博客转自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50490490

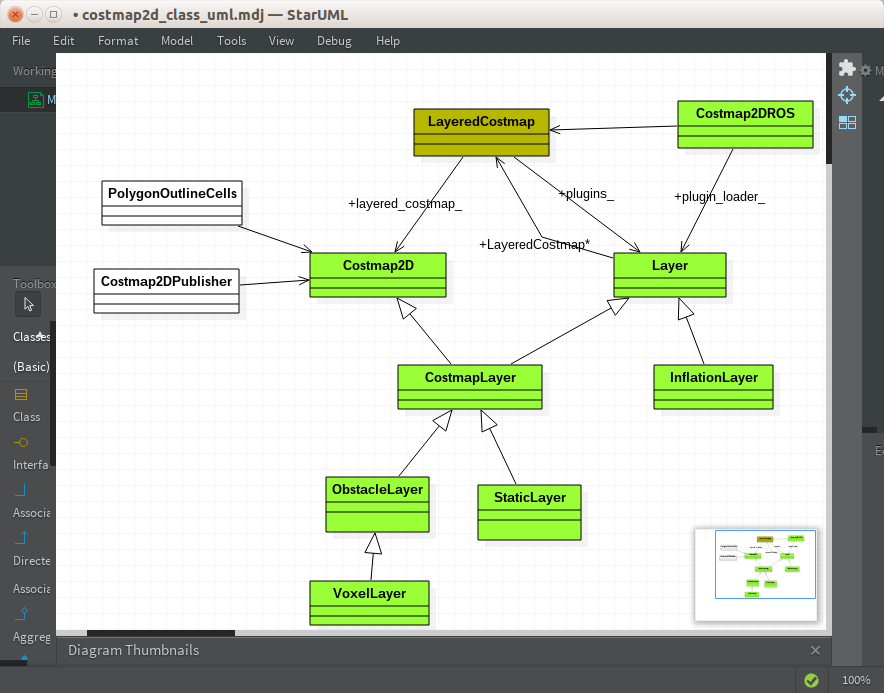
在数据成员中,有两个重要的变量:Costmap2D costmap_和 std::vector<boost::shared_ptr<Layer> > plugins_ 。
这个类相对比较简单,首先来看构造函数:
LayeredCostmap::LayeredCostmap(std::string global_frame, bool rolling_window, bool track_unknown) :
costmap_(), global_frame_(global_frame), rolling_window_(rolling_window), initialized_(false), size_locked_(false)
{
if (track_unknown)
costmap_.setDefaultValue(255);
else
costmap_.setDefaultValue(0);
}
调用costmap_ 的setDefaultValue 方法,实际上设定了类costmap_2d 的一个成员变量default_value_ 这个值在class costmap_2d 中是这样使用的:memset(costmap_, default_value_, size_x_ * size_y_ * sizeof(unsigned char)),实际存储地图的变量就是class costmap_2d 的 costmap_ 数据成员。析构函数中,所有的操作就是弹出plugin: plugins_.pop_back()。函数LayeredCostmap::resizeMap 就是给class costmap_2d 的 costmap_ 成员的大小重新做分配。然后根据plugin对每一层的地图调用其父类Costmap2D成员的initial 方法,实际效果就是将plugin所指向的每一层地图的大小都设置为和LayeredCostmap::costmap_ 数据成员一样的空间大小。
{
size_locked_ = size_locked;
costmap_.resizeMap(size_x, size_y, resolution, origin_x, origin_y);
for (vector<boost::shared_ptr<Layer> >::iterator plugin = plugins_.begin(); plugin != plugins_.end();
++plugin)
{
(*plugin)->matchSize();
}
}
函数 LayeredCostmap::updateMap 完成对每一层地图的更新,更新过程分为两步updateBounds和updateCosts
void LayeredCostmap::updateMap(double robot_x, double robot_y, double robot_yaw)
{
if (rolling_window_)
{
double new_origin_x = robot_x - costmap_.getSizeInMetersX() / 2;
double new_origin_y = robot_y - costmap_.getSizeInMetersY() / 2;
costmap_.updateOrigin(new_origin_x, new_origin_y);
}
if (plugins_.size() == 0)
return;
minx_ = miny_ = 1e30;
maxx_ = maxy_ = -1e30;
for (vector<boost::shared_ptr<Layer> >::iterator plugin = plugins_.begin(); plugin != plugins_.end();
++plugin)
{
(*plugin)->updateBounds(robot_x, robot_y, robot_yaw, &minx_, &miny_, &maxx_, &maxy_);
}
int x0, xn, y0, yn;
costmap_.worldToMapEnforceBounds(minx_, miny_, x0, y0);
costmap_.worldToMapEnforceBounds(maxx_, maxy_, xn, yn);
x0 = std::max(0, x0);
xn = std::min(int(costmap_.getSizeInCellsX()), xn + 1);
y0 = std::max(0, y0);
yn = std::min(int(costmap_.getSizeInCellsY()), yn + 1);
ROS_DEBUG("Updating area x: [%d, %d] y: [%d, %d]", x0, xn, y0, yn);
if (xn < x0 || yn < y0)
return;
{
// Clear and update costmap under a single lock
boost::unique_lock<Costmap2D::mutex_t> lock(*(costmap_.getMutex()));
costmap_.resetMap(x0, y0, xn, yn);
for (vector<boost::shared_ptr<Layer> >::iterator plugin = plugins_.begin(); plugin != plugins_.end();
++plugin)
{
(*plugin)->updateCosts(costmap_, x0, y0, xn, yn);
}
}
}
这里我们来看这两个更新过程参数:
(*plugin)->updateBounds(robot_x, robot_y, robot_yaw, &minx_, &miny_, &maxx_, &maxy_); (*plugin)->updateCosts(costmap_, x0, y0, xn, yn);
更新Bounds过程由于传入的参数是&minx_, &miny_, &maxx_, &maxy_ 构成了一个矩形范围。由于针对不同的类的实例,调用不同的类的方法。对于Static Map:
{
if (!map_received_ || !(has_updated_data_ || has_extra_bounds_))
return;
useExtraBounds(min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y);
double wx, wy;
mapToWorld(x_, y_, wx, wy);
*min_x = std::min(wx, *min_x);
*min_y = std::min(wy, *min_y);
mapToWorld(x_ + width_, y_ + height_, wx, wy);
*max_x = std::max(wx, *max_x);
*max_y = std::max(wy, *max_y);
has_updated_data_ = false;
}
Static map 只在第一次做更新,Bounds 范围是整张Map的大小,而且在UpdateBounds过程中没有对Static Map层的数据做过任何的更新。而对于 ObstacleLayer::updateBounds :主要的操作是更新Obstacles Map层的数据,然后才是更新Bounds
std::vector<Observation> observations, clearing_observations;
// get the marking observations
current = current && getMarkingObservations(observations);
// get the clearing observations
current = current && getClearingObservations(clearing_observations);
// update the global current status
current_ = current;
// raytrace freespace
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < clearing_observations.size(); ++i)
{
raytraceFreespace(clearing_observations[i], min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y);
}
for (std::vector<Observation>::const_iterator it = observations.begin(); it != observations.end(); ++it)
{
const Observation& obs = *it;
const pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>& cloud = *(obs.cloud_);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < cloud.points.size(); ++i)
{
double px = cloud.points[i].x, py = cloud.points[i].y, pz = cloud.points[i].z;
// now we need to compute the map coordinates for the observation
unsigned int mx, my;
if (!worldToMap(px, py, mx, my))
{
continue;
}
unsigned int index = getIndex(mx, my);
costmap_[index] = LETHAL_OBSTACLE;
touch(px, py, min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y);
}
}
updateFootprint(robot_x, robot_y, robot_yaw, min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y);
对于InflationLayer::updateBounds 则保持上一次的min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y 。
对于VoxelLayer::updateBounds 更新过程和 ObstacleLayer::updateBounds 基本一致,只是增加了z 作为判断是否将2d地图的点设定为LETHAL_OBSTACLE 。
updateCosts: 完成updateBounds 后,开始调用(*plugin)->updateCosts(costmap_, x0, y0, xn, yn)。函数的第一个参数是指的master map,后面的bounds是对每个plugin自己维护的map的更新界限做设定。这里需要分析每一个单独的costmap和master map是哪些类在维护。
Master map: 这是由类LayeredCostmap 的 Costmap2D costmap_ 维护。 StaticLayer StaticLayer VoxelLayer: 这些类是继承于Costmap2D ,因此可以直接操作Costmap2D 的数据成员 unsigned char* costmap_;。因此可以看成每一层地图都是类Costmap2D 的一个实例。 InflationLayer 没有继承于Costmap2D 是因为这个类并不需要维护一张自己的地图,它仅仅是需要直接操作master map的数据就可以了。
每个plugin调用自己代表的层的updateCosts方法: StaticLayer 和ObstacleLayer 基本上都是调用了CostmapLayer::updateWithOverwrite,CostmapLayer::updateWithTrueOverwrite, CostmapLayer::updateWithMax 等方法。因为CostmapLayer 是这两个的父类。 但是InflationLayer::updateCosts 则不同,因为它既没有自己层的map实例,也不是从CostmapLayer 继承而来。它的updateCosts 是这个类的核心操作。关于他的updateCosts 操作,将在InflationLayer 篇具体分析这个算法的实现过程,这个算法实现了对障碍物膨胀操作。函数bool LayeredCostmap::isCurrent() 主要的操作是对操作的实时性提供保证,提供是否发生超时的信息。
bool current = (ros::Time::now() - last_updated_).toSec() <= expected_update_rate_.toSec();
函数void LayeredCostmap::setFootprint(conststd::vector<geometry_msgs::Point>& footprint_spec)
{
footprint_ = footprint_spec;
costmap_2d::calculateMinAndMaxDistances(footprint_spec, inscribed_radius_, circumscribed_radius_);
for (vector<boost::shared_ptr<Layer> >::iterator plugin = plugins_.begin(); plugin != plugins_.end();
++plugin)
{
(*plugin)->onFootprintChanged();
}
}
inscribed_radius_, circumscribed_radius_ 是计算得到的机器人尺寸的内切圆和外切圆半径。
这里重点关注InflationLayer 类是如何调用onFootprintChanged() 的。对于其他类型的plugin实例来说,其本身并没有重载这个函数,所以都是调用的Layer类的空函数virtual void onFootprintChanged() {}。
cell_inflation_radius_ = cellDistance(inflation_radius_); computeCaches();
函数computeCaches()
void InflationLayer::computeCaches()
{
if (cell_inflation_radius_ == 0)
return;
// based on the inflation radius... compute distance and cost caches
if (cell_inflation_radius_ != cached_cell_inflation_radius_)
{
deleteKernels();
cached_costs_ = new unsigned char*[cell_inflation_radius_ + 2];
cached_distances_ = new double*[cell_inflation_radius_ + 2];
for (unsigned int i = 0; i <= cell_inflation_radius_ + 1; ++i)
{
cached_costs_[i] = new unsigned char[cell_inflation_radius_ + 2];
cached_distances_[i] = new double[cell_inflation_radius_ + 2];
for (unsigned int j = 0; j <= cell_inflation_radius_ + 1; ++j)
{
cached_distances_[i][j] = hypot(i, j);
}
}
cached_cell_inflation_radius_ = cell_inflation_radius_;
}
for (unsigned int i = 0; i <= cell_inflation_radius_ + 1; ++i)
{
for (unsigned int j = 0; j <= cell_inflation_radius_ + 1; ++j)
{
cached_costs_[i][j] = computeCost(cached_distances_[i][j]);
}
}
}
在函数定义中,维护两个指针:
cached_costs_ = new unsigned char*[cell_inflation_radius_ + 2]; cached_distances_ = new double*[cell_inflation_radius_ + 2];
第一阶段,计算出cached_distances_: cached_distances_[i][j] = hypot(i, j); ,其中i j 的范围都是0:cell_inflation_radius_ + 1。
第二阶段,通过计算得到的cached_distances_ 计算cached_costs_:cached_costs_[i][j] = computeCost(cached_distances_[i][j])。通过这个操作,现在可以任意给出在0-cell_inflation_radius_ cell范围的两个cells的costs,以后对地图做膨胀时,只需要查看某个cell(i1,j1)和obstacle cell(i,j)的下标就可以通过查表知道这个cell的代价是多少。这个表的大小仅仅和机器人的几何尺寸相关,一旦机器人尺寸发生改变,这个函数就需要再次被调用。
OK, LayeredCostmap的分析就这么多了~相信这样来来回回反复的分析这些类之间的调用关系,对于理解costmap_2d这个小怪兽是必要的。