNode* pNode = new TreeNode(value);
pNode->val = value;
pNode->left = nullptr;
pNode->right = nullptr;
return pNode;
}
// 连接三个节点
void ConnectTreeNodes(TreeNode* pParent, TreeNode* pLeft, TreeNode* pRight){
if(pParent != nullptr){
pParent->left = pLeft;
pParent->right = pRight;
}
}
// 打印节点
void PrintTreeNode(const TreeNode* pNode){
if(pNode != nullptr)
{
printf("value of this node is: %d
", pNode->val);
if(pNode->left != nullptr)
printf("value of its left child is: %d.
", pNode->left->val);
else
printf("left child is nullptr.
");
if(pNode->right != nullptr)
printf("value of its right child is: %d.
", pNode->right->val);
else
printf("right child is nullptr.
");
}
else
{
printf("this node is nullptr.
");
}
printf("
");
}
// 打印二叉树(更仔细点儿的前序遍历)
void PrintTree(const TreeNode* pRoot){
PrintTreeNode(pRoot);
if(pRoot != nullptr){
if(pRoot->left != nullptr)
PrintTree(pRoot->left);
if(pRoot->right != nullptr)
PrintTree(pRoot->right);
}
}
// 前序遍历二叉树
void preOrderPrintTree(TreeNode* pRoot){
if(pRoot == nullptr)
return ;
cout<<pRoot->val<<endl;
preOrderPrintTree(pRoot->left);
preOrderPrintTree(pRoot->right);
}
// 中序遍历二叉树
void midOrderPrintTree(TreeNode* pRoot){
if(pRoot == nullptr)
return ;
midOrderPrintTree(pRoot->left);
cout<<pRoot->val<<endl;
midOrderPrintTree(pRoot->right);
}
// 后续遍历二叉树
void postOrderPrintTree(TreeNode* pRoot){
if(pRoot == nullptr)
return ;
postOrderPrintTree(pRoot->left);
postOrderPrintTree(pRoot->right);
cout<<pRoot->val<<endl;
}
// 非递归法前序遍历二叉树(辅助栈)
void preOrderPrintTreePlus(TreeNode* pRoot){
if(pRoot == nullptr)
return ;
stack<TreeNode* > stack1;
// 先入栈根节点
stack1.push(pRoot);
while(!stack1.empty()){
// 获取栈顶节点
TreeNode* pNode = stack1.top();
cout<<pNode->val<<endl;
// 出栈
stack1.pop();
if(pNode->right != nullptr)
stack1.push(pNode->right);
if(pNode->left != nullptr)
stack1.push(pNode->left);
}
}
// 非递归法中序遍历二叉树(辅助栈)
void midOrderPrintTreePlus(TreeNode* pRoot){
if(pRoot == nullptr)
return ;
stack<TreeNode* > stack1;
TreeNode* pNode = pRoot;
while(!stack1.empty() || pNode != nullptr){
// 从根节点开始,不断访问左节点,沿路径入栈
while(pNode != nullptr){
stack1.push(pNode);
pNode = pNode->left;
}
// 获取栈顶节点
pNode = stack1.top();
cout<<pNode->val<<endl;
// 出栈
stack1.pop();
// 对右节点执行相同的操作
pNode = pNode->right;
}
}
// 非递归法后序遍历二叉树(辅助栈)
void postOrderPrintTreePlus(TreeNode* pRoot){
if(pRoot == nullptr)
return ;
stack<TreeNode* > stack1;
stack<TreeNode* > stack2;
TreeNode* pNode = pRoot;
stack1.push(pNode);
while(!stack1.empty()){
pNode = stack1.top();
stack1.pop();
stack2.push(pNode);
if(pNode->left != nullptr)
stack1.push(pNode->left);
if(pNode->right != nullptr)
stack1.push(pNode->right);
}
while(!stack2.empty()){
cout<<stack2.top()->val;
stack2.pop();
}
}
// 清除二叉树
void DestroyTree(TreeNode* pRoot){
if(pRoot != nullptr){
TreeNode* left = pRoot->left;
TreeNode* right = pRoot->right;
delete pRoot;
pRoot = nullptr;
DestroyTree(left);
DestroyTree(right);
}
}
// 二叉查找树查找某一个节点(二叉搜索树)
TreeNode* findNode(TreeNode* pRoot, int val){
if(pRoot == nullptr)
return nullptr;
TreeNode* pNode = pRoot;
while(pNode != nullptr){
if(pNode->val < val)
pNode = pNode->right;
else if(pNode->val > val)
pNode = pNode->left;
else
return pNode;
}
return nullptr;
}
// 二叉查找树的插入操作(这里应该用二级指针,因为可能插入根节点)
void insertTreeNode(TreeNode** pRoot, int val){
if(*pRoot == nullptr){
(*pRoot) = new TreeNode(val);
(*pRoot)->left = nullptr;
(*pRoot)->right = nullptr;
return ;
}
TreeNode* pNode = *pRoot;
while(pNode != nullptr){
// 查看右子树
if(val > pNode->val){
if(pNode->right == nullptr){
TreeNode* newNode = new TreeNode(val);
pNode->right = newNode;
return ;
}
pNode = pNode->right;
}
// 查看左子树
else{
if(pNode->left == nullptr){
TreeNode* newNode = new TreeNode(val);
pNode->left = newNode;
return ;
}
pNode = pNode->left;
}
}
return ;
}
// 二叉搜索树删除某个节点(这里应该用二级指针,因为可能删除根节点,这里就稍微有些复杂了)
void deleteTreeNode(TreeNode** pRoot, int val){
if(*pRoot == nullptr)
return ;
// deleteNode指向要删除的节点,初始化指向根节点
TreeNode* deleteNode = *pRoot;
// prevNode指向删除节点的父节点
TreeNode* prevNode = nullptr;
while(deleteNode != nullptr && deleteNode->val != val){
prevNode = deleteNode;
if(val > deleteNode->val)
deleteNode = deleteNode->right;
else
deleteNode = deleteNode->left;
}
// 没找到这个要删除的节点,直接返回
if(deleteNode == nullptr)
return ;
TreeNode* pLeft = deleteNode->left;
TreeNode* pRight = deleteNode->right;
// 如果要删除的节点有两个子节点
if(pLeft != nullptr && pRight != nullptr){
prevNode = deleteNode;
// 找到要删除节点右子树中最小节点,最小节点没有左子节点(特征)
while(pRight->left != nullptr){
prevNode = pRight;
pRight = pRight->left;
}
// 修改当前删除位置的值
deleteNode->val = pRight->val;
// 删除的节点指向最小节点
deleteNode = pRight;
}
TreeNode* child = nullptr;
// 如果只有左子节点
if(pLeft != nullptr)
child = pLeft;
// 如果只有右子节点
else if(pRight != nullptr)
child = pRight;
// 如果是叶子节点,不做操作直接删除
else
child = nullptr;
// 删除的是根节点
if(prevNode == nullptr){
*pRoot = child;
}
// 删除的是左子节点
else if(prevNode->left == deleteNode){
prevNode->left = child;
}
else
prevNode->right = child;
// 最后删除节点,释放内存
delete deleteNode;
deleteNode = nullptr;
}
主函数如下
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include "TreeNode.h"
#include "ListNode.h"
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
TreeNode* pNode8 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
insertTreeNode(&pNode8, 1);
insertTreeNode(&pNode8, 2);
insertTreeNode(&pNode8, 3);
insertTreeNode(&pNode8, 4);
insertTreeNode(&pNode8, 5);
insertTreeNode(&pNode8, 6);
deleteTreeNode(&pNode8, 8);
PrintTree(pNode8);
return 0;
}
